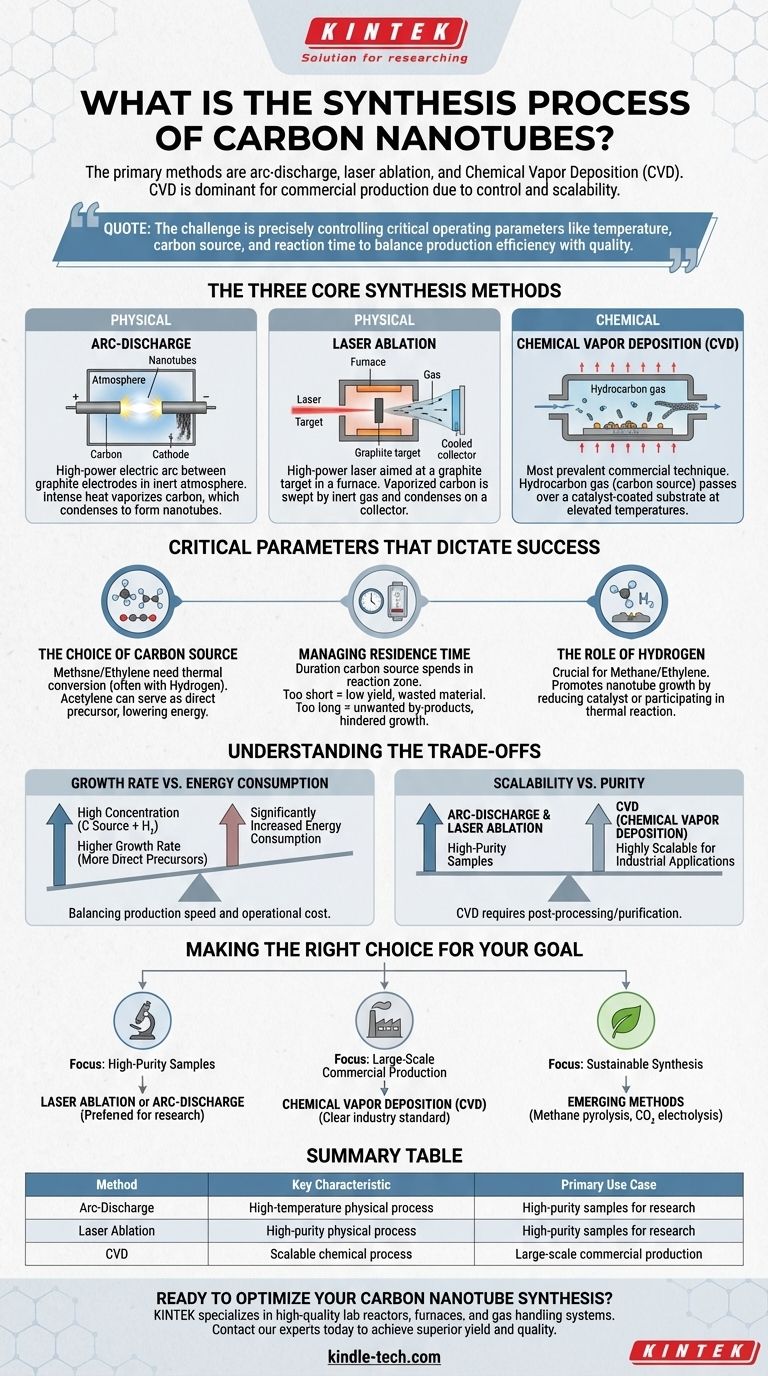
The primary methods for synthesizing carbon nanotubes are arc-discharge, laser ablation, and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). While arc-discharge and laser ablation are traditional high-temperature techniques, CVD has become the dominant process for commercial-scale production due to its superior control and scalability.
The challenge in carbon nanotube synthesis is not merely choosing a method, but precisely controlling a set of critical operating parameters—like temperature, carbon source, and reaction time—to balance production efficiency with the desired material quality.
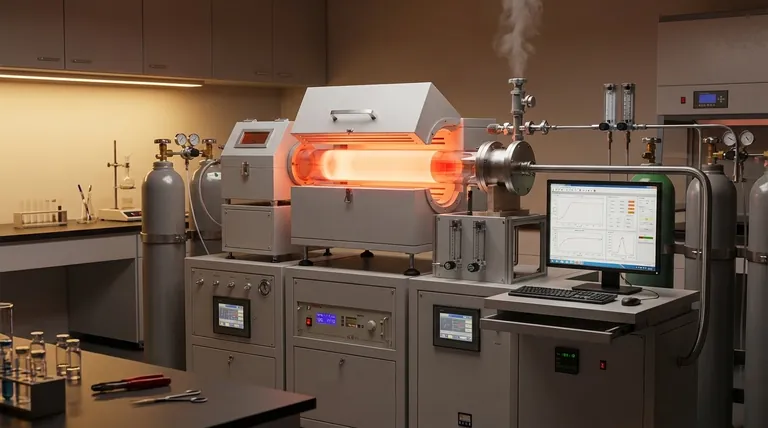

The Three Core Synthesis Methods
At a high level, the methods for producing carbon nanotubes fall into two categories: physical and chemical deposition. The first two methods are physical, relying on high energy to vaporize pure carbon, while the third is chemical, relying on the breakdown of a carbon-containing gas.
Arc-Discharge
This method uses a high-power electric arc between two graphite electrodes in an inert atmosphere. The intense heat vaporizes the carbon from the positive electrode, which then condenses to form carbon nanotubes on the cooler negative electrode.
Laser Ablation
In this process, a high-power laser is aimed at a graphite target inside a high-temperature furnace. The laser's energy vaporizes the carbon, which is then swept away by an inert gas onto a cooled collector, where the nanotubes assemble.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is the most prevalent commercial technique. It involves passing a hydrocarbon gas (the carbon source) over a substrate coated with metal catalyst particles at elevated temperatures. The catalyst breaks down the gas, and the liberated carbon atoms reassemble into nanotubes.
Critical Parameters That Dictate Success
The final quality, yield, and efficiency of any synthesis process are determined by a few key variables. Mastering these parameters is essential for consistent and predictable results.
The Choice of Carbon Source
The type of hydrocarbon gas used in CVD significantly impacts the energy required. Gases like methane and ethylene need a thermal conversion process, often assisted by hydrogen, to form the direct carbon precursors needed for nanotube growth.
In contrast, acetylene can serve as a direct precursor without additional thermal conversion, lowering the overall energy requirement of the process.
Managing Residence Time
Residence time is the duration the carbon source spends in the reaction zone. This parameter must be carefully optimized.
A residence time that is too short results in insufficient accumulation of the carbon source, leading to wasted material and low yield.
A residence time that is too long can cause limited replenishment of the carbon source and an accumulation of unwanted by-products, which can hinder growth.
The Role of Hydrogen
For carbon sources like methane and ethylene, hydrogen plays a crucial role. It can promote the growth of nanotubes by helping to reduce the catalyst or by participating directly in the thermal reaction that creates the carbon precursors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing carbon nanotube synthesis is a constant balancing act between competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is key to developing an efficient process.
Growth Rate vs. Energy Consumption
Using a high concentration of the carbon source and hydrogen can lead to a higher growth rate because more direct carbon precursors are available.
However, this strategy also leads to significantly increased energy consumption. The process must be tuned to find the optimal balance between production speed and operational cost.
Scalability vs. Purity
Traditional methods like arc-discharge and laser ablation are known for producing high-purity carbon nanotubes but are generally difficult and expensive to scale for large-volume production.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is highly scalable, making it the standard for industrial applications. However, the resulting nanotubes often require post-processing and purification to remove residual catalyst material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal synthesis strategy depends entirely on your end objective.
- If your primary focus is high-purity samples for research: Laser ablation or arc-discharge are often the preferred methods.
- If your primary focus is large-scale commercial production: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the clear industry standard due to its scalability and process control.
- If your primary focus is sustainable synthesis: Emerging methods using green feedstocks, such as methane pyrolysis or electrolysis of captured CO2, represent the future of production.
Ultimately, mastering carbon nanotube synthesis lies in the precise control of its core variables to match your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Characteristic | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Arc-Discharge | High-temperature physical process | High-purity samples for research |
| Laser Ablation | High-purity physical process | High-purity samples for research |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Scalable chemical process | Large-scale commercial production |
Ready to optimize your carbon nanotube synthesis? The right lab equipment is critical for precise control of parameters like temperature, gas flow, and catalyst preparation. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab reactors, furnaces, and gas handling systems designed for advanced materials research and development. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve superior yield and quality in your nanotube production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- What role does Ar+ ion sputtering cleaning play before Al-Zr thin film deposition? Boost Coating Adhesion Strength
- What is the temperature of the CVD chamber? A Guide to High & Low-Temp Processes
- How plasma is formed in sputtering? The Essential First Step for Precise Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the process of CVD machine? A Step-by-Step Guide to Chemical Vapor Deposition
- What is the temperature of CVD? From 200°C to 2000°C for Any Material
- What are the different types of chemical vapour deposition process? A Guide to CVD Methods for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of MCVD? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Precision in Optical Fiber Fabrication
- What is the principle of chemical vapor deposition? Unlock the Power of High-Purity Thin Film Deposition



















