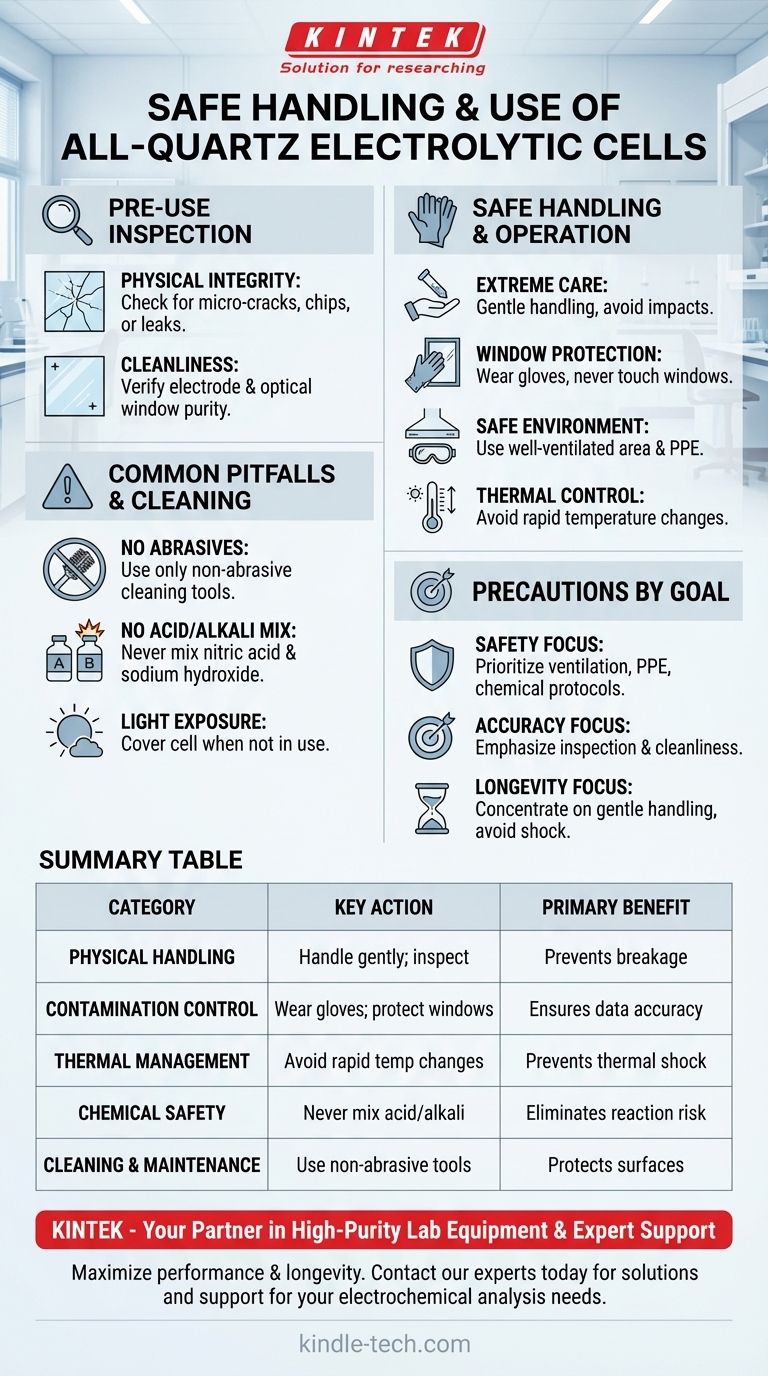
To safely handle an all-quartz electrolytic cell, you must prioritize four key areas: gentle physical handling to prevent breakage, careful temperature control to avoid thermal shock, strict contamination prevention to ensure data integrity, and adherence to correct operating procedures for both safety and experimental success. Quartz is an exceptional material for its purity and optical clarity, but it is also unforgiving of mishandling.
The core challenge of working with an all-quartz cell is balancing its superior analytical properties against its physical fragility. Your success depends on a disciplined approach that protects the equipment's physical integrity and the chemical purity of your experiment at every stage.

Pre-Use Inspection: The Foundation of a Successful Experiment
Before any experiment begins, a thorough inspection is non-negotiable. This simple step prevents catastrophic failure and ensures the reliability of your data from the outset.
Check for Physical Integrity
Always examine the cell body for any micro-cracks, chips, or leaks. Quartz is brittle, and a small, unnoticed flaw can quickly become a major failure under thermal or physical stress during an experiment.
Verify Electrode and Window Cleanliness
Ensure the electrode surfaces are clean and undamaged. Critically, inspect the optical windows for smudges or residues, as these will directly interfere with any spectroelectrochemical measurements.
Safe Handling and Operation
During the experiment, your direct interaction with the cell requires methodical care. The primary risks involve physical damage, environmental hazards, and thermal stress.
Handle with Extreme Care
Treat the cell as the fragile instrument it is. Never allow it to impact hard surfaces. When moving or setting it down, do so deliberately and gently.
Protect Optical Windows
The optical windows are the most critical surfaces for many experiments. Never touch them with bare hands, as skin oils can affect measurements. Always wear clean gloves.
Maintain a Safe Environment
Many electrolysis processes can produce harmful gases or involve high temperatures. Ensure you are working in a well-ventilated area, such as a fume hood, and use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to avoid direct contact with electrolytes and electrodes.
Control Thermal Stress
While quartz is highly resistant to heat, it is not immune to thermal shock. Avoid rapid and extreme temperature changes, which can cause the material to crack.
Common Pitfalls and Cleaning Procedures
Post-experiment cleaning and maintenance are where many preventable accidents and damages occur. A disciplined cleaning protocol is essential for the cell's longevity.
Avoid Abrasive Tools
Never use metal brushes or other hard, abrasive tools to clean the cell. These will inevitably scratch the quartz surfaces, especially the polished optical windows, permanently damaging the cell.
Never Mix Acid and Alkaline Cleaners
Under no circumstances should you mix acidic and alkaline cleaning agents (e.g., nitric acid and sodium hydroxide) within the cell. This combination can trigger a dangerous exothermic reaction, posing a significant safety risk and potentially destroying the cell.
Protect from Prolonged Light Exposure
When not in use, cover the cell or turn off any strong light sources. Prolonged exposure to high-intensity light can cause the window material to age or degrade over time, affecting its optical properties.
Matching Precautions to Your Primary Goal
Your specific experimental goal will determine which precautions require the most attention.
- If your primary focus is safety: Prioritize excellent ventilation, correct use of PPE, and strict adherence to chemical cleaning protocols, especially the rule against mixing acids and bases.
- If your primary focus is data accuracy: Emphasize meticulous pre-use inspection, contamination prevention, and absolute cleanliness of the optical windows.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Concentrate on gentle handling, avoiding thermal shock, and using non-abrasive cleaning methods to prevent scratches.
Ultimately, a systematic and careful approach is the key to leveraging the unique advantages of an all-quartz cell while mitigating its inherent risks.
Summary Table:
| Precaution Category | Key Action | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Handling | Handle gently; inspect for micro-cracks | Prevents catastrophic breakage |
| Contamination Control | Wear gloves; avoid touching optical windows | Ensures data integrity and accuracy |
| Thermal Management | Avoid rapid temperature changes | Prevents thermal shock and cracking |
| Chemical Safety | Never mix acidic and alkaline cleaners | Eliminates risk of dangerous reactions |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Use non-abrasive tools only | Protects quartz surfaces from scratches |
Maximize the performance and longevity of your sensitive experiments with the right equipment and support. KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment, including quartz cells, and provides expert guidance to ensure your laboratory operates safely and efficiently. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your electrochemical analysis needs and learn how we can support your research with reliable products and unparalleled technical service.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
People Also Ask
- What are the available volumes and dimensions for the all-quartz electrolytic cell? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Lab
- What materials are used to construct the all-quartz electrolytic cell? A Guide to Purity and Performance
- What is the proper procedure for post-experiment cleanup and storage of an all-quartz electrolytic cell? Ensure Longevity and Reproducibility
- Why is a quartz electrolytic cell used for acrylic acid wastewater? Ensure Chemical Stability & Data Integrity
- What are the necessary steps to prepare an all-quartz electrolytic cell before an experiment? Ensure Accuracy and Safety



















