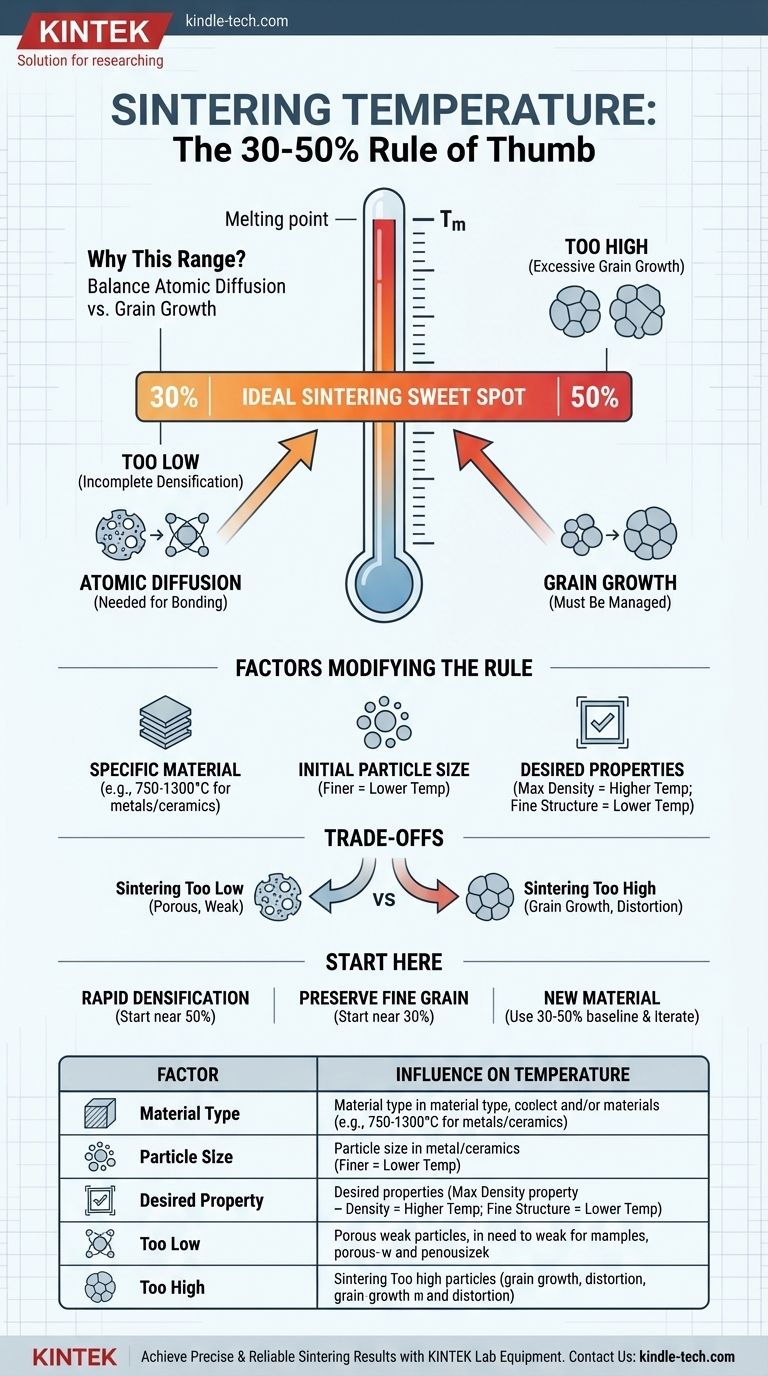
A widely accepted rule of thumb is that the ideal sintering temperature for a crystalline material is typically between 30% and 50% of its absolute melting temperature. This range provides a starting point that is hot enough to enable the bonding of particles but cool enough to prevent undesirable changes in the material's microstructure.
Sintering is fundamentally a balancing act. You need enough thermal energy to promote atomic diffusion and bond particles together, but not so much that you cause excessive grain growth, which can weaken the final part.

Why This Temperature Range is the Standard
The 30% to 50% window is not arbitrary; it represents a critical thermodynamic sweet spot for most crystalline materials. Understanding the two competing mechanisms at play—diffusion and grain growth—is key to controlling the process.
The Need for Atomic Diffusion
Sintering works by causing atoms on the surfaces of individual powder particles to move and form strong chemical bonds with neighboring particles. This process, known as atomic diffusion, requires energy.
Below 30% of the material's melting point, atomic mobility is simply too low. The process would take an impractically long time to achieve any meaningful densification or strength.
The Risk of Excessive Grain Growth
As a material is heated, its microscopic crystal structures, or "grains," have a natural tendency to merge and grow larger. This is known as grain growth.
While some grain growth is unavoidable, excessive growth can be detrimental, often leading to reduced strength and increased brittleness. This process accelerates dramatically as you approach the material's melting point.
Finding the Optimal Balance
The 30-50% range is where atomic diffusion is reasonably fast, allowing particles to bond effectively, while grain growth remains manageable. This allows you to create a dense, strong part without compromising its internal structure.
Factors That Modify the Rule of Thumb
This rule of thumb is an excellent starting point, but it is not a universal law. Several factors can shift the ideal sintering temperature for your specific application.
The Specific Material
The rule is most applicable to single-component, crystalline materials. For many common industrial metals and ceramics, this often falls within a practical range of 750°C to 1300°C.
Complex alloys or multi-material systems may have different optimal windows depending on how their components interact at high temperatures.
Initial Particle Size
Finer powders have a much higher surface area-to-volume ratio. This increased surface energy means they require less thermal energy to begin the sintering process.
As a result, materials with smaller starting particles can often be sintered at the lower end of the temperature range.
Desired Final Properties
The end goal dictates the process. If achieving the absolute maximum density is the only priority, you might push the temperature higher, towards the 50% mark.
Conversely, if preserving a very fine grain structure is critical for achieving specific mechanical or electrical properties, you would use a lower temperature and potentially a longer sintering time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a temperature is about managing compromises. Deviating too far from the optimal window has clear consequences.
Sintering Too Low
Heating the material below the effective diffusion threshold results in incomplete densification. The final part will be porous, weak, and likely unusable for any load-bearing application.
Sintering Too High
Exceeding the optimal temperature introduces significant risks. You will experience rapid and excessive grain growth, which can severely degrade the material's mechanical properties.
Furthermore, getting too close to the melting point can cause partial melting, leading to part distortion, loss of dimensional accuracy, and an uncontrolled final microstructure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use this rule of thumb not as a final answer, but as the basis for a methodical approach to developing your specific sintering process.
- If your primary focus is rapid densification: Start your process development closer to 50% of the material's melting point, but carefully monitor grain size to avoid unacceptable degradation.
- If your primary focus is preserving a fine grain structure: Begin your trials near the 30% mark and plan for a longer hold time to achieve the necessary density without coarsening the microstructure.
- If you are working with a new material: Use the 30-50% range to establish a baseline for your initial experiments, then iterate based on material characterization and performance testing.
Ultimately, this guideline is an expert starting point that empowers you to begin the critical work of process optimization.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Influence on Sintering Temperature |
|---|---|
| Material Type | Single-component, crystalline materials fit the rule best. Complex alloys may differ. |
| Particle Size | Finer powders can often be sintered at the lower end of the range. |
| Desired Property | Maximum density favors higher temps; fine grain structure favors lower temps. |
| Temperature Too Low | Results in incomplete densification, weak and porous parts. |
| Temperature Too High | Causes excessive grain growth, part distortion, and property degradation. |
Achieve precise and reliable sintering results for your laboratory. The ideal sintering process is critical for developing strong, high-performance materials. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert support you need to master thermal processing.
Our range of high-temperature furnaces is designed for precise control and uniformity, ensuring you can perfectly execute the 30-50% rule for your specific materials. Let our team help you optimize your sintering parameters to achieve superior density and microstructure.
Contact KINTALK today to discuss your sintering challenges and discover the right equipment solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs



















