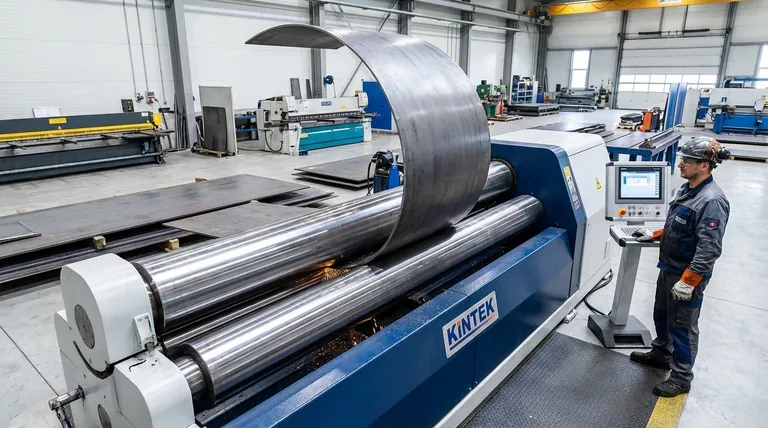
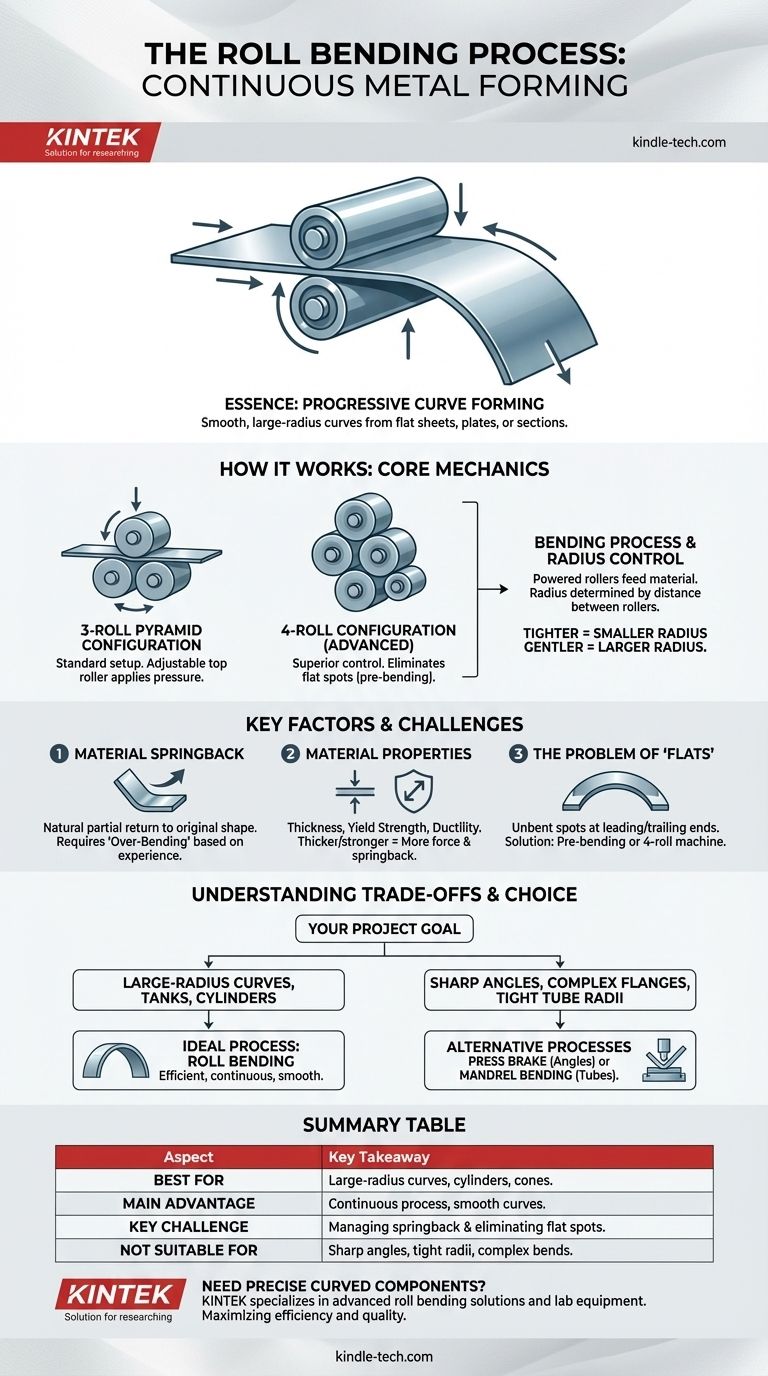
In essence, roll bending is a continuous metal forming process that uses a set of rollers to progressively shape flat metal sheets, plates, or structural sections into curved arcs, cones, or complete cylinders. Unlike press braking, which creates sharp, discrete bends, roll bending excels at producing smooth, large-radius curves without altering the material's thickness.
Roll bending is the most efficient method for creating large-radius curves in metal. Success, however, depends entirely on understanding the interplay between machine configuration, material properties, and the inherent challenge of material springback.

How Roll Bending Works: The Core Mechanics
At its heart, roll bending is a straightforward mechanical process. A flat piece of metal is fed between multiple rollers that apply pressure, inducing a permanent curve along its length.
The Machine Configuration
Most roll bending machines use a pyramid configuration of three rollers, with two lower rollers supporting the material and a single, adjustable top roller applying downward pressure.
More advanced machines use a four-roll configuration, which adds a fourth roller. This setup offers superior control, particularly for pre-bending the ends of the material to eliminate the flat spots common in three-roll systems.
The Bending Process
The process begins by feeding the flat stock into the machine. The adjustable top roller is lowered to apply a precise amount of force.
As the powered rollers feed the material through the machine, it is continuously bent into a specific radius. This process can be repeated, with incremental adjustments to the top roller, to achieve the final desired curvature.
Controlling the Bend Radius
The radius of the curve is determined by the distance between the rollers. Moving the top roller closer to the bottom rollers creates a tighter curve (smaller radius), while moving it farther away produces a gentler curve (larger radius).
Key Factors Influencing the Outcome
Achieving an accurate bend is not as simple as setting the rollers. Several material and process factors must be managed carefully.
Material Springback
Springback is the natural tendency of metal to partially return to its original flat shape after the bending force is removed.
Operators must over-bend the material past the target radius, anticipating the degree of springback. This requires experience and a deep understanding of the material's yield strength and elasticity.
Material Properties
The material's thickness, yield strength, and ductility are critical variables. Thicker and stronger materials require significantly more force to bend and will exhibit greater springback.
The Problem of "Flats"
In a standard three-roll process, the sections of material at the leading and trailing ends do not pass fully under the bending point of the top roller. This leaves unbent flat spots.
This issue is often resolved by pre-bending the ends in a separate operation (like on a press brake) or by using a four-roll machine designed to handle this initial bend.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Roll bending is a powerful process, but it is not a universal solution for all bending needs. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Best for Large Radii
Roll bending is the ideal process for creating large, sweeping curves. It is not suitable for producing tight radii or sharp, 90-degree corners, which are the domain of press brake forming.
Limited Geometric Complexity
The process is designed for creating simple, constant-radius curves, cylinders, or cones. It cannot easily produce parts with multiple, complex bends or varying radii in a single pass.
Potential for Distortion
Improper setup can lead to defects. For example, if the rollers are not perfectly parallel, the material can begin to form a cone instead of a cylinder. This requires careful machine calibration and operator skill.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Selecting the correct forming process is critical for achieving your design intent both efficiently and cost-effectively.
- If your primary focus is creating large-radius structural components, tanks, or cylinders: Roll bending is almost always the most efficient and economical method.
- If your primary focus is creating parts with sharp, discrete angles or complex flanges: A press brake offers the necessary precision and control for angular bending.
- If your primary focus is bending pipe or tube to a tight radius without it collapsing: Mandrel tube bending is the specialized process required to support the tube from the inside.
Ultimately, your part's geometry dictates the best manufacturing process for the job.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Best For | Large-radius curves, cylinders, and cones |
| Main Advantage | Continuous process for smooth curves without thickness change |
| Key Challenge | Managing material springback and eliminating flat spots |
| Not Suitable For | Sharp angles, tight radii, or complex geometric bends |
Need to create precise, curved metal components for your project?
KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and machinery, including advanced roll bending solutions, that empower your manufacturing and R&D processes. Our expertise ensures you select the right process for your material and design requirements, maximizing efficiency and quality.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and production needs with the right equipment and consumables.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- Open Type Two Roll Mixing Mill Machine for Rubber Crusher
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are pill presses called? The Correct Term is Tablet Press for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- What is the use of tablet press? Transforming Powder into Precise, Uniform Tablets
- What are the disadvantages of press working? High Costs and Design Limits for Mass Production
- How does a larger area affect the pressure of the same force? Master the Physics of Force Distribution
- How does a rotary tablet press work? A Guide to High-Speed Tablet Manufacturing



















