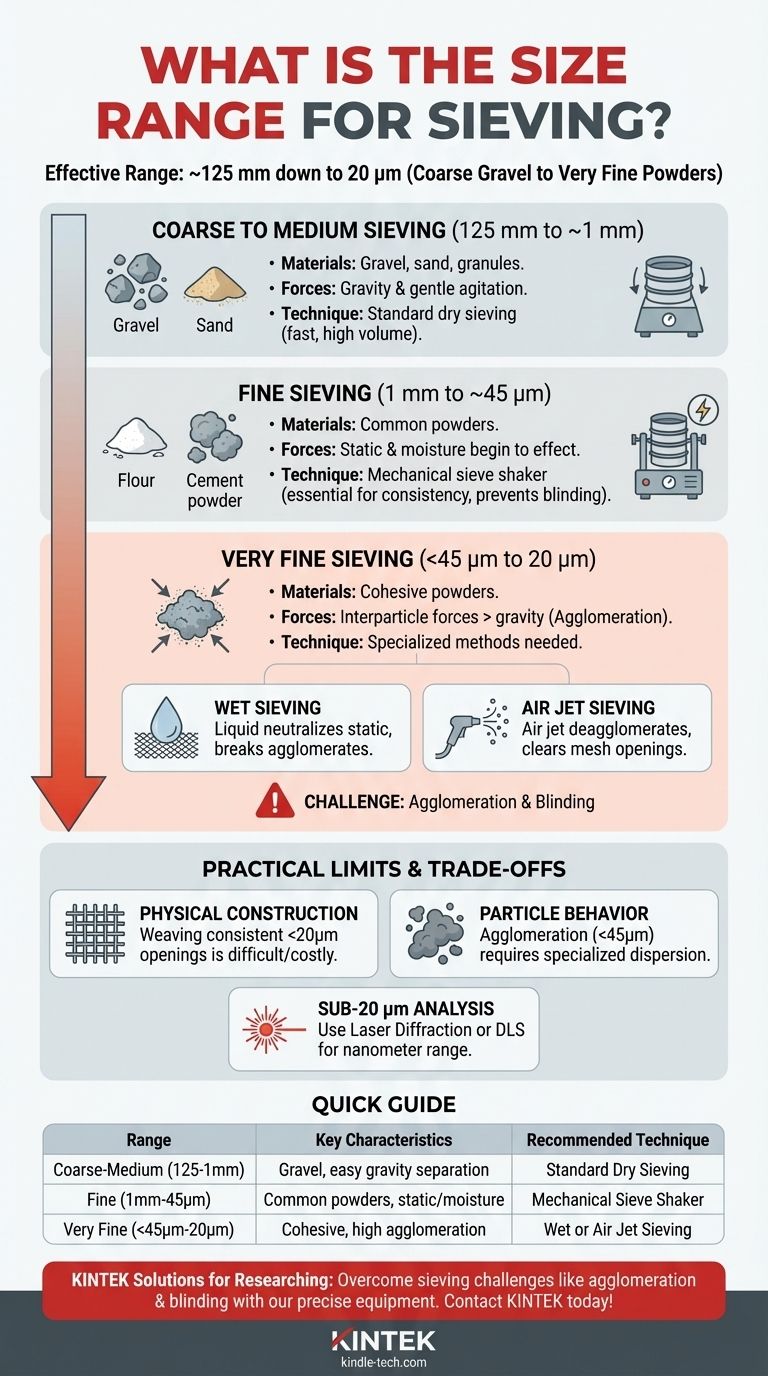
In practice, the effective size range for particle separation using woven wire test sieves spans from approximately 125 millimeters (about 5 inches) down to 20 micrometers (µm). This range covers everything from coarse gravel to very fine powders. However, the effectiveness and methodology change significantly as you approach the lower end of this spectrum.
The true challenge of sieving isn't just knowing the size range, but understanding how particle physics and sieve technology interact. While the theoretical range is wide, practical limits are dictated by particle agglomeration and the physical constraints of the sieve mesh itself.

Defining the Sieving Spectrum
Sieving is not a single process but a spectrum of techniques tailored to different particle sizes. The equipment and methods used for large aggregates are fundamentally different from those used for fine powders.
Coarse to Medium Sieving (125 mm down to ~1 mm)
This is the most straightforward range for particle separation. Materials include gravel, sand, agricultural products, and coarse granules.
The sieves used here have large, visible openings. Particles separate easily under gravity and gentle agitation, making the process fast and efficient for large-volume applications.
Fine Sieving (1 mm down to ~45 µm)
This range covers common powders like flour, cement, and many pharmaceutical ingredients. Woven wire mesh sieves are the standard tool.
As particles get smaller, forces other than gravity—like static electricity and moisture—begin to have an effect. A mechanical sieve shaker becomes essential to provide consistent, repeatable agitation and prevent the sieve from clogging (blinding).
Very Fine Sieving (Below ~45 µm to 20 µm)
This is the most challenging range for traditional dry sieving. Particles are so small and light that interparticle forces (van der Waals, electrostatic) can be stronger than the gravitational and kinetic forces trying to move them through the mesh.
This causes particles to clump together, a phenomenon known as agglomeration, which prevents them from passing through openings they would otherwise fit through. The 20 µm mark represents the practical lower limit for standard woven wire mesh due to both manufacturing difficulty and these particle behavior issues.
What Determines the Practical Limits of Sieving?
The theoretical range of sieving is limited by real-world physics and engineering. Understanding these constraints is key to achieving accurate results.
Physical Sieve Construction
Weaving a wire cloth with consistent, precise openings becomes exponentially more difficult and expensive as the hole size decreases. The 20 µm threshold is a practical limit for creating durable, reliable woven wire mesh for test sieves.
Particle Behavior and Agglomeration
For particles below 45 µm, the tendency to agglomerate is the primary obstacle. Dry agitation alone is often insufficient to break these clumps apart, leading to inaccurate results where fine particles are incorrectly measured as coarse.
Advanced Sieving Techniques
To overcome the limits of dry sieving, specialized methods are used for fine powders.
- Wet Sieving: Involves washing the sample through the sieve stack with a liquid. The liquid helps to neutralize static charges and physically break apart agglomerates, allowing fine particles to pass through the mesh.
- Air Jet Sieving: Uses a rotating nozzle to blow a jet of air up through the sieve mesh from below. This disperses the particles, deagglomerates them, and clears the mesh openings, providing highly accurate results for single-sieve analysis down to 20 µm.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sieving method involves balancing precision, speed, and cost.
Precision vs. Throughput
Finer sieves provide more detailed analysis but are much slower and have a lower capacity. They are prone to blinding (clogging), which requires more aggressive or specialized agitation to overcome, increasing analysis time.
Sieving vs. Other Analysis Methods
For particles below 20 µm, or when a full particle size distribution is needed (not just discrete fractions), other methods often become more suitable. Techniques like laser diffraction or dynamic light scattering can measure particles well into the nanometer range and are not limited by the physical constraints of a sieve.
Cost and Complexity
Standard woven wire sieves for coarse and fine analysis are relatively inexpensive. However, specialized equipment like air jet sieves represents a significant investment. Furthermore, techniques like wet sieving add complexity and cleanup time to the analytical process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Your material's characteristics will determine the best approach.
- If your primary focus is coarse materials (above 1 mm): Standard dry sieving with a mechanical shaker is fast, reliable, and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is fine powders (45 µm to 1 mm): A high-quality sieve shaker is essential for repeatable results and to prevent blinding.
- If your primary focus is very fine or cohesive powders (below 45 µm): You must plan for particle agglomeration; consider wet sieving or an air jet sieve for accurate analysis.
- If your primary focus is sub-20 µm particle analysis: Sieving may not be the appropriate tool, and you should investigate alternative methods like laser diffraction.
Ultimately, successful particle analysis depends on matching the right technique to the specific challenges presented by your material.
Summary Table:
| Sieving Range | Particle Size | Key Characteristics | Recommended Technique |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coarse to Medium | 125 mm to ~1 mm | Gravel, sand, granules; easy gravity separation | Standard dry sieving |
| Fine | 1 mm to ~45 µm | Common powders (flour, cement); static/moisture effects | Mechanical sieve shaker |
| Very Fine | Below 45 µm to 20 µm | Cohesive powders; high agglomeration risk | Wet sieving or air jet sieving |
Struggling with accurate particle size analysis? Whether you're working with coarse aggregates or fine, cohesive powders below 45µm, KINTEK has the right lab equipment to overcome sieving challenges like agglomeration and blinding. Our range of mechanical sieve shakers, wet sieving apparatus, and air jet sieves are designed to deliver precise, repeatable results for your specific material.
Let our experts help you select the perfect sieving solution. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and ensure your particle analysis is both efficient and accurate.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- What size are test sieves? A Guide to Frame Diameters and Mesh Sizes
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Which Cannot be separated by sieving? Understanding the Limits of Particle Size Separation
- Can sieving be used to separate a solid substance from a liquid substance? Learn the Right Technique for Your Mixture
- What is the operating procedure of a sieve shaker? Master Accurate Particle Size Analysis



















