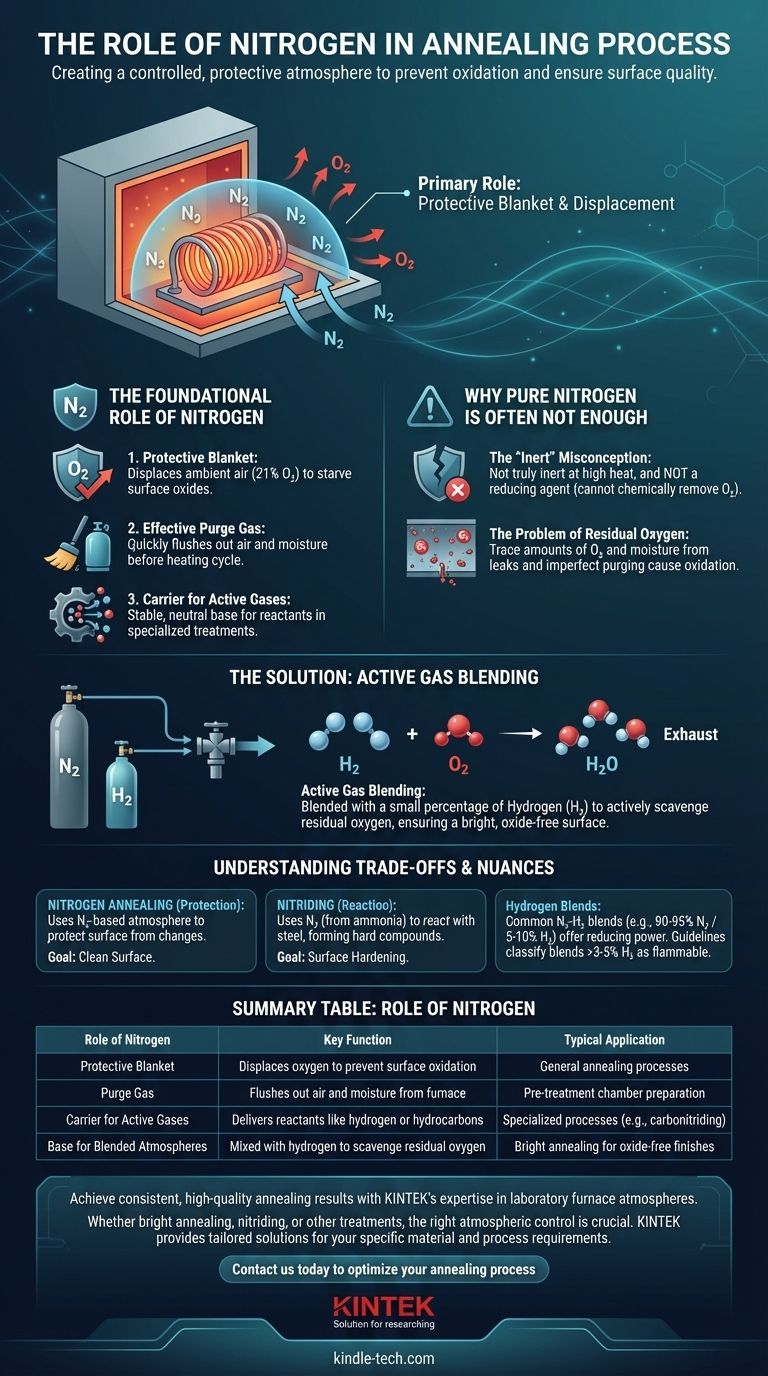
In annealing processes, nitrogen's primary role is to create a controlled, protective atmosphere that displaces oxygen, thereby preventing oxidation, scaling, and discoloration on the metal's surface. It serves as a foundational "blanket" gas and can also act as a carrier for other chemically active gases required for more specialized heat treatments.
Nitrogen is best understood not as a perfect inert shield, but as the essential starting point for atmosphere control. Because it cannot chemically remove residual oxygen, it is almost always blended with a small amount of an active gas—typically hydrogen—to achieve a truly protective and oxide-free environment.
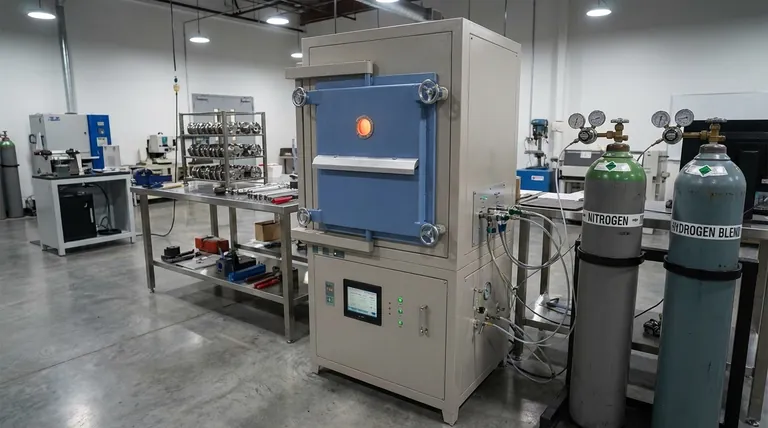

The Foundational Role of Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the workhorse gas for creating a base atmosphere in many heat treatment operations. Its function can be broken down into three distinct but related roles.
A Protective Blanket
The most fundamental purpose of introducing nitrogen into an annealing furnace is to displace the ambient air, which contains about 21% oxygen.
By creating a nitrogen-rich environment, you starve the surface of the hot metal part of the oxygen it needs to form oxides (scale or tarnish).
An Effective Purge Gas
Before the heating cycle begins, the furnace chamber must be purged of any lingering air. Nitrogen is ideal for this task.
Its high flow rate can quickly and cost-effectively flush out oxygen and moisture, preparing the furnace for the desired treatment atmosphere.
A Carrier for Active Gases
In more complex processes like carbonitriding or certain types of brazing, nitrogen serves as a stable, neutral carrier gas.
Specific amounts of active gases, such as hydrocarbons (methane, propane) or ammonia, are mixed into the base nitrogen flow. Nitrogen's role here is to deliver these reactants to the metal surface in a highly controlled and diluted manner.
Why Pure Nitrogen Is Often Not Enough
While nitrogen is excellent at displacing oxygen, it has a critical limitation that prevents its use in a pure state for high-quality annealing.
The "Inert" Misconception
Although often referred to as inert, nitrogen is not truly inert, especially at high annealing temperatures. More importantly, it is not a reducing agent.
This means it can displace oxygen, but it has no ability to chemically react with and remove any oxygen that remains or enters the furnace through small leaks.
The Problem of Residual Oxygen
No furnace is perfectly sealed, and purging is never 100% efficient. Trace amounts of oxygen and moisture will always be present.
When the metal is heated, this residual oxygen is more than enough to cause surface oxidation, defeating the purpose of a protective atmosphere for applications requiring a bright, clean finish.
The Solution: Active Gas Blending
To counteract residual oxygen, nitrogen is almost always blended with a small percentage of a reducing gas, most commonly hydrogen (H₂).
The hydrogen actively "scavenges" any free oxygen (O₂) by reacting with it to form water vapor (H₂O), which is then flushed from the furnace. This chemical cleaning action is what ensures a truly bright, oxide-free surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Using nitrogen effectively requires understanding the distinction between different processes and the importance of precise control.
Nitrogen Annealing vs. Nitriding
These terms are often confused but describe fundamentally different processes.
Nitrogen Annealing uses a nitrogen-based atmosphere to protect the metal from chemical changes like oxidation. The goal is a clean surface.
Nitriding, conversely, is a surface-hardening process that uses nitrogen (often from dissociated ammonia) to react with the steel, forming hard nitride compounds on the surface.
The Role of Hydrogen Blends
Nitrogen-hydrogen (N₂-H₂) blends are common, but the percentage of hydrogen matters. A typical blend might be 90-95% nitrogen and 5-10% hydrogen for strong reducing power.
However, for safety reasons, some guidelines now classify any blend with over 3-5% hydrogen as flammable. Blends below this threshold can be considered non-flammable, offering a safer way to achieve oxygen scavenging.
Control is Paramount
The success of any annealing process depends on strict atmospheric control. Flow rates and gas mixture ratios are determined by a pre-defined "recipe" specific to the material, part geometry, and desired outcome.
Without proper control, the atmosphere can fail to be protective or, in the case of active gas blends, may unintentionally alter the surface chemistry of the part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct atmosphere, you must first define your primary objective for the heat treatment process.
- If your primary focus is preventing basic oxidation on non-critical parts: A high-purity nitrogen purge may be sufficient, but it carries the risk of some surface discoloration.
- If your primary focus is achieving a bright, oxide-free finish (Bright Annealing): A nitrogen-hydrogen (N₂-H₂) blend is essential to actively scavenge any residual oxygen and ensure a clean surface.
- If your primary focus is altering surface chemistry (e.g., hardening): You need a specialized atmosphere where nitrogen is a carrier for active gases, as seen in nitriding or carbonitriding processes.
Ultimately, understanding nitrogen not as a perfect shield but as a controllable foundation for your furnace atmosphere is the key to achieving consistent and high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Role of Nitrogen | Key Function | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Protective Blanket | Displaces oxygen to prevent surface oxidation | General annealing processes |
| Purge Gas | Flushes out air and moisture from the furnace | Pre-treatment chamber preparation |
| Carrier for Active Gases | Delivers reactants like hydrogen or hydrocarbons | Specialized processes (e.g., carbonitriding) |
| Base for Blended Atmospheres | Mixed with hydrogen to scavenge residual oxygen | Bright annealing for oxide-free finishes |
Achieve consistent, high-quality annealing results with KINTEK's expertise in laboratory furnace atmospheres.
Whether you're working on bright annealing, nitriding, or other heat treatments, the right atmospheric control is crucial. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions tailored to your specific material and process requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how we can help you optimize your annealing process for superior surface quality and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What is nitrogen atmosphere for annealing? Achieve Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment
- What are the functions of nitrogen (N2) in controlled furnace atmospheres? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment Results



















