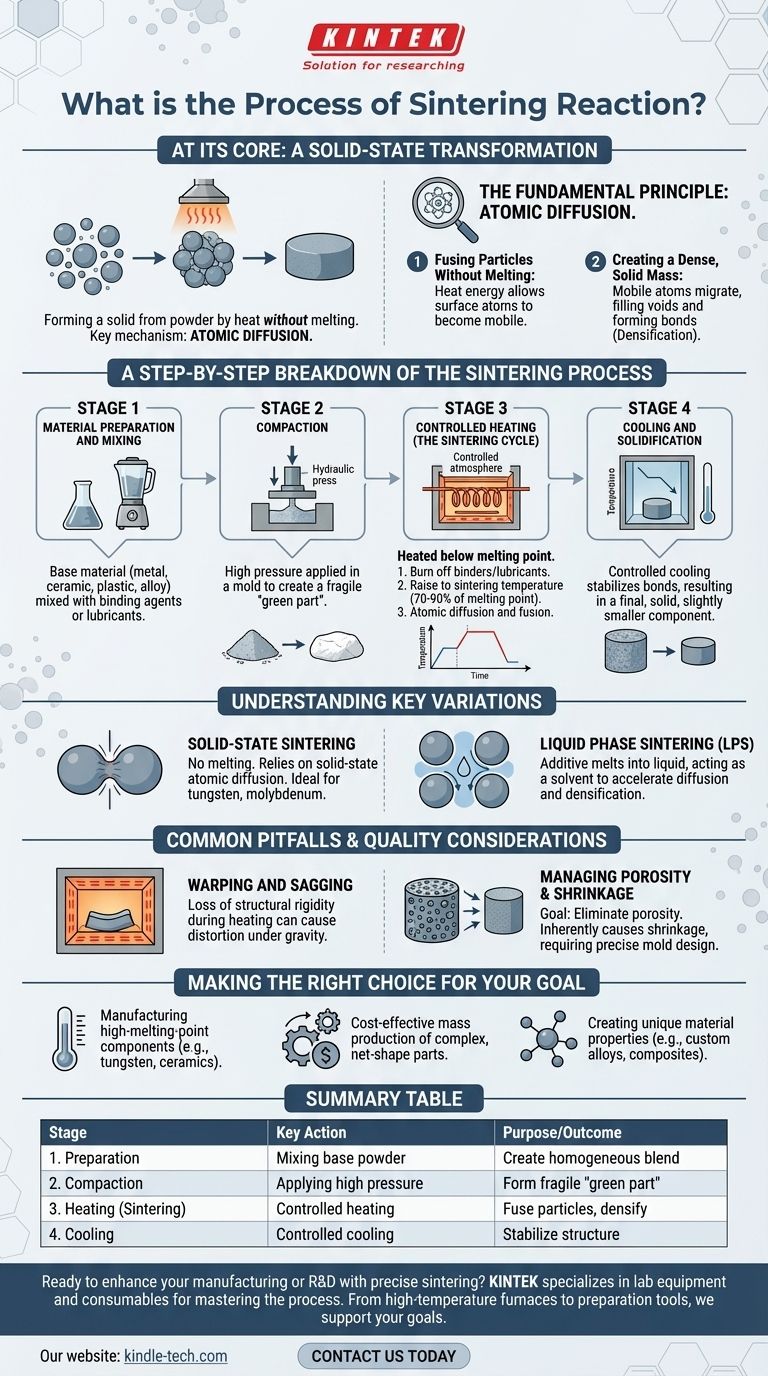
At its core, the sintering process is a method of forming a solid, dense object from a powder by applying heat without melting the material into a liquid state. The fundamental steps involve preparing and compacting a powder into a desired shape, then heating it in a controlled environment to a temperature just below its melting point, causing the individual particles to fuse together.
Sintering is not a melting process; it is a solid-state transformation. The key mechanism is atomic diffusion, where heat gives atoms the energy to move across particle boundaries, effectively welding the powder into a single, cohesive mass with reduced porosity.

The Fundamental Principle: Atomic Diffusion
Fusing Particles Without Melting
Sintering works because heat provides energy. Even well below a material's melting point, this energy allows atoms at the surface of each powder particle to become mobile.
These mobile atoms migrate across the contact points between adjacent particles. This process, known as atomic diffusion, gradually fills the voids between particles and forms strong metallic or chemical bonds.
Creating a Dense, Solid Mass
The result of this atomic movement is densification. The overall object shrinks slightly as the pores between particles are eliminated, and its density increases, transforming the loose or lightly-pressed powder into a strong, solid part.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Sintering Process
While specifics vary by material, the manufacturing process generally follows four distinct stages.
Step 1: Material Preparation and Mixing
The process begins with the base material in powdered form. This could be a pure metal, a ceramic, a plastic, or a pre-defined alloy.
Often, other substances are added. These can include binding agents to hold the powder together or lubricants to aid in compaction. For certain applications, different material powders are mixed to create a composite or a specific alloy.
Step 2: Compaction
The prepared powder is placed into a die or mold that reflects the final desired shape. Immense pressure is then applied to compact the powder.
This step forces the particles into close contact, creating a fragile object with the consistency of chalk. This pre-sintered object is often called a "green part."
Step 3: Controlled Heating (The Sintering Cycle)
The green part is placed into a specialized furnace with a controlled atmosphere. The heating cycle is precise and critical to success.
First, the temperature is raised slowly to burn off any lubricants or binders used in the preparation phase. The atmosphere in the furnace is often controlled to prevent oxidation of the material.
Next, the temperature is increased to the sintering temperature—typically 70-90% of the material's melting point. The part is held at this temperature, allowing atomic diffusion to occur and the particles to fuse together.
Step 4: Cooling and Solidification
Finally, the part is cooled in a controlled manner. This allows the newly formed bonds to stabilize and the final crystalline structure to set, resulting in a single, unified, and solid component. The final dimensions will be slightly smaller than the green part due to densification, a factor that must be accounted for in the initial mold design.
Understanding the Key Variations
Not all sintering is the same. The process can be modified to achieve different results or to work with different materials.
Solid-State Sintering
This is the most common form of sintering, where the entire process occurs without any part of the material melting. It relies purely on atomic diffusion in the solid state and is essential for materials with extremely high melting points, like tungsten and molybdenum.
Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS)
In this variation, an additive with a lower melting point is mixed with the primary powder. During heating, this additive melts into a liquid while the main material remains solid.
This liquid flows into the pores between the solid particles. It acts as a solvent, accelerating diffusion and helping the solid particles rearrange into a denser configuration, which speeds up the entire process.
Common Pitfalls and Quality Considerations
Achieving a perfect sintered part requires careful control over the process to avoid common defects.
The Risk of Warping and Sagging
During the heating stage, the component loses some of its structural rigidity before the new bonds are fully formed. Under the force of gravity, unsupported or complex parts can warp, sag, or distort. Proper support within the furnace is crucial.
Managing Porosity and Shrinkage
The primary goal of sintering is to eliminate porosity (the empty space between particles). Incomplete sintering will leave the part porous and weak.
Conversely, the densification process inherently causes the part to shrink. This shrinkage must be precisely calculated and factored into the initial mold design to ensure the final part meets dimensional tolerances.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Sintering is a versatile and powerful technique, but its application depends on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing high-melting-point components: Sintering is the ideal method, as it avoids the extreme energy costs and technical challenges of trying to melt-cast materials like tungsten or ceramics.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production: Sintering excels at creating complex, net-shape parts with minimal material waste and reduced need for post-process machining, making it highly economical for large volumes.
- If your primary focus is creating unique material properties: Sintering allows you to combine materials in ways not possible through melting, enabling the design of custom alloys, metal-matrix composites, and cermets.
By controlling heat and pressure, sintering transforms simple powders into complex, high-performance components.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Purpose/Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Mixing base powder with binders/lubricants | Create a homogeneous blend for consistent compaction |
| 2. Compaction | Applying high pressure in a mold | Form a fragile "green part" in the desired shape |
| 3. Heating (Sintering) | Controlled heating below melting point | Fuse particles via atomic diffusion; densify the part |
| 4. Cooling | Controlled cooling in a furnace | Stabilize bonds and finalize the component's structure |
Ready to enhance your manufacturing or R&D with precise sintering?
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables essential for mastering the sintering process. Whether you are developing new materials, optimizing production cycles, or ensuring consistent quality, our expertise and reliable products support your goals—from high-temperature furnaces with controlled atmospheres to material preparation tools.
Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve stronger, more complex parts with greater efficiency and less waste.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Does liquid pressure depend on the size and shape of the container? Discover the Hydrostatic Paradox.
- What is ethylene cracking furnace? The High-Temperature Heart of Petrochemical Production
- Why is an industrial-grade oven required during the final stage of modified H-beta zeolite catalyst preparation?
- What machine is used for casting? The Definitive Guide to Die Casting Machines
- What is the grain size of sputter coating? Control Nanoscale Structure for Your Application
- What are types of pharmaceutical mixers? Choose the Right Mixer for Your Formulation
- What is the difference between electric furnace and electric arc furnace? A Guide to Industrial Heating Methods
- What are the applications of thin films in semiconductors? Powering Modern Electronics from Transistors to Solar Cells



















