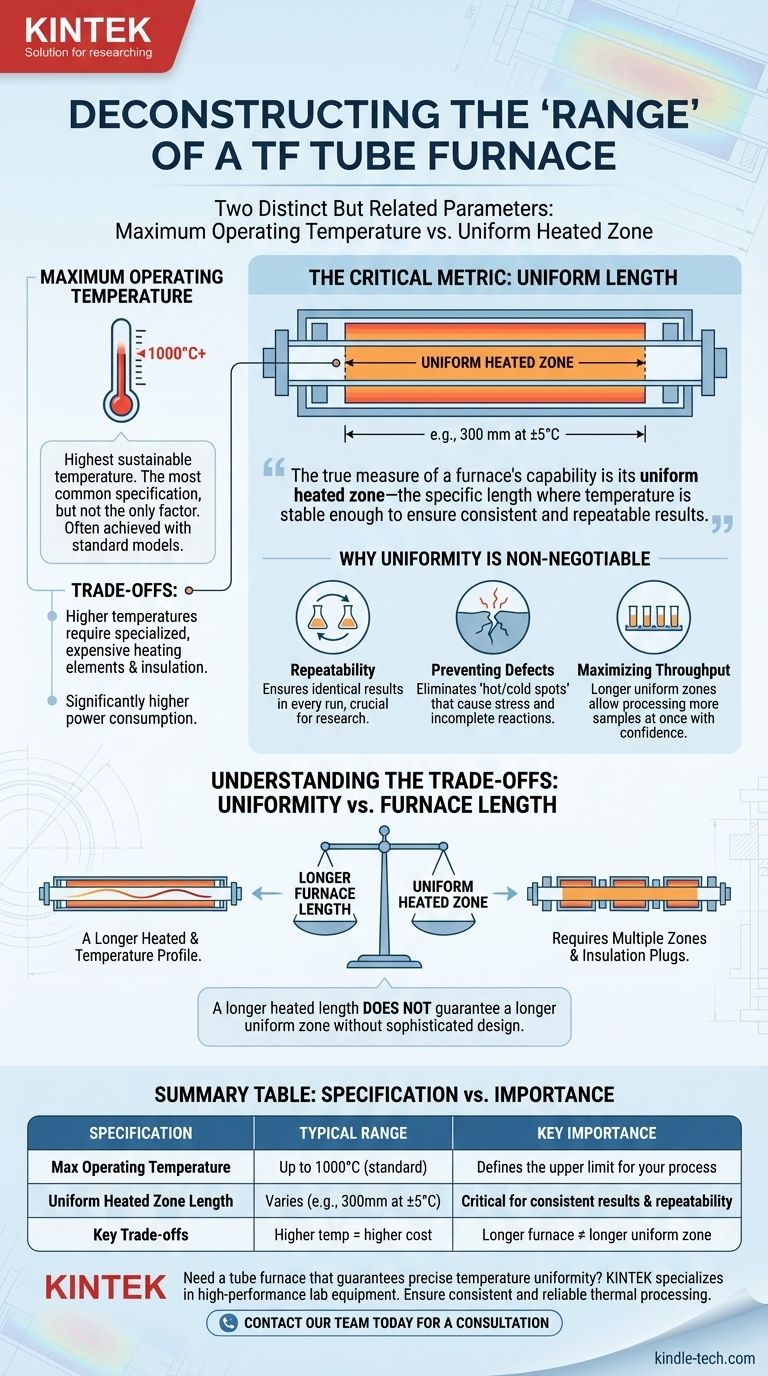
The 'range' of a TF tube furnace refers to two distinct but related parameters: its maximum operating temperature and the length of its uniform heated zone. While many standard models operate at temperatures up to 1000°C, the more critical factor for process success is the 'uniform length'—the physical region within the tube where temperature variation is minimal, ensuring your material is processed correctly.
Focusing solely on a furnace's maximum temperature is a common oversight. The true measure of a furnace's capability is its uniform heated zone—the specific length where temperature is stable enough (e.g., ±5°C) to ensure consistent and repeatable results for your material.

Deconstructing Furnace "Range"
To properly evaluate a tube furnace, you must understand how its temperature and physical dimensions interact. These two aspects of "range" define its true performance envelope.
Maximum Operating Temperature
This is the highest temperature the furnace can safely and sustainably reach. It is the most commonly advertised specification.
Many general-purpose tube furnaces, including rotary models, are designed for applications up to 1000°C. Specialized models using different heating elements and insulation can achieve significantly higher temperatures.
The Critical Metric: Uniform Length
This is the area inside the furnace where the temperature is most consistent and adheres to a specified tolerance.
This zone is typically defined with a tolerance like ±5°C over a specific length (e.g., 300 mm). Any part of your sample outside this zone will not be at the target temperature, leading to inconsistent results.
Why Temperature Uniformity is Non-Negotiable
A furnace's maximum temperature is irrelevant if it cannot hold that temperature steadily across your entire sample. Uniformity is the foundation of reliable thermal processing.
Ensuring Process Repeatability
For scientific experiments or manufacturing, your results must be repeatable. A well-defined uniform zone ensures that a process run today will be identical to one run a month from now.
Preventing Material Defects
Temperature gradients, or "hot spots" and "cold spots," across a sample can induce stress, cause incomplete reactions, or damage sensitive materials. Uniformity eliminates this risk.
Maximizing Sample Throughput
A longer uniform zone allows you to process larger samples or a greater number of smaller samples in a single run, confident that all of them are receiving the same thermal treatment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace involves balancing performance with practical and financial constraints. Higher performance in one area often comes at the cost of another.
The Cost of Higher Temperatures
Furnaces capable of temperatures well above 1000°C require more exotic (and expensive) heating elements and insulation materials. They also consume significantly more power.
Uniformity vs. Furnace Length
A longer heated length does not automatically guarantee a longer uniform zone. Achieving excellent uniformity over a greater distance requires sophisticated design, such as multiple, independently controlled heated zones and high-efficiency insulation plugs at the tube ends to prevent heat loss.
Atmosphere and Tube Material
The furnace's temperature range may exceed the limits of your work tube. A standard quartz tube, for example, has a much lower maximum operating temperature than an alumina tube. The process atmosphere can also limit the life of the heating elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your ideal furnace specifications are dictated entirely by your end goal. Match the furnace's capabilities to your specific application, paying closest attention to the factor that most impacts your results.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: Prioritize a furnace with a well-documented and stable uniform heated zone over one with a slightly higher maximum temperature.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput or large samples: Invest in a furnace with a longer uniform heated zone, which may require a multi-zone configuration.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature materials research: Verify the maximum temperature, but also confirm the compatibility of the work tube materials and insulation for that range.
Ultimately, understanding and verifying the furnace's uniform temperature zone is the key to predictable and successful thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Specification | Typical Range | Key Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Max Operating Temperature | Up to 1000°C (standard); higher for specialized models | Defines the upper limit for your process |
| Uniform Heated Zone Length | Varies (e.g., 300mm at ±5°C) | Critical for consistent results and repeatability |
| Key Trade-offs | Higher temp = higher cost; Longer furnace ≠ longer uniform zone | Balance performance with budget and application needs |
Need a tube furnace that guarantees precise temperature uniformity for your lab processes?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including tube furnaces designed for maximum repeatability and throughput. Whether you're working with materials research, heat treatment, or sample processing, our experts can help you select a furnace with the ideal temperature range and uniform heated zone for your specific application.
Ensure your thermal processing is consistent and reliable. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of corundum tubes in oxygen permeation testing? Ensure Integrity for Bi-doped Membranes
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere



















