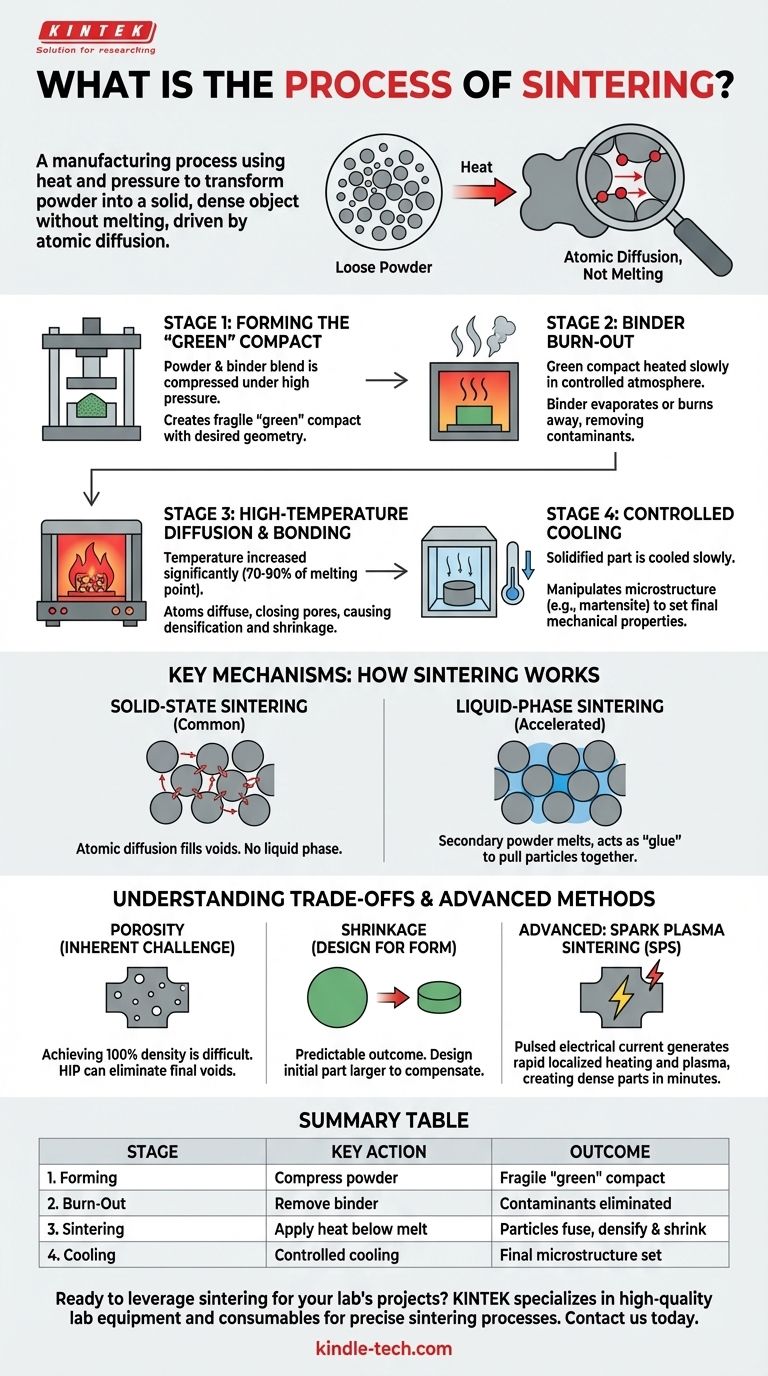
In short, sintering is a manufacturing process that uses heat and pressure to transform a powder-based material into a solid, dense object. Unlike casting, which involves completely melting the material into a liquid, sintering heats the powder to a temperature just below its melting point. At this high temperature, the individual particles fuse together at their contact points, dramatically reducing the empty space between them and creating a single, solid piece.
The fundamental principle behind sintering is not melting, but atomic diffusion. By applying heat, you give atoms the energy to migrate across the boundaries of individual powder particles, effectively "welding" them together on a microscopic level to form a strong, unified component.

The Foundational Stages of Sintering
The sintering process can be broken down into four distinct, critical stages. Each step is carefully controlled to ensure the final part meets its required density, strength, and dimensional specifications.
Stage 1: Forming the "Green" Compact
First, a precise blend of primary powders (such as metal or ceramic) is created. Often, a temporary bonding agent like a wax, polymer, or water is mixed in to help the particles stick together.
This mixture is then loaded into a die or mold and compressed under high pressure. The result is a fragile, pre-formed shape known as a "green" compact, which has the desired geometry but very little mechanical strength.
Stage 2: Binder Burn-Out
The green compact is carefully placed into a specialized sintering furnace. The temperature is slowly raised in a controlled atmosphere to the point where the binder evaporates or burns away.
This "burn-out" phase is critical for removing contaminants. The furnace atmosphere can be engineered so that gaseous by-products, like hydrocarbons from the binder, react to form harmless substances like CO2.
Stage 3: High-Temperature Diffusion and Bonding
Once the binder is gone, the temperature is increased significantly, typically to around 70-90% of the primary material's absolute melting point. The part is held at this temperature for a set period.
This is the core of sintering. The intense heat energizes the atoms, causing them to move and diffuse across the particle surfaces. This process closes the pores between particles, causing the component to densify and shrink as it bonds into a solid mass.
Stage 4: Controlled Cooling
Finally, the newly solidified part is cooled in a controlled manner. The rate of cooling can be manipulated to achieve specific crystalline microstructures, such as martensite in steels, which determine the final mechanical properties like hardness and toughness.
Key Mechanisms: How Sintering Actually Works
While the stages appear simple, the underlying physics determines the final outcome. The two primary mechanisms are solid-state and liquid-phase sintering.
Solid-State Sintering: Atomic Diffusion in Action
This is the most common form of sintering. The driving force is the reduction of surface energy; a single solid object is more energetically stable than a collection of fine powders.
At high temperatures, atoms from the particles migrate to the "necks" forming between them, gradually filling the voids. No part of the primary material ever becomes a liquid in this process.
Liquid-Phase Sintering: Using a Metallic "Glue"
To accelerate densification, a small amount of a secondary powder with a lower melting point can be added to the mix.
During heating, this secondary material melts while the primary particles remain solid. The resulting liquid flows into the pores via capillary action, pulling the solid particles closer together and acting as a cement when it cools.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Sintering is a powerful technology, but it requires understanding its inherent limitations to be used effectively.
Porosity: The Inherent Challenge
Achieving 100% density is extremely difficult with conventional sintering. Most sintered parts retain a small amount of residual porosity, which can influence properties like strength and ductility. For critical applications, secondary operations like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) may be needed to eliminate these final voids.
Shrinkage: Designing for the Final Form
Because the process works by eliminating the space between particles, shrinkage is a natural and predictable outcome. The initial "green" compact must be designed to be larger than the final desired part to compensate for this reduction in volume. Precise control of this shrinkage is essential for dimensional accuracy.
Advanced Methods: Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)
Modern variations on the process exist to overcome traditional limitations. In Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), a pulsed electrical current is passed directly through the powder and its tooling.
This generates rapid, localized heating and even plasma discharges between particles, dramatically accelerating the diffusion and densification process. SPS can create highly dense parts in minutes instead of hours, often at lower overall temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the principles of sintering allows you to select the correct approach for creating complex and high-performance parts.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: Conventional press-and-sinter (solid-state) is the industry standard for creating parts like automotive gears, bushings, and structural components.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and performance: Liquid-phase sintering is often used, and may be combined with secondary processes to create cutting tools or wear-resistant parts with minimal porosity.
- If your primary focus is speed or processing novel materials: Advanced techniques like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) offer unparalleled control for research and the development of next-generation composites and ceramics.
By mastering the interplay of powder, pressure, and heat, sintering empowers engineers to build robust and intricate components from the ground up.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Forming | Powder is compressed in a mold. | A fragile "green" compact is created. |
| 2. Burn-Out | Temperature is raised to remove binder. | Contaminants are eliminated. |
| 3. Sintering | Heat is applied below melting point. | Particles fuse; part densifies and shrinks. |
| 4. Cooling | Part is cooled at a controlled rate. | Final microstructure and properties are set. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's projects?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for precise sintering processes. Whether you're engaged in research, development, or production, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for creating robust, complex components from powders.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your sintering outcomes and drive your innovations forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of heat treatment? Managing the Risks of Distortion and Cost
- What is pressureless sintering? Achieve Complex Shapes and High Purity Without External Pressure
- How thick is vacuum deposition? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings
- What is vacuum heat treating? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Purity and Surface Integrity
- How does the cooling rate control of a furnace influence slow-cooled solid-state electrolytes? Achieve Crystal Perfection
- What are the technical consequences of failing to maintain distinct boundaries in a furnace? Master Process Control
- Why use a vacuum drying oven for PEO/LiTFSI? Achieve High-Performance PEO/LLZTO Composite Solid Electrolytes
- Why is a high-temperature pyrolysis furnace necessary for single-atom catalysts? Unlock Atomic Precision



















