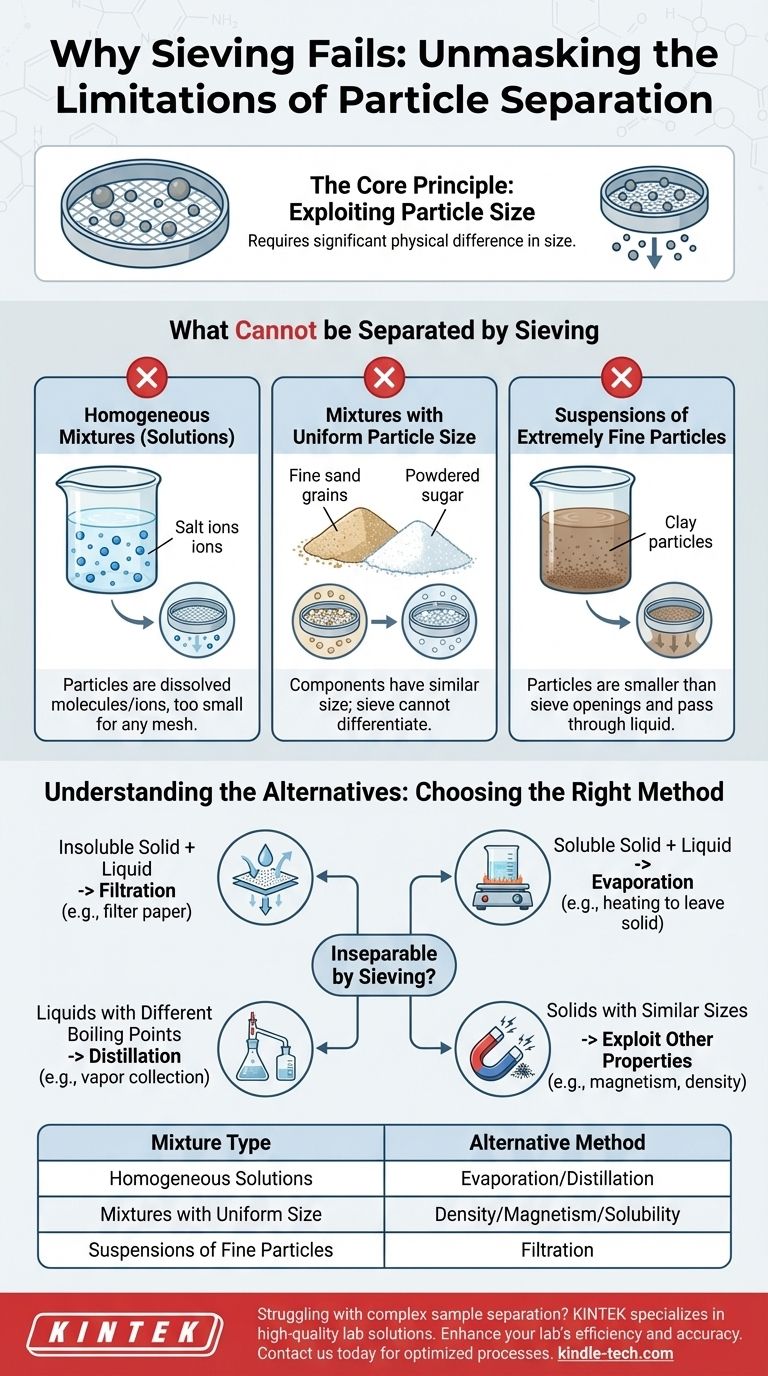
At its core, sieving is a technique that cannot separate components of a mixture that have a similar particle size. Furthermore, it is entirely ineffective for separating substances that are dissolved in a liquid, as the individual molecules or ions are far too small to be captured by any physical mesh.
Sieving relies exclusively on a physical difference in particle size to work. When components are either too close in size or are chemically integrated into a solution, the method fails, forcing the use of techniques that exploit other physical properties like density, boiling point, or solubility.

The Core Principle of Sieving
To understand its limitations, we must first establish how sieving functions. It is one of the most straightforward methods of mechanical separation.
How Sieving Works
A sieve is simply a mesh or screen with uniform openings of a specific size. When a mixture is passed over it, particles smaller than the openings fall through, while particles larger than the openings are retained.
Think of it like a coin sorter. The slots of a certain size only allow dimes to pass, while catching larger nickels and quarters.
The Critical Prerequisite: Particle Size Difference
The entire process hinges on one non-negotiable condition: a significant difference in the size of the components. If this condition is not met, the sieve cannot distinguish between the particles, rendering the technique useless.
What Makes a Mixture Inseparable by Sieving?
Several types of mixtures will not separate when sieved. These fall into predictable categories based on their physical and chemical properties.
Homogeneous Mixtures (Solutions)
A solution, such as salt or sugar dissolved in water, is a homogeneous mixture. The dissolved particles (solute) break down into individual molecules or ions, which are orders of magnitude smaller than the finest sieve mesh.
Therefore, pouring saltwater through a sieve will result in saltwater coming out; nothing is separated.
Mixtures with Uniform Particle Size
A mixture of fine sand and powdered sugar cannot be separated by a sieve. Although they are different substances, their individual grains are approximately the same size and will either both be retained or both pass through the mesh together.
Sieving has no mechanism to differentiate particles based on their chemical composition, color, or density—only their physical dimensions.
Suspensions of Extremely Fine Particles
A suspension involves insoluble particles floating in a liquid, like mud in water. If the suspended particles are very fine (e.g., clay or silt), they may be smaller than the sieve's openings.
In this case, the particles will simply pass through with the liquid, similar to what happens with a solution. For these mixtures, filtration—which uses a medium with much smaller pores—is required.
Understanding the Alternatives
When sieving is not an option, you must turn to methods that exploit other differences between the components. This is not a failure but a simple matter of choosing the right tool for the job.
When to Use Filtration
Filtration is the correct method for separating an insoluble solid from a liquid, regardless of particle size. Filter paper has microscopic pores that can trap even very fine particles while allowing the liquid to pass.
When to Use Evaporation
Evaporation is used to separate a soluble, non-volatile solid from a liquid (a solvent). By heating the solution, the liquid evaporates, leaving the solid solute behind. This is the standard method for recovering salt from saltwater.
When to Use Distillation
Distillation separates liquids with different boiling points or a liquid from a dissolved solid when you need to recover the liquid. The mixture is heated until one component boils, the vapor is collected, and then cooled back into a pure liquid.
When to Use Other Physical Properties
For mixtures of solids with similar particle sizes, you must find another property to exploit. If one component is magnetic (like iron filings), a magnet can be used. If the components have different densities, you might use a process like decantation or a centrifuge.
Choosing the Right Separation Method
Your choice of technique must be guided by the physical properties of the mixture you are trying to separate.
- If your primary focus is to separate large solids from much smaller solids: Sieving is highly effective as long as there is a clear size difference.
- If your primary focus is to separate an undissolved solid from a liquid: Use filtration to ensure all solid particles are captured.
- If your primary focus is to recover a dissolved solid from a liquid: You must use a thermal method like evaporation.
- If your primary focus is to separate components with identical particle sizes: You must exploit other physical properties, such as density, magnetism, or solubility.
Ultimately, understanding the physical nature of your mixture is the key to selecting a successful separation strategy.
Summary Table:
| Mixture Type | Reason Sieving Fails | Alternative Method |
|---|---|---|
| Homogeneous Solutions (e.g., saltwater) | Particles are dissolved molecules/ions, too small for any sieve | Evaporation or Distillation |
| Mixtures with Uniform Particle Size (e.g., sand & sugar powder) | Components have similar particle size; sieve cannot differentiate | Exploit density, magnetism, or solubility |
| Suspensions of Extremely Fine Particles (e.g., mud/clay in water) | Particles are smaller than sieve openings and pass through | Filtration using fine-pored media |
Struggling with complex sample separation in your lab? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to meet all your separation needs. Whether you require advanced filtration systems, evaporation equipment, or specialized sieves for precise particle analysis, our experts can help you select the perfect solution for your specific application.
Enhance your lab's efficiency and accuracy – Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK's reliable products can optimize your separation processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why is a standardized sieving system necessary for elephant grass research? Ensure Reliable Sample Consistency
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance



















