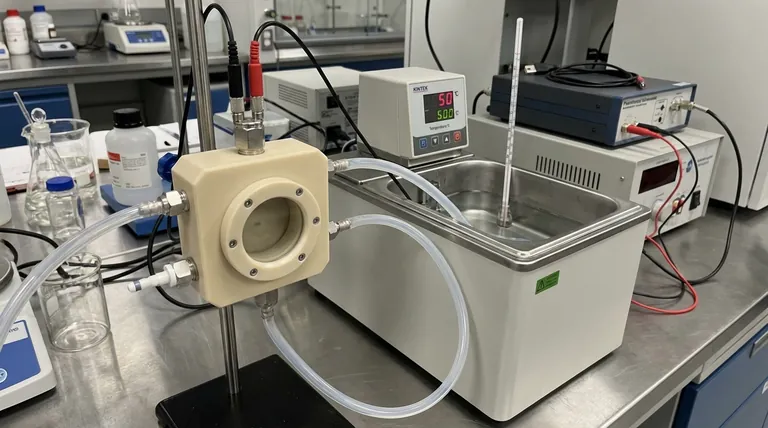
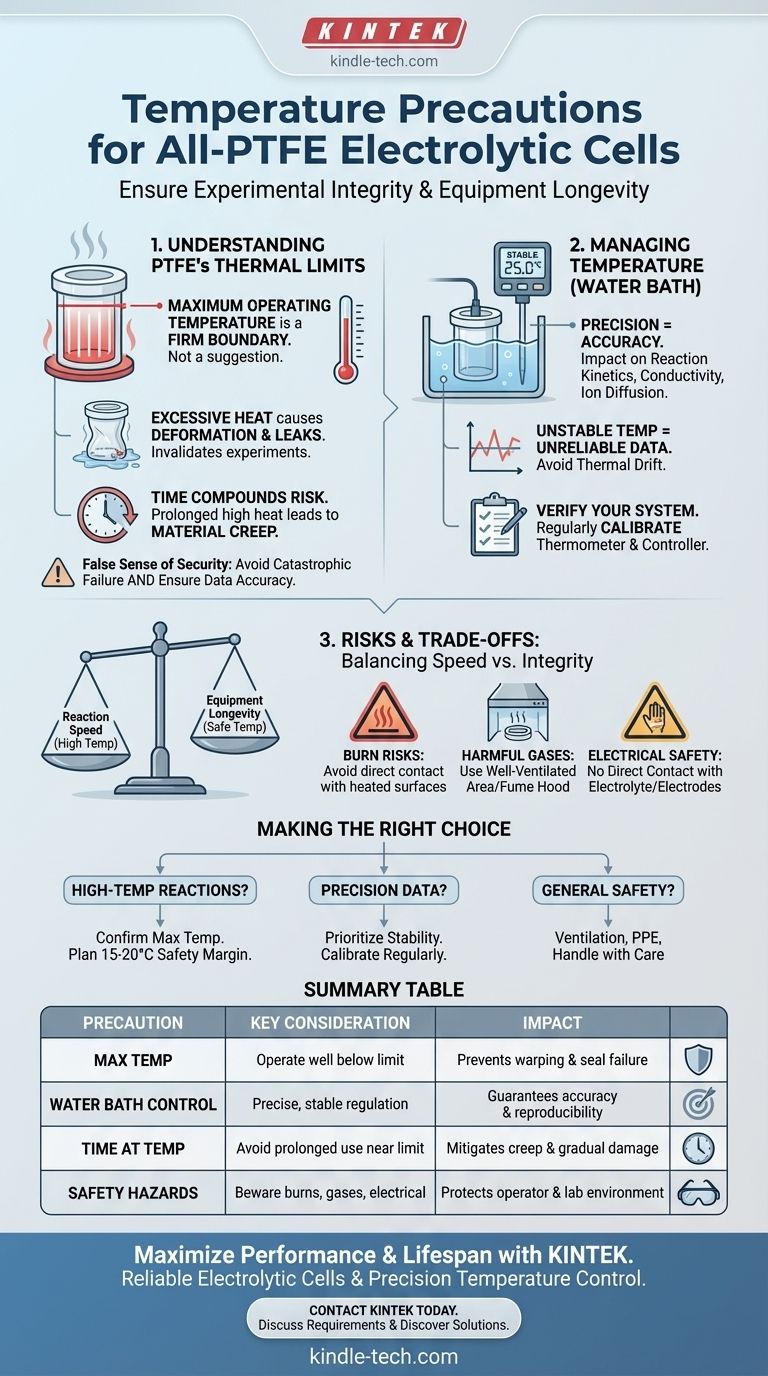
At its core, an all-PTFE electrolytic cell offers excellent chemical inertness and high-temperature resistance, but it is not immune to damage. The primary precaution is to operate the cell strictly below its specified maximum temperature limit, as prolonged exposure to excessive heat can cause irreversible deformation, compromise the cell's seal, and impact experimental integrity.
PTFE's reputation for heat resistance can create a false sense of security. The true challenge is not merely avoiding catastrophic failure, but maintaining precise, stable temperature control to ensure both the longevity of your equipment and the accuracy of your electrochemical data.

Understanding PTFE's Thermal Limits
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a fluoropolymer known for its stability. However, like all materials, its properties change with temperature, and exceeding its operational limits introduces significant risk.
The Maximum Operating Temperature
Every all-PTFE cell has a maximum tolerated temperature, which should be provided by the manufacturer. Operating near or above this limit, even for short periods, can cause the material to soften, warp, or expand. This can compromise the cell's structural integrity and the precision of its seals.
The Impact of Excessive Heat
When PTFE is overheated, it doesn't just risk physical damage. The deformation can lead to leaks in the cell, invalidating your experiment. It is critical to treat the manufacturer's temperature rating as a firm boundary, not a suggestion.
The Compounding Factor of Time
The references correctly note that damage can occur from use over "extended periods." This means that the risk isn't just from high temperature spikes. Maintaining a temperature that is even moderately high but close to the material's limit for a long duration can cause gradual material creep and deformation.
Managing Temperature with a Water Bath
For most applications, a constant temperature water bath is used to control the cell's environment. The precision of this external system is just as important as the properties of the cell itself.
Precision for Experimental Accuracy
Electrochemical reactions are highly sensitive to temperature. Parameters like reaction kinetics, electrolyte conductivity, and ion diffusion rates all change with temperature. An unstable or inaccurate water bath temperature directly translates to unreliable and non-reproducible experimental results.
Stability for Reliable Data
Even small fluctuations in temperature during an experiment can introduce noise into your measurements. Strictly controlling the water bath temperature ensures that any observed changes are due to the electrochemical variables you are studying, not thermal drift.
Verifying Your Control System
Trusting your equipment is essential, but verification is better. Regularly check the thermometer and temperature controller of your water bath against a calibrated external reference. An inaccurate controller is a primary source of experimental error and can inadvertently push your cell past its safe operating limits.
Understanding the Associated Risks and Trade-offs
Using an all-PTFE cell at elevated temperatures involves balancing the needs of your experiment against the physical limitations of the equipment and safety protocols.
Trade-off: Material Integrity vs. Reaction Speed
Researchers often increase temperature to accelerate reaction kinetics. However, this creates a direct trade-off with the longevity of the PTFE cell. Pushing for higher temperatures increases the risk of material damage. A conservative approach, operating well below the maximum temperature, is always the safer path.
Hazard: High Temperatures and Chemical Exposure
Always remember the two primary physical hazards. First, the water bath and the heated cell are burn risks; avoid direct contact. Second, electrolysis at high temperatures can increase the rate of evaporation or the production of harmful gases. Ensure your setup is in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood.
Hazard: Operator Contact and Electrical Safety
During operation, avoid all direct contact with the electrolyte and the electrodes. This is a fundamental precaution to prevent chemical burns, poisoning, and the risk of electric shock, which are amplified in a heated, conductive environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Experiment
Your experimental goal should dictate your primary focus for temperature management.
- If your primary focus is running high-temperature reactions: Your first step is to confirm the manufacturer's maximum temperature rating for your specific cell and plan to operate with a significant safety margin (e.g., 15-20°C below the limit).
- If your primary focus is generating high-precision, repeatable data: Your priority must be the stability and accuracy of your temperature control system. Regularly calibrate and verify your water bath's controller and thermometer.
- If your primary focus is general safety and equipment longevity: Your non-negotiable rule is to operate in a well-ventilated space, use appropriate personal protective equipment, and always handle the cell and associated heated apparatus with care.
Ultimately, disciplined temperature management is foundational to safe, repeatable, and accurate electrochemical research.
Summary Table:
| Precaution | Key Consideration | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature | Operate well below the manufacturer's specified limit. | Prevents warping, deformation, and seal failure. |
| Water Bath Control | Ensure precise and stable temperature regulation. | Guarantees experimental accuracy and reproducibility. |
| Time at Temperature | Avoid prolonged use near the thermal limit. | Mitigates risks of material creep and gradual damage. |
| Safety Hazards | Beware of burns, harmful gases, and electrical risks. | Protects the operator and the laboratory environment. |
Maximize the performance and lifespan of your lab equipment.
Proper temperature management is crucial for both safety and data integrity. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reliable electrolytic cells and precision temperature control systems designed for demanding electrochemical applications.
Let our expertise support your research:
- Ensure your experiments are safe, accurate, and repeatable.
- Protect your investment in sensitive equipment.
- Access the right tools and consumables for your specific laboratory needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your lab's requirements and discover how we can help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Thin-Layer Spectral Electrolysis Electrochemical Cell
People Also Ask
- What is the precaution regarding temperature when using an all-PTFE electrolytic cell? Essential Thermal Safety Tips
- What functions do electrolytic cells perform in PEC water splitting? Optimize Your Photoelectrochemical Research
- What advantages do flow electrolytic cells offer over H-type cells? Optimize CO2 Electrolysis Efficiency
- What are the advantages of using a PTFE deposition tank for EPD? Achieve Unmatched Coating Precision on Stainless Steel
- Which parameters must be strictly controlled using an all-PTFE electrolytic cell? Ensure Precision and Safety



















