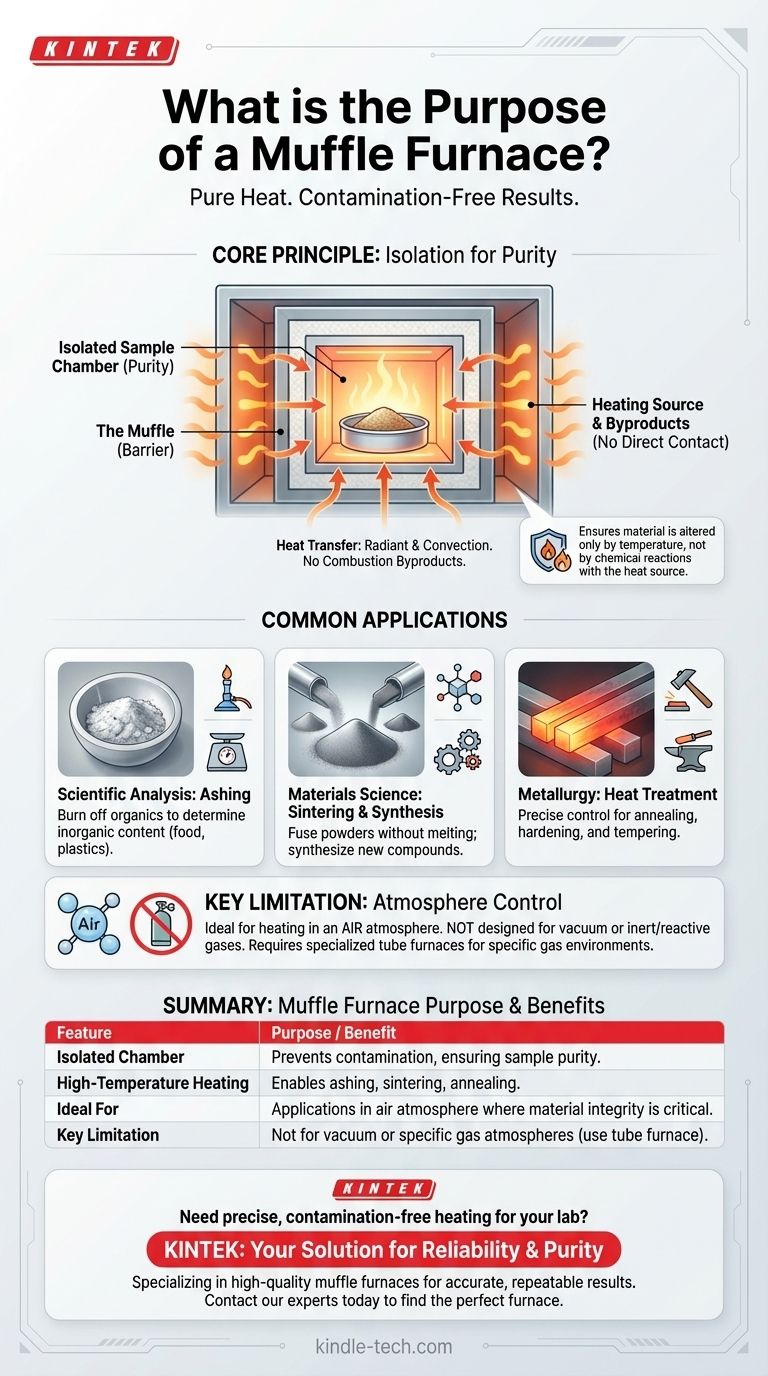
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven designed to heat materials in an environment that is completely isolated from the heat source and any byproducts of combustion. This separation prevents contamination from gases, ash, or other residues, ensuring the purity of the material being processed.
The essential purpose of a muffle furnace is not just to generate intense heat, but to do so cleanly. By creating a barrier—or "muffle"—between the heating elements and the sample chamber, it guarantees that the material is altered only by temperature, not by chemical reactions with the heat source itself.

The Core Principle: Isolation for Purity
A muffle furnace's unique value comes from its fundamental design, which prioritizes a controlled and uncontaminated heating environment. This makes it an indispensable tool in both industrial and laboratory settings.
How a Muffle Furnace Achieves Isolation
The defining feature is its use of separate chambers. The material to be heated is placed inside an inner chamber, which is effectively a sealed box.
The heating elements (in an electric furnace) or the combustion chamber (in a fuel-fired furnace) are located outside this inner chamber. Heat is transferred through the chamber walls to the sample without any direct contact.
The Evolution from Fuel to Electric
Historically, these were "re-type" furnaces that burned coal or wood. The muffle was critical to keep smoke and ash away from the workpiece.
Modern muffle furnaces are overwhelmingly electric. They use high-resistance heating elements to generate heat, which completely eliminates combustion byproducts. This provides far greater temperature control, uniformity, and purity.
How Heat is Transferred
The furnace uses a combination of radiant and convection heat. The insulated walls radiate thermal energy inward, ensuring the workpiece is heated evenly from all sides for a homogenous treatment.
Common Applications Across Industries
The ability to heat materials without contamination makes the muffle furnace essential for processes where material composition and integrity are critical.
For Scientific Analysis: Ashing
One of the most common uses is ashing. This involves heating a sample to burn off all organic material, leaving behind only the inorganic, non-combustible ash. This is vital for determining the mineral content of food, plastics, and other materials.
For Materials Science: Sintering and Synthesis
In materials science, furnaces are used for sintering, a process that uses heat to fuse powders into a solid, dense mass without melting them. They are also used for high-temperature synthesis of new compounds.
For Metallurgy: Heat Treatment
Muffle furnaces are used for various heat treatments of metals like steel and copper. Processes like annealing (softening), hardening, and tempering (reducing brittleness) all require precise temperature control in a clean environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not the universal solution for all high-temperature needs. Understanding its specific design purpose is key to using it correctly.
When a Muffle Furnace is Ideal
A muffle furnace excels at general-purpose, high-temperature heating of solid materials in an air atmosphere. It is a cost-effective and easy-to-use solution for applications like ashing, basic heat treatments, and drying, where the primary goal is pure thermal exposure.
Key Limitation: Atmosphere Control
The standard muffle furnace is not designed for processes that require a specific gas environment. Because the chamber is built for heating in ambient air, it is unsuitable for applications needing a vacuum, inert gas (like nitrogen or argon), or reactive gas atmosphere. For those tasks, a specialized device like a tube furnace is required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating instrument depends entirely on your process requirements.
- If your primary focus is determining the non-combustible content of a sample (ashing): A muffle furnace is the industry-standard tool designed precisely for this task.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment or sintering of materials in air: A muffle furnace provides a reliable, straightforward, and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is heating a sample under vacuum or in a specific gas atmosphere: You must use a different instrument, such as a tube furnace, that is engineered for atmospheric control.
By understanding that its purpose is defined by thermal purity, you can leverage the muffle furnace for its intended strengths and achieve precise, repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Purpose / Benefit |
|---|---|
| Isolated Chamber | Prevents contamination from heat source, ensuring sample purity. |
| High-Temperature Heating | Enables processes like ashing, sintering, and annealing. |
| Ideal For | Applications in air atmosphere where material integrity is critical. |
| Key Limitation | Not designed for vacuum or specific gas atmospheres (requires a tube furnace). |
Need precise, contamination-free heating for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality muffle furnaces designed for reliability and purity in critical processes like ashing and heat treatment. Our equipment helps laboratories achieve accurate, repeatable results by ensuring your samples are altered only by temperature, not by contamination.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect muffle furnace for your specific application and enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of ashing analysis? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Results
- Does melting point ever change? Unlock the Secrets of Pressure and Purity
- Why is ceramic used in making furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Resistance and Efficiency
- What are the factors affecting the rate of melting process? Master Heat Transfer for Faster Results
- Why refractory materials are used in furnaces? Ensure Safety, Efficiency, and Process Purity



















