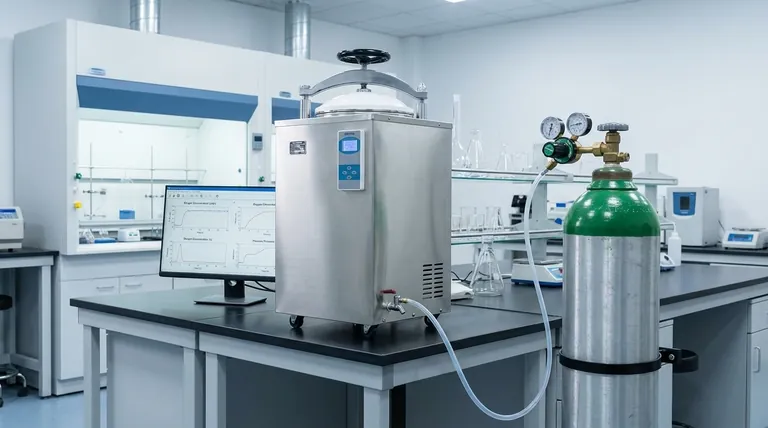
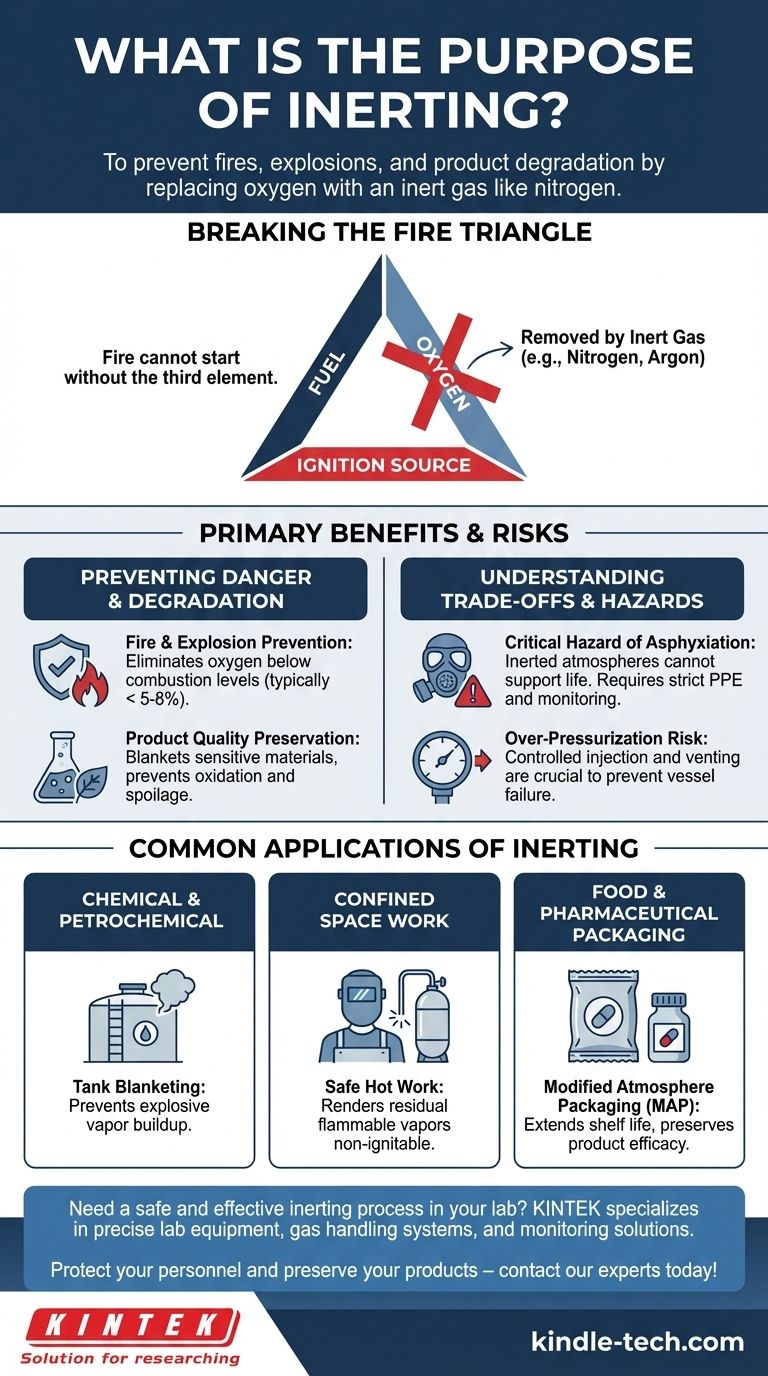
In short, the purpose of inerting is to prevent fires, explosions, and product degradation. It is a safety and quality control process that involves replacing the oxygen-rich air in a confined space with a non-reactive, or "inert," gas like nitrogen. This eliminates the possibility of combustion and other unwanted oxidative reactions.
At its core, inerting is a proactive safety measure. It operates on the simple principle that by removing oxygen from an environment, you remove the key ingredient required for fires to start or for sensitive products to spoil.

How Inerting Prevents Danger
Inerting is not just a procedure; it is the practical application of basic chemistry to control risk. The process is centered on manipulating the atmosphere within a vessel, pipeline, or package.
Breaking the Fire Triangle
For a fire or explosion to occur, three elements must be present: fuel, an ignition source (heat or a spark), and oxygen. This is often called the "fire triangle."
Inerting works by systematically removing the oxygen leg of the triangle. By purging a space with a gas like nitrogen, the oxygen concentration is lowered below the point that can sustain combustion, typically less than 5-8%.
Even if fuel and an ignition source are present, a fire cannot start because the essential third element is missing.
Preventing Oxidation and Degradation
Beyond fire prevention, inerting is critical for preserving product quality. Oxygen is a highly reactive element that can degrade sensitive materials.
This process, known as oxidation, can ruin foods, compromise pharmaceutical compounds, or alter the properties of specialty chemicals. Inerting blankets the product in a non-reactive atmosphere, significantly extending its shelf life and ensuring its integrity.
The Role of Inert Gases
The gas used must be non-reactive with the product or process. Nitrogen is the most common choice due to its relative abundance and low cost.
Other gases, such as argon or carbon dioxide, are also used in specific applications where their unique properties are beneficial. The key is that they do not participate in the chemical reactions you are trying to prevent.
Common Applications of Inerting
This principle is applied across numerous industries where atmospheric control is critical.
Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
Storing flammable liquids or volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in tanks creates a dangerous vapor space above the liquid. Inerting this space, a practice known as tank blanketing, prevents the buildup of an explosive atmosphere.
Confined Space Work
Before maintenance like welding or "hot work" can be performed inside a vessel that once held flammable materials, the space must be made safe. Inerting ensures that any residual flammable vapors cannot be ignited by sparks from the work.
Food and Pharmaceutical Packaging
The "modified atmosphere packaging" (MAP) used to keep your salad greens fresh or protect medicines in vials is a form of inerting. Replacing oxygen with nitrogen prevents spoilage and preserves the product's efficacy.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While highly effective, inerting is a serious industrial process that introduces its own set of hazards that must be managed.
The Critical Hazard of Asphyxiation
The primary danger of an inerted atmosphere is that it cannot support life. By design, it has displaced the oxygen humans need to breathe.
Entering an inerted space without the proper personal protective equipment (PPE), specifically a supplied-air respirator, is immediately fatal. This makes rigorous atmospheric testing and strict confined space entry protocols absolutely essential.
Cost and Complexity
Implementing an inerting system requires a reliable supply of inert gas, specialized delivery and monitoring equipment, and trained personnel. These factors add cost and operational complexity compared to simply venting a space with air.
Over-Pressurization
Injecting gas into a sealed vessel can lead to over-pressurization if not properly controlled and vented. This poses a significant risk of catastrophic failure to the tank or equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying inerting correctly depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is process safety: Inerting is a non-negotiable control for preventing fires and explosions when handling flammable materials in enclosed systems.
- If your primary focus is product quality: Inerting is the most effective method for protecting oxygen-sensitive goods from degradation during storage and transport.
- If your primary focus is personnel safety: You must treat any inerted environment as immediately dangerous to life and enforce strict atmospheric testing and supplied-air protocols.
Understanding the purpose of inerting is fundamental to managing risk in any industrial or chemical environment.
Summary Table:
| Purpose of Inerting | Key Benefit | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Fire & Explosion Prevention | Eliminates the oxygen required for combustion | Chemical processing, tank blanketing |
| Product Quality Preservation | Prevents oxidation and spoilage | Food & pharmaceutical packaging |
| Safe Confined Space Work | Renders flammable vapors non-ignitable | Vessel maintenance and hot work |
Need to implement a safe and effective inerting process in your lab? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables, including gas handling systems and monitoring solutions, to ensure your inerting applications are both safe and efficient. Protect your personnel and preserve your products—contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What is the primary function of a laboratory autoclave in the pre-treatment of medical plastic waste for liquid fuel?
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing



















