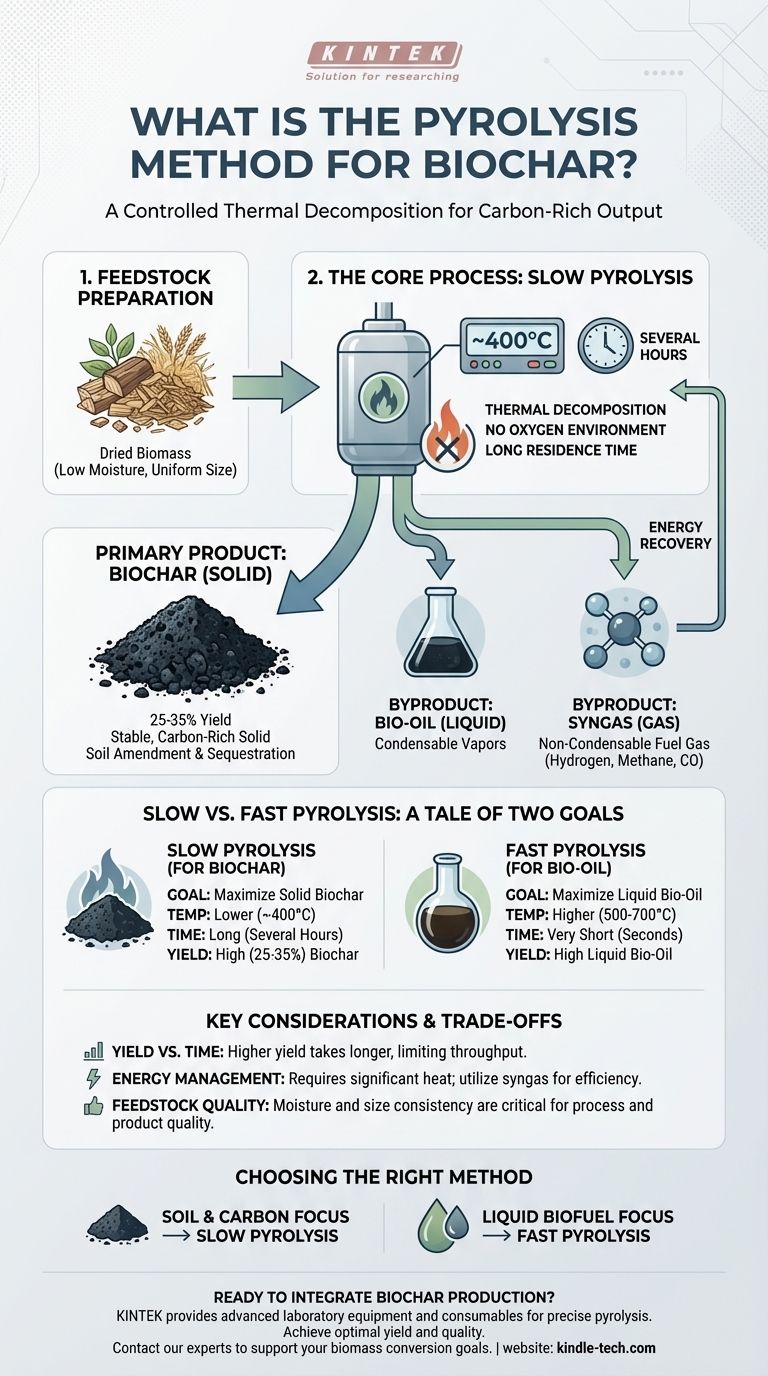
At its core, the pyrolysis method for biochar is a controlled thermal decomposition process. It involves heating organic materials, known as biomass, to moderately high temperatures (around 400°C) over a long duration (several hours) in an environment with no oxygen. This specific technique, known as slow pyrolysis, is intentionally designed to break down the biomass in a way that maximizes the output of a stable, solid, carbon-rich product: biochar.
The critical distinction is not just pyrolysis, but specifically slow pyrolysis. By carefully controlling the process with lower temperatures and longer heating times, the biomass is converted primarily into a solid char, unlike fast pyrolysis which uses high heat to maximize liquid bio-oil production.

The Core Mechanics of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a simple concept with precise requirements. Understanding these fundamentals is key to understanding how biochar is created.
What is Thermal Decomposition?
Pyrolysis is the process of heating a material until its chemical bonds break down. The defining characteristic is that this happens in a reactor with no oxygen.
Without oxygen, the biomass cannot combust or burn. Instead of turning to ash and releasing its carbon as CO2, the material thermally deconstructs into new, simpler substances.
The Role of Feedstock
A wide variety of organic materials can be used as feedstock. Common examples include pine wood, wheat straw, green waste, and even dried algae.
Before undergoing pyrolysis, this biomass must be prepared. This typically involves drying to remove moisture and mechanical comminution (grinding or chipping) to create a uniform size for even heating.
The Three Products of Pyrolysis
Every pyrolysis reaction breaks biomass down into three distinct forms:
- Solid: This is the carbon-rich char, which we call biochar.
- Liquid: These are vapors that, when cooled and condensed, form a liquid known as bio-oil.
- Gas: This is a non-condensable synthesis gas (syngas), which is a mixture of gases like hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide.
The ratio of these three products is determined almost entirely by the temperature and the heating rate.
Slow vs. Fast Pyrolysis: A Tale of Two Goals
The term "pyrolysis" is broad. The specific conditions dictate the final output, leading to two primary methods with very different results.
Slow Pyrolysis for Biochar
This is the method used to create biochar. The conditions are optimized to favor the formation of the solid char.
The key parameters are lower temperatures (around 400°C) and a long residence time (several hours). This slow "cooking" process allows stable, complex carbon structures to form, resulting in a high yield of solid biochar, typically 25-35% of the original biomass weight.
Fast Pyrolysis for Bio-Oil
In contrast, fast pyrolysis is designed to produce liquid biofuel.
This method uses much higher temperatures (500°C–700°C) and heats the biomass extremely quickly. These conditions "crack" the biomass molecules into vapors, which are then rapidly cooled to condense them into a liquid bio-crude oil. In this process, char is merely a low-yield byproduct.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While slow pyrolysis is effective for creating biochar, it is not without its operational challenges and considerations.
Yield vs. Process Time
Slow pyrolysis provides the highest possible yield of biochar from a given amount of biomass. However, the process takes several hours, which limits the total throughput of any given pyrolysis unit.
Energy Management
The process requires a significant input of energy to maintain its temperature for hours. Efficient systems capture the bio-gas byproduct and burn it to provide some or all of the heat needed for the reaction, creating a more self-sustaining loop.
Feedstock Quality is Critical
The process is sensitive to the quality of the input material. Biomass that is too wet requires a massive amount of extra energy to evaporate the water before pyrolysis can even begin. Inconsistent particle size leads to uneven heating and a lower-quality, inconsistent final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The pyrolysis method you choose is determined entirely by the end product you want to create.
- If your primary focus is soil amendment and carbon sequestration: Slow pyrolysis is the correct method, as it is specifically designed to maximize the yield of stable, solid biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing a liquid biofuel: Fast pyrolysis is the necessary approach, as its high temperatures and rapid heating rates favor the creation of condensable vapors that form bio-oil.
Ultimately, mastering pyrolysis is about controlling heat, time, and oxygen to precisely dictate the final form of the biomass.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Method | Primary Goal | Temperature Range | Residence Time | Primary Product Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | Maximize Biochar Production | ~400°C | Several Hours | 25-35% Solid Biochar |
| Fast Pyrolysis | Maximize Bio-Oil Production | 500°C–700°C | Very Short (Seconds) | High Liquid Bio-Oil |
Ready to integrate high-quality biochar production into your operations? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for precise pyrolysis processes. Our solutions help you achieve optimal biochar yield and quality for your research or application. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific biomass conversion and carbon sequestration goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time



















