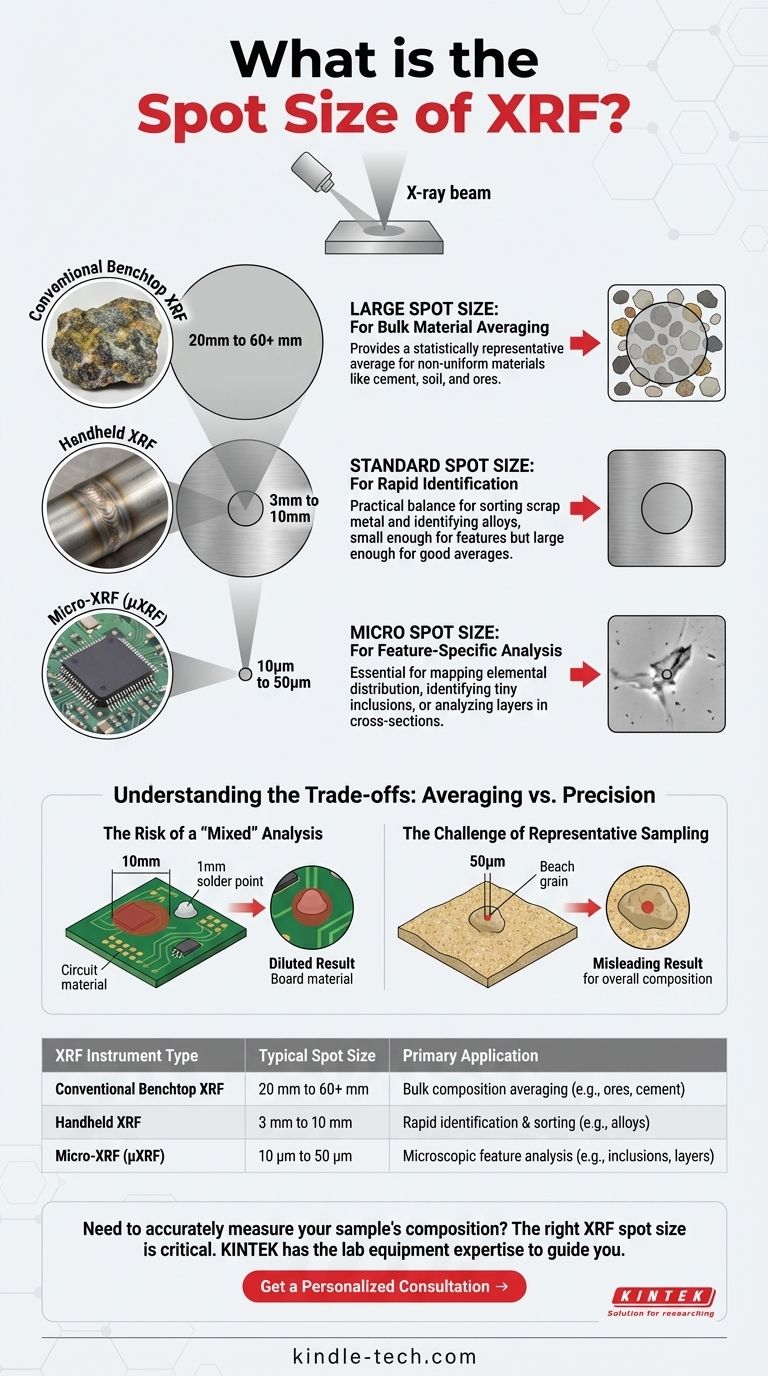
The spot size of an X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) analyzer is not a single value but varies dramatically depending on the type of instrument. For large, conventional XRF systems, the analysis spot can be quite large, typically ranging from 20 mm to over 60 mm. This large area is intentionally used to calculate an average composition over a significant volume of the sample.
The critical takeaway is that XRF spot size is not a "one-size-fits-all" specification. The correct spot size is dictated entirely by your analytical goal: whether you need a bulk average composition or a precise analysis of a microscopic feature.

Why Spot Size Dictates Your Analytical Result
The size of the X-ray beam, or "spot size," defines the area on the sample from which the elemental data is collected. This single parameter fundamentally determines whether you are performing a bulk analysis, a general surface scan, or a micro-level investigation.
Large Spots for Bulk Material Averaging
Conventional, high-power benchtop XRF instruments often use a very large spot size, sometimes several centimeters in diameter.
This is a deliberate design choice. For non-uniform (heterogeneous) materials like cement, soil, or mineral ores, a large spot provides a more statistically representative average of the overall composition. Analyzing a tiny point on such a sample would give a misleading result.
Standard Spots for Rapid Identification
Handheld XRF analyzers, which are widely used for tasks like scrap metal sorting and alloy grade identification, typically use a smaller spot size.
While not specified in all documentation, these spots are commonly in the 3 mm to 10 mm range. This size is a practical compromise, small enough to isolate specific components like a weld seam but large enough to provide a good average on relatively uniform metal surfaces.
Micro Spots for Feature-Specific Analysis
At the other end of the spectrum are micro-XRF (µXRF) systems. These specialized instruments can focus the X-ray beam down to incredibly small spots, often in the range of 10 to 50 micrometers (µm).
This capability is essential for analyzing microscopic features. Applications include mapping the elemental distribution across a semiconductor, identifying a tiny inclusion in a metal, or analyzing individual layers in a paint cross-section.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Averaging vs. Precision
Choosing the wrong spot size for your application is one of the most common sources of error in XRF analysis. You must understand the inherent compromise between getting a representative average and isolating a specific feature.
The Risk of a "Mixed" Analysis
Using a spot size that is too large for your feature of interest will produce a "mixed" or diluted result.
For example, if you try to measure a 1 mm solder point with a 10 mm XRF spot, your results will be heavily averaged with the surrounding 9 mm of circuit board. The elemental composition reported will not be representative of the solder itself.
The Challenge of Representative Sampling
Conversely, using a micro-spot on a bulk, heterogeneous material can be equally misleading.
If you analyze a single grain of sand on a beach with a 50 µm spot, you might find it is pure silicon dioxide. This result is accurate for that single grain but tells you nothing about the overall composition of the beach, which includes shells, minerals, and organic matter.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your analytical question dictates the instrument and spot size you need. Before choosing an XRF method, define what you are trying to measure.
- If your primary focus is bulk composition of a large, mixed sample (e.g., mining ores, cement): You need a large spot size found on a conventional benchtop XRF to ensure a statistically representative average.
- If your primary focus is rapid identification of common materials (e.g., alloy sorting, consumer product screening): A standard spot size (3-10 mm) on a handheld XRF is the most practical and efficient tool.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a microscopic defect, contaminant, or layer: You require the small spot size (micrometer-scale) of a specialized micro-XRF system.
Choosing the correct spot size ensures that the data you collect accurately represents the material you intend to measure.
Summary Table:
| XRF Instrument Type | Typical Spot Size | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional Benchtop XRF | 20 mm to 60+ mm | Bulk composition averaging (e.g., ores, cement) |
| Handheld XRF | 3 mm to 10 mm | Rapid identification & sorting (e.g., alloys) |
| Micro-XRF (µXRF) | 10 µm to 50 µm | Microscopic feature analysis (e.g., inclusions, layers) |
Need to accurately measure your sample's composition?
The right XRF spot size is critical for reliable results. Whether you're analyzing bulk materials, identifying alloys, or investigating microscopic features, KINTEK has the lab equipment expertise to guide you.
We specialize in providing the right analytical solutions for your laboratory's unique needs. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and ensure you get the precise data you require.
Get a Personalized Consultation →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer CaF2 Substrate Window Lens
People Also Ask
- What are the limitations of the IR spectroscopy? Understanding Its Boundaries for Accurate Analysis
- What is the difference between XRF and XRD techniques? A Guide to Choosing the Right Analytical Tool
- What is the minimum sample required for XRD analysis? Optimize Your Material Analysis
- Does higher heat capacity mean higher melting point? Unraveling the Critical Difference
- How can corrosion of the sample holder be prevented when using corrosive chemicals? Protect Your Lab's Integrity






