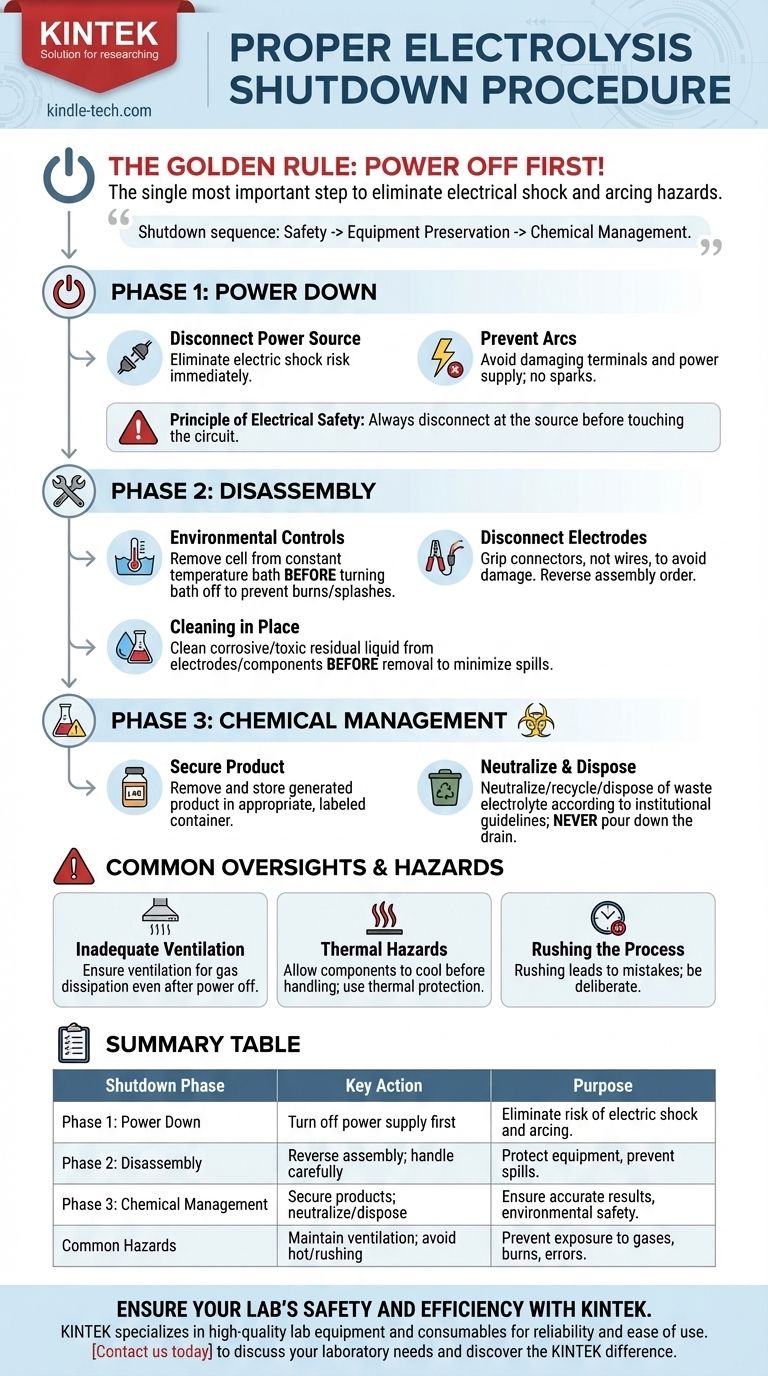
The single most important step in shutting down an electrolysis experiment is to turn off the power supply before touching or disassembling any other component. This initial action is the cornerstone of a safe procedure, followed by the systematic disassembly of the apparatus and responsible handling of all chemical products and waste.
The proper shutdown procedure is a sequence driven by safety and preservation. It prioritizes eliminating electrical hazards first, then carefully disassembling equipment to prevent damage, and finally, managing chemical materials to ensure personal and environmental safety.

The Critical First Step: Power Disconnection
The entire shutdown process is built upon one non-negotiable rule: electrical power must be the first thing you turn off and the last thing you turn on.
The Principle of Electrical Safety
Always disconnect the electrical power supply at the source before touching any part of the circuit or cell.
This action immediately eliminates the risk of electric shock, which is the most acute and immediate hazard present during the disassembly of an active electrical apparatus.
Preventing Accidental Arcs
Attempting to disconnect wires from the electrodes while the power is still on can create an electrical arc. This can damage the electrode terminals, the power supply, and poses a significant burn or fire hazard.
Sequential Disassembly: Protecting Your Equipment
Once the electrical hazard is removed, the goal shifts to safely dismantling the physical setup without causing damage. The general principle is to reverse the order of assembly.
Handling Environmental Controls
If your electrolytic cell is in a constant temperature water bath, remove the cell from the bath before turning the bath off. This prevents accidental contact with hot surfaces or splashing while handling the cell.
Disconnecting Electrodes and Components
Carefully disconnect the wires from the electrodes. Avoid pulling directly on the wires; instead, grip the connectors firmly to prevent damage to the terminals.
After the electrodes are free, you can then proceed to remove the auxiliary equipment and finally, the electrolytic cell from its stand or support structure.
The Importance of Cleaning in Place
If the electrolyte is corrosive (like a strong acid or base) or toxic, it is best practice to clean the residual liquid from the electrodes and cell components before fully removing them from the stand. This minimizes the risk of drips, spills, and chemical exposure.
Managing Chemicals, Products, and Waste
The final stage of the shutdown involves the responsible handling of the chemical contents of the cell. This is critical for both accurate experimental results and environmental protection.
Securing Your Product
If the goal of the electrolysis was to generate a specific product, remove it from the cell as required by your procedure. Ensure it is stored in an appropriate, labeled container for any further analysis or processing.
Neutralizing and Disposing of Electrolyte
Waste electrolyte must never be poured down the drain without consideration. Based on its chemical properties, it may require neutralization, recycling, or disposal as hazardous waste.
Always follow your institution's specific guidelines for chemical waste management to prevent environmental pollution and ensure compliance with regulations.
Common Oversights and Hazards to Avoid
A successful shutdown is an attentive one. Rushing the process introduces unnecessary risks to yourself and your equipment.
Inadequate Ventilation
Many electrolysis reactions can produce harmful or flammable gases. Ensure the area remains well-ventilated throughout the shutdown process, even after the power is off, to allow any residual gases to dissipate safely.
Thermal Hazards
Remember that the electrolytic cell and the electrolyte may be hot, especially if run at high current or in a heated bath. Allow components to cool to a safe temperature before handling them directly, or use appropriate thermal protection.
Rushing the Process
Each step in the shutdown sequence exists for a reason. Rushing leads to mistakes like pulling on wires, spilling corrosive chemicals, or forgetting to handle waste properly. A deliberate and methodical approach is always safer and more effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The shutdown procedure should be adapted to the specifics of your experiment, always prioritizing safety.
- If your primary focus is personal safety: Always turn the power off first, wear appropriate PPE, and be mindful of hot surfaces and chemical hazards.
- If your primary focus is preserving the product: Plan the extraction and storage of your product before starting the shutdown, ensuring you have the right containers and quenching agents ready.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Disconnect components carefully without straining wires or terminals, and clean corrosive materials from surfaces promptly.
- If your primary focus is environmental responsibility: Identify the proper disposal or neutralization procedure for your specific electrolyte and waste products before you even begin the experiment.
Ultimately, a safe and effective shutdown is an integral part of the experimental process, not an afterthought.
Summary Table:
| Shutdown Phase | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Power Down | Turn off power supply first. | Eliminates risk of electric shock and arcing. |
| Phase 2: Disassembly | Reverse assembly order; handle electrodes and baths carefully. | Protects equipment from damage and prevents chemical spills. |
| Phase 3: Chemical Management | Securely collect products; neutralize/dispose of electrolyte properly. | Ensures accurate results and environmental safety. |
| Common Hazards | Maintain ventilation; beware of hot surfaces; avoid rushing. | Prevents exposure to gases, burns, and procedural errors. |
Ensure Your Lab's Safety and Efficiency with KINTEK
Properly shutting down experiments is just one part of maintaining a safe and productive laboratory. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including electrolysis cells, power supplies, and safety gear, designed for reliability and ease of use.
Let us help you build a safer, more efficient lab. Our experts can assist in selecting the right equipment for your specific applications, ensuring your procedures—from setup to shutdown—are optimized for success.
Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover the KINTEK difference.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Thin-Layer Spectral Electrolysis Electrochemical Cell
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of the all-quartz electrolytic cell? Essential for High-Purity & Optical Analysis
- What are the necessary steps to prepare an all-quartz electrolytic cell before an experiment? Ensure Accuracy and Safety
- What are the operational procedures and safety precautions during an experiment using an all-quartz electrolytic cell? Ensure Safety and Accuracy in Your Lab
- How should an all-quartz electrolytic cell and its components be maintained for long-term use? A Guide to Maximizing Equipment Lifespan
- What are the standard opening specifications for sealed and unsealed all-quartz electrolytic cells? Optimize Your Electrochemistry Setup



















