Technically, ash and moisture content are independent physical properties of a material. However, in the context of measurement and reporting, they are critically linked. The amount of moisture present in a sample directly impacts the calculated percentage of ash, making it essential to account for water content to get an accurate and comparable result.
The core relationship is one of calculation and standardization. Failing to account for moisture dilutes the perceived concentration of ash. Therefore, reporting ash content on a "dry basis" is the universally accepted method for ensuring results are accurate, consistent, and comparable across different samples.

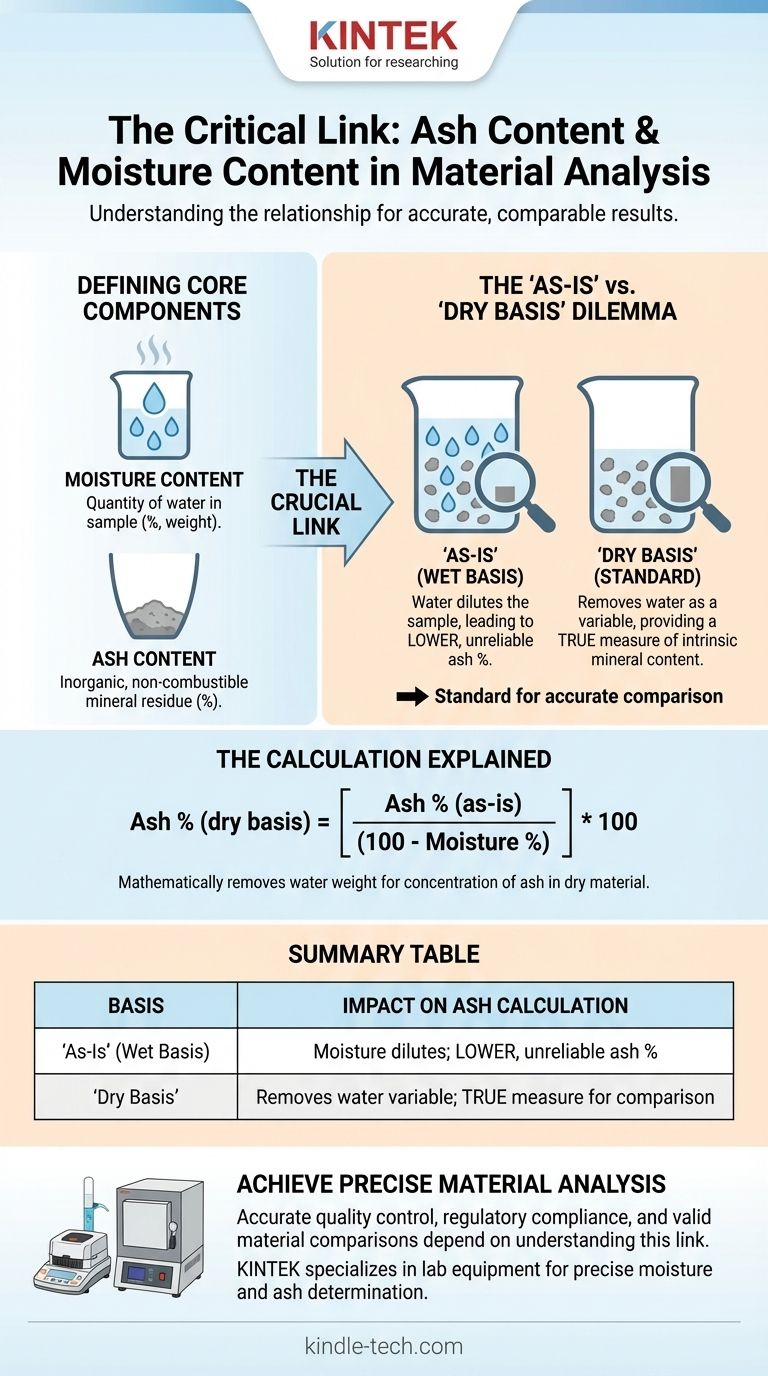
Defining the Core Components
To understand the relationship, we must first be precise about what each term means in material analysis, a process often called proximate analysis.
What is Moisture Content?
Moisture content is simply the quantity of water contained within a sample. It is typically expressed as a percentage of the total weight.
This value is determined by weighing a sample, heating it at a standardized temperature (e.g., 105°C) to evaporate the water, and then weighing it again. The difference in weight is the moisture content.
What is Ash Content?
Ash is the inorganic, non-combustible residue that remains after a sample is completely burned at high temperatures (e.g., 550-600°C).
This residue consists of minerals like calcium, potassium, silica, and magnesium. Ash content represents the total mineral content of the material.
The Crucial Link: "As-Is" vs. "Dry Basis"
The central issue connecting moisture and ash is how you define the "total weight" of the sample in your percentage calculation. This gives rise to two different ways of reporting, which are not interchangeable.
The Problem with the "As-Is" Basis
Reporting on an "as-is" or "wet basis" means you calculate the ash percentage based on the initial weight of the sample, including its moisture.
The water acts as a diluent. A sample with high moisture will have a lower reported ash percentage on an "as-is" basis than the exact same material with less moisture, even though their intrinsic mineral content is identical.
This makes "as-is" values unreliable for comparing different samples, as you might be comparing water content rather than the material itself.
Why the "Dry Basis" is the Standard
To solve this problem, results are standardized by reporting them on a "dry basis". This means the ash content is expressed as a percentage of the sample's weight after all moisture has been removed.
This creates a stable, consistent baseline for analysis. By removing the variable of water, a dry basis measurement allows for a true apples-to-apples comparison of the mineral content of different materials.
The Calculation Explained
The conversion between these two reporting methods is straightforward. If you have the percentages on an "as-is" basis, you can calculate the dry basis percentage.
Ash % (dry basis) = [ Ash % (as-is) / (100 - Moisture %) ] * 100
This formula mathematically removes the weight of the water from the denominator, showing you what the concentration of ash is in the dry material alone.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding this relationship is critical for avoiding common and costly errors in quality control, research, and industrial processes.
Inconsistent Reporting and Flawed Comparisons
The most frequent error is comparing an "as-is" value from one report to a "dry basis" value from another. This is fundamentally invalid and will lead to incorrect conclusions about which material has a higher or lower mineral content.
Propagation of Measurement Error
The formula for converting to a dry basis shows that any error in your initial moisture measurement will be magnified in the final dry-basis ash calculation. A precise and accurate determination of moisture content is the foundation for a reliable ash value.
Ignoring Sample Handling
Moisture content can change depending on ambient humidity and storage conditions. A sample left exposed to air can gain or lose moisture, altering its "as-is" weight and any subsequent calculations. Proper sample handling is paramount for repeatable results.
How to Ensure Accurate Analysis
Your approach should be dictated by your end goal, whether it's for internal process control, material comparison, or regulatory compliance.
- If your primary focus is quality control: Standardize your internal reporting. Always use a dry basis for tracking material properties over time to ensure you are monitoring the material, not its ambient moisture level.
- If your primary focus is comparing different materials: Never make a decision without converting all data to a dry basis. This is the only way to ensure you are making a fair comparison of the materials' intrinsic properties.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency (e.g., biomass energy): You need both values. Moisture content directly impacts the energy required for combustion, while high ash content can cause operational problems like slagging and fouling in boilers.
By properly accounting for moisture, you ensure your ash analysis reflects the true composition of your material, not just its temporary water content.
Summary Table:
| Basis | Definition | Impact on Ash Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| As-Is (Wet Basis) | Ash % calculated from initial sample weight (includes water). | Moisture dilutes the sample, leading to a lower, unreliable ash percentage. |
| Dry Basis | Ash % calculated from sample weight after moisture removal. | Removes water as a variable, providing a true measure of intrinsic mineral content for valid comparisons. |
Achieve precise and reliable material analysis in your lab.
Understanding the critical link between moisture and ash content is fundamental for accurate quality control, regulatory compliance, and valid material comparisons. Inconsistent reporting can lead to costly errors and flawed data.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables that deliver the accuracy and repeatability your laboratory needs. From precise moisture analyzers to robust muffle furnaces for ash determination, our solutions help you standardize your processes and generate dependable, dry-basis results.
Let us help you eliminate uncertainty from your analysis. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and ensure your lab equipment is optimized for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the cooling rate for a muffle furnace? Achieve Optimal Cooling for Your Lab Processes
- Why do we use a muffle furnace? For Pure, Precise, and Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- How does the calcination process work? Master Thermal Decomposition for Material Purification
- What is the primary use of furnace in the chemical industry? Master Thermal Treatment for Material Transformation
- What is the tolerance of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Temperature Accuracy & Uniformity



















