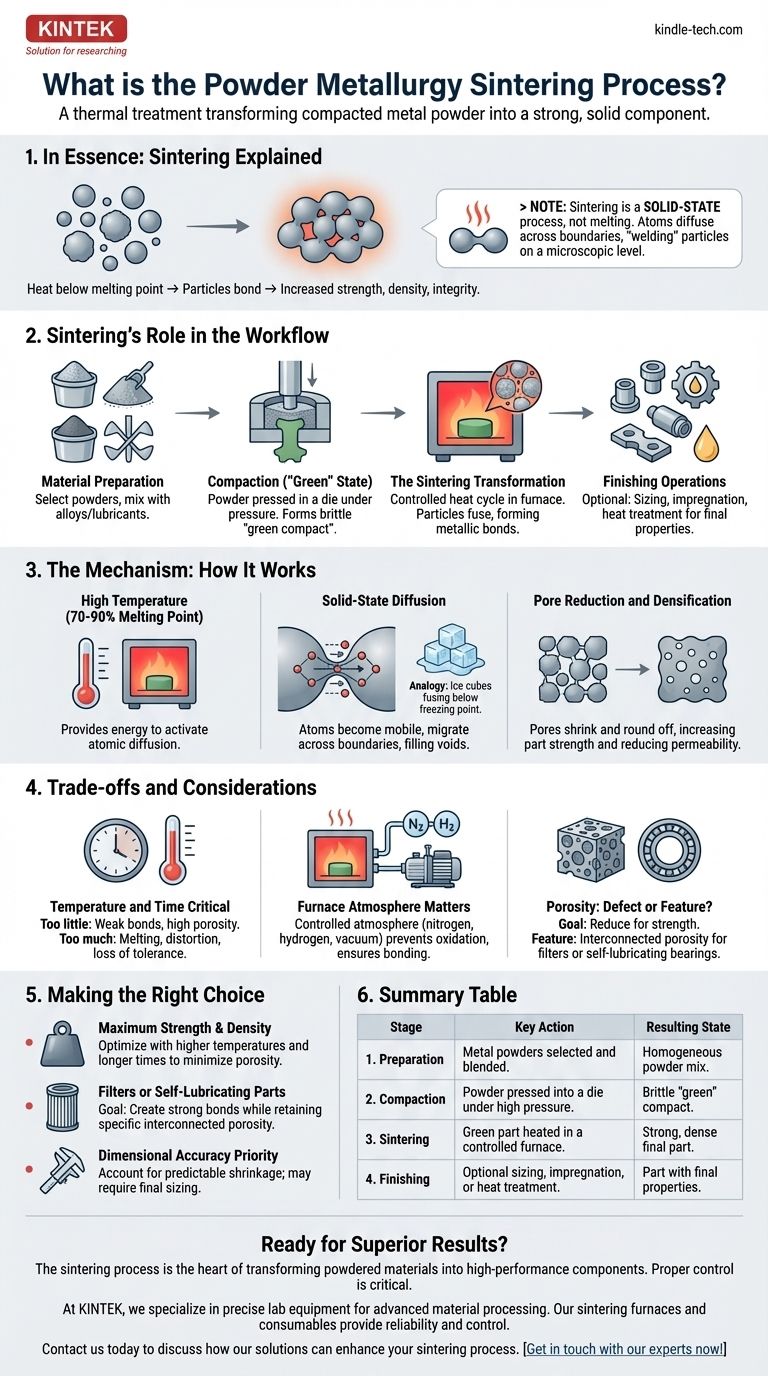
In essence, sintering is a thermal treatment that transforms a fragile, compacted metal powder into a strong, solid component. By heating the material in a controlled furnace to a temperature just below its melting point, the individual powder particles bond together, dramatically increasing the part's strength, density, and structural integrity. This process is the critical step that gives a powder metallurgy part its final, usable properties.
Sintering should not be confused with melting. It is a solid-state process where heat gives atoms enough energy to diffuse across the boundaries of adjacent particles, effectively welding them together on a microscopic level.

Sintering's Role in the Powder Metallurgy Process
Sintering is not an isolated step but a crucial phase within a larger manufacturing workflow. Understanding its position in this sequence is key to appreciating its function.
Stage 1: Material Preparation
Before any heating occurs, the base materials are selected. This involves choosing metal powders—such as iron, copper, or aluminum—and often mixing them with alloying elements or lubricants to achieve the desired final properties.
Stage 2: Compaction and the "Green" State
The blended powder is poured into a die and compressed under immense pressure. This action forms the powder into the desired net shape, creating what is known as a "green compact." This part is solid enough to be handled but is brittle and has low mechanical strength.
Stage 3: The Sintering Transformation
The green compact is then placed in a furnace. The carefully controlled heat cycle causes the particles to fuse, closing the porous spaces between them and forming strong metallic bonds. This is the stage where the part gains its definitive strength and density.
Stage 4: Finishing Operations
After sintering, some parts are ready for use. Others may undergo secondary operations like sizing for dimensional accuracy, impregnation with oil, or heat treatment to further enhance their properties.
The Mechanism: How Sintering Actually Works
The transformation from a fragile powder compact to a robust metal part occurs through a precise atomic-level phenomenon driven by thermal energy.
The Power of High Temperature
The furnace temperature is raised to a point that is typically 70-90% of the metal's absolute melting temperature. This high heat does not melt the material but provides the necessary energy to activate atomic diffusion.
Solid-State Diffusion
At sintering temperatures, atoms at the contact points between powder particles become highly mobile. They migrate across the particle boundaries, filling in voids and creating shared crystalline structures. This is analogous to how several ice cubes in a glass of water will fuse together at their contact points over time, even well below the melting point of water.
Pore Reduction and Densification
As the atoms move and the particles bond, the spaces, or pores, between the original powder particles shrink and become more rounded. This process, known as densification, reduces the overall porosity of the part, making it stronger and less permeable.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, the sintering process requires precise control to achieve the desired outcome. Mismanagement can lead to failed parts.
Temperature and Time are Critical
The final properties of a sintered part are a direct function of temperature and time in the furnace. Insufficient heat or time results in weak bonds and high porosity. Conversely, excessive heat can cause the part to melt, distort, or lose its dimensional tolerances.
Furnace Atmosphere Matters
Sintering is almost always performed in a controlled atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen, hydrogen, or a vacuum). This is critical to prevent the hot metal powder from oxidizing, which would inhibit proper bonding and ruin the final part.
Porosity Isn't Always a Defect
While sintering typically aims to reduce porosity for strength, some applications leverage it as a feature. For example, self-lubricating bearings are designed with controlled, interconnected porosity that is later impregnated with oil.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific parameters of the sintering cycle are adjusted based on the intended application of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: The process will be optimized with higher temperatures and longer furnace times to minimize porosity.
- If you are creating a filter or self-lubricating part: The goal is to create strong bonds while intentionally retaining a specific volume of interconnected porosity.
- If dimensional accuracy is your top priority: You must precisely account for the predictable shrinkage that occurs during sintering and may need to incorporate a final sizing operation.
Mastering the sintering process is fundamental to unlocking the full potential of powder metallurgy for producing complex, high-performance parts.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Resulting State |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Metal powders are selected and blended. | Homogeneous powder mix. |
| 2. Compaction | Powder is pressed into a die under high pressure. | Brittle "green" compact. |
| 3. Sintering | Green part is heated in a controlled furnace. | Strong, dense final part. |
| 4. Finishing | Optional sizing, impregnation, or heat treatment. | Part with final properties. |
Ready to achieve superior results with your powder metallurgy projects?
The sintering process is the heart of transforming powdered materials into high-performance components. Proper control over temperature, atmosphere, and time is critical for success.
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precise lab equipment needed for advanced material processing. Whether you are developing new alloys or optimizing production parameters, our sintering furnaces and consumables provide the reliability and control your laboratory requires.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your sintering process and help you produce stronger, more precise parts.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is sintering temperature determined? Master the balance between density and distortion.
- What is annealing and why is it done? Achieve Softer, More Stable Materials
- How does heat treating make metal stronger? Optimize Your Metal's Strength and Durability
- Which type of metals can be melted using tilting furnace? Your Guide to Ferrous, Non-Ferrous & Precious Metals
- What are the limitations of sintering? Understanding the Trade-offs in Powder Metallurgy
- What is the role of an arc-melting furnace in the synthesis of uranium silicide? Master Nuclear Fuel Composition
- How does temperature monitoring affect nickel alloys in SPS? Ensure Precision for High-Performance Sintering
- What is the concept of quenching? Master the Rapid Cooling Process for Stronger Metals



















