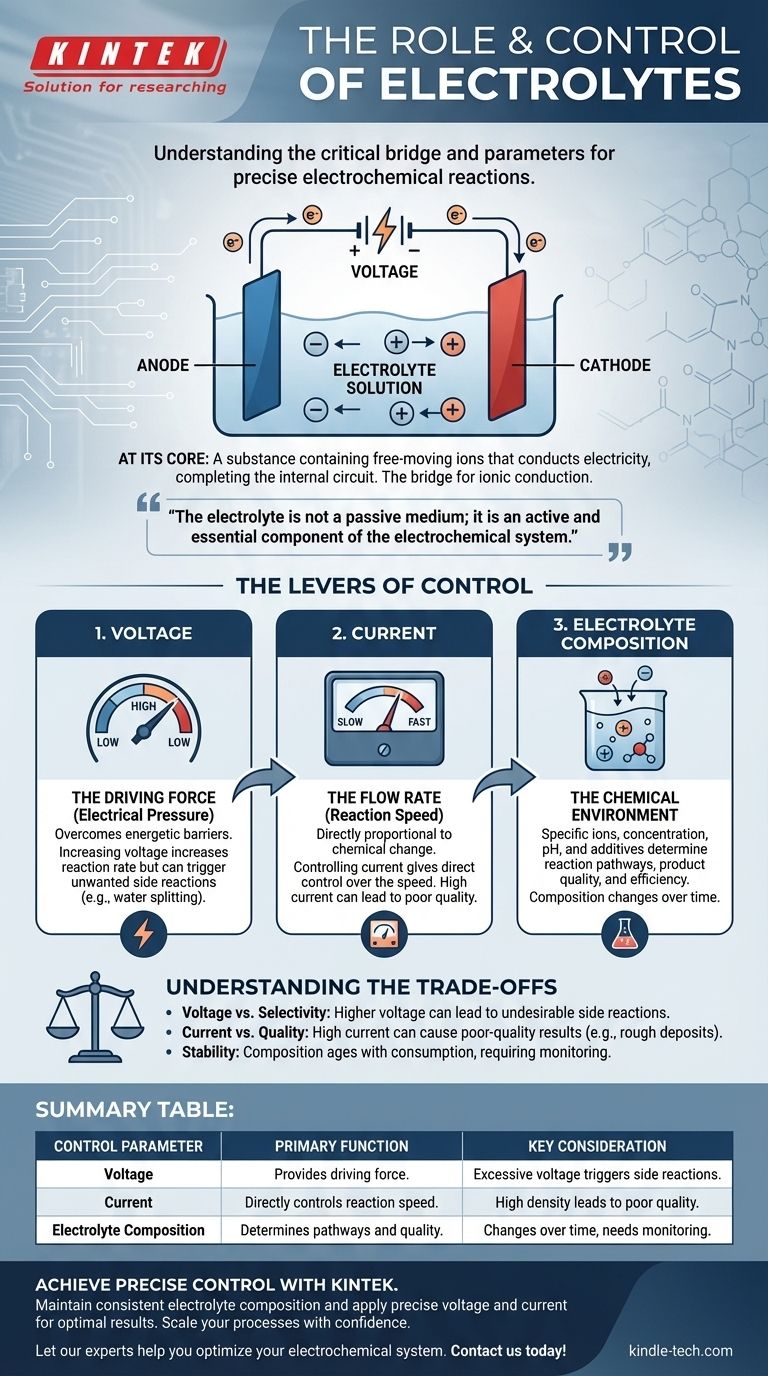
At its core, an electrolyte is a substance containing free-moving ions that conducts electricity, completing the circuit inside an electrochemical cell. It is the critical bridge that allows a chemical reaction to be driven by an external power source. The reaction itself is precisely controlled by adjusting three key parameters: the applied voltage, the resulting current, and the chemical composition of the electrolyte.
The electrolyte is not a passive medium; it is an active and essential component of the electrochemical system. Understanding how to manipulate the electrical inputs and the electrolyte's chemistry is the key to transforming a reaction from a brute-force process into a precisely controlled operation.
The Fundamental Role of the Electrolyte
To control a system, you must first understand its non-negotiable components. In electrochemistry, the electrolyte is the internal pathway that makes the entire process possible.
What is an Electrolyte?
An electrolyte is typically a solution containing dissolved salts, acids, or bases, which dissociate into positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. While often an aqueous (water-based) solution, they can also be based on organic solvents or even exist as molten salts at high temperatures.
The key property is the presence of mobile ions. Without them, the internal circuit is broken, and no electrochemical reaction can occur.
The Bridge for Ionic Conduction
An electrochemical cell has two circuits. The external circuit is the wiring through which electrons travel from one electrode to the other.
The internal circuit is the electrolyte. As electrons arrive at one electrode (the cathode) and depart from the other (the anode), ions must move through the electrolyte to balance the charge. Cations move toward the cathode and anions move toward theanode, completing the electrical circuit.
More Than Just a Conductor
The electrolyte also actively participates in the reaction. Its composition determines which chemical species are available to be oxidized or reduced, what the reaction products will be, and how quickly the reaction can proceed.
The Levers of Control: How to Manage the Reaction
Controlling an electrochemical reaction means manipulating the rate and outcome of the chemical changes occurring at the electrodes. This is achieved by managing the system's electrical and chemical properties.
Controlling Voltage (The Driving Force)
Voltage can be thought of as the "electrical pressure" pushing the reaction forward. A certain minimum voltage is required to overcome the energetic barrier of a specific reaction.
Increasing the voltage generally increases the reaction rate. However, applying excessive voltage is a blunt instrument that can trigger unwanted side reactions.
Controlling Current (The Flow Rate)
Current is the measure of how many electrons are flowing through the circuit per unit of time. According to Faraday's laws of electrolysis, the amount of chemical change is directly proportional to the amount of charge passed.
Therefore, controlling the current gives you direct control over the speed of the reaction. A constant current (galvanostatic control) ensures the reaction proceeds at a steady, predictable rate.
Adjusting Electrolyte Composition (The Chemical Environment)
This is the most nuanced level of control. The specific ions, their concentration, the solvent, and any additives fundamentally change the reaction environment.
Key factors include concentration (which affects conductivity and ion availability), pH (which can dictate which reactions are possible in water), and the presence of specialized additives that can inhibit corrosion, brighten a plated finish, or otherwise modify the outcome.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Precise control requires awareness of the limitations and consequences of each adjustment. Pushing one parameter to its extreme often compromises another.
The Voltage vs. Selectivity Problem
While higher voltage increases the rate, it can also provide enough energy to initiate undesirable reactions. For example, in an aqueous solution, excessive voltage can begin splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen, consuming energy and reducing the efficiency of your primary goal.
Current Density and Quality
Pushing for a very high current (and thus a high reaction rate) can lead to poor-quality results. In electroplating, a current that is too high can cause ions to be depleted near the electrode surface, resulting in a rough, porous, or burnt deposit. Quality often requires patience and a lower current density.
Electrolyte Stability and Lifespan
The electrolyte is not static. Its composition changes during the reaction as ions are consumed and contaminants are introduced. Solvents can evaporate, and additives can be used up. This "aging" of the electrolyte is a primary source of inconsistency in long-running industrial processes and requires monitoring and maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your strategy for control depends entirely on what you want to achieve. Use these principles to guide your approach.
- If your primary focus is maximizing reaction speed: Use a higher current and ensure the electrolyte concentration is high enough to support this rate without significant ion depletion near the electrodes.
- If your primary focus is achieving high precision or quality: Use a lower, carefully controlled current density or apply a specific voltage (potentiostatic control) to ensure the reaction proceeds smoothly and selectively.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting an inconsistent process: Begin by analyzing the electrolyte. Its composition, concentration, and potential contamination are the most common sources of process variability.
Mastering these principles transforms an electrochemical process from a black box into a precisely tunable system.
Summary Table:
| Control Parameter | Primary Function | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | Provides the driving force for the reaction. | Excessive voltage can trigger unwanted side reactions. |
| Current | Directly controls the speed of the reaction. | High current density can lead to poor-quality results. |
| Electrolyte Composition | Determines reaction pathways and product quality. | Composition changes over time, requiring monitoring. |
Ready to achieve precise control over your electrochemical processes?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need to master your reactions. Whether you are developing new materials, performing electroplating, or conducting research, our solutions help you:
- Maintain consistent electrolyte composition for reliable results.
- Apply precise voltage and current control for optimal selectivity and quality.
- Scale your processes from the lab bench to production with confidence.
Let our experts help you optimize your electrochemical system. Contact us today to discuss your specific application and challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- PTFE Electrolytic Cell Electrochemical Cell Corrosion-Resistant Sealed and Non-Sealed
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
People Also Ask
- Which parameters must be strictly controlled using an all-PTFE electrolytic cell? Ensure Precision and Safety
- What are the advantages of using a PTFE deposition tank for EPD? Achieve Unmatched Coating Precision on Stainless Steel
- What role does a two-electrode electrochemical reactor play in TiO2 growth? Achieve Ordered Nanostructures Today
- What is the purpose of the double-layer structure in the H-type electrolytic cell? Achieve Precise Thermal Control
- What functions do electrolytic cells perform in PEC water splitting? Optimize Your Photoelectrochemical Research



















