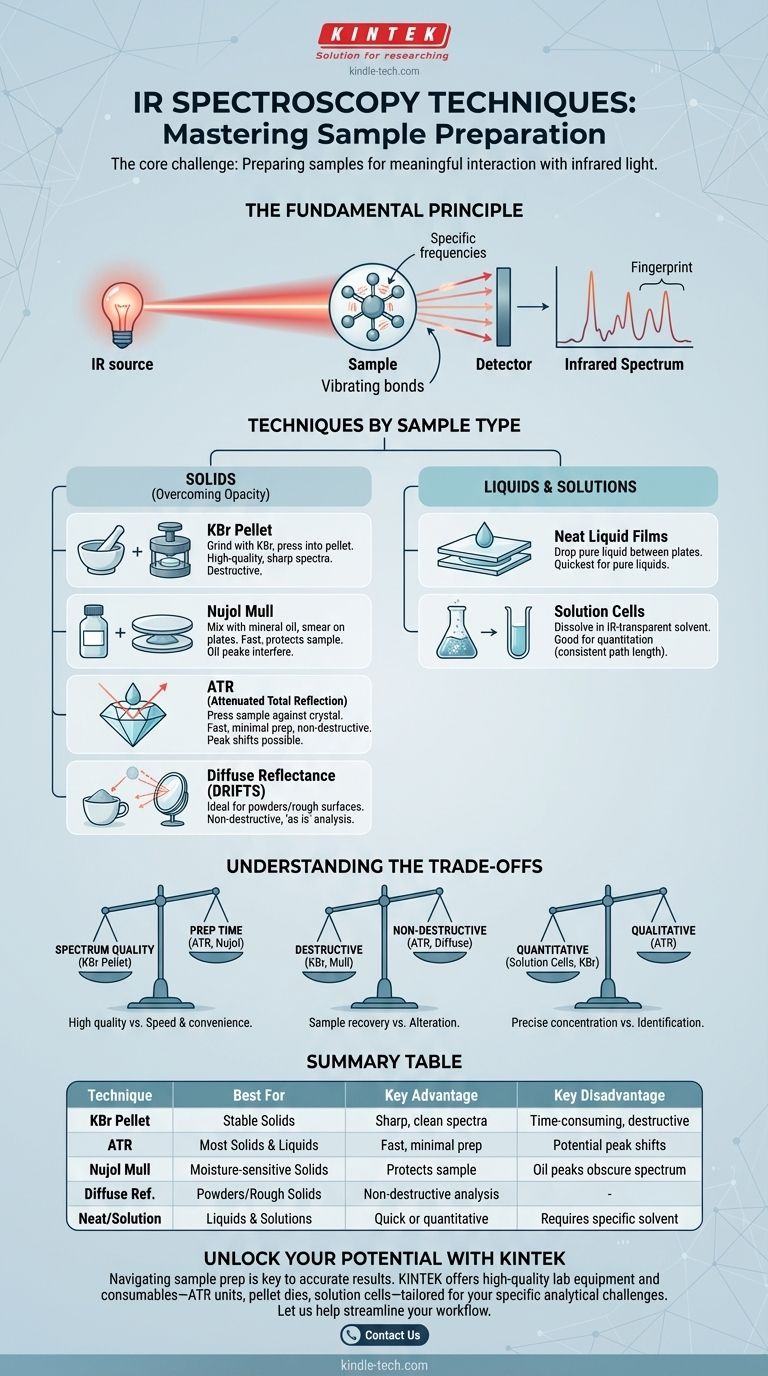
At its core, infrared (IR) spectroscopy is an analytical technique used to identify chemical substances by measuring how they interact with infrared light. The specific "technique" is not one single method, but rather a collection of sample handling and measurement approaches chosen based on the physical state of the sample—whether it is a solid, liquid, or gas.
The central challenge in IR spectroscopy isn't generating the light, but preparing the sample so the light can interact with it meaningfully. Therefore, the "technique" of IR is fundamentally about choosing the right sample preparation method for your specific material and analytical goal.

The Fundamental Principle: Sample Meets Light
How IR Spectroscopy Works
An IR spectrometer directs a beam of infrared light through or onto a sample. Molecules within the sample absorb specific frequencies of this light, corresponding to the vibrations of their chemical bonds.
A detector measures which frequencies of light were absorbed and by how much. This creates an infrared spectrum, a unique fingerprint that allows for the identification of the molecule's functional groups and, ultimately, the substance itself.
The Problem of Sample Preparation
The primary goal is to place the sample into the instrument's light path in a form that is sufficiently transparent to IR radiation. Many materials, especially solids, are opaque, scattering or blocking the light entirely. The various IR techniques are simply solutions to this problem.
Common Techniques by Sample Type
The most critical decision is choosing a technique that matches your sample's physical form.
For Solids: Overcoming Opacity
Solid samples present the biggest challenge and have the widest variety of techniques.
The KBr Pellet (Pressed Pellet) Method This classic technique involves finely grinding a small amount of the solid sample with potassium bromide (KBr) powder, which is transparent to IR light. The mixture is then pressed under high pressure to form a small, translucent pellet that can be placed directly in the spectrometer's beam path.
The Nujol Mull (Mull Technique) In this method, the solid sample is ground into a fine paste with a mulling agent, typically a mineral oil like Nujol. A thin film of this paste is then smeared between two salt plates (like NaCl or KBr) for analysis.
Attenuated Total Reflection (ATR) ATR is a modern and extremely popular technique that requires minimal sample preparation. The solid (or liquid) is simply pressed against a high-refractive-index crystal (often diamond or zinc selenide). The IR beam is reflected internally within the crystal, creating a wave that penetrates a few micrometers into the sample, generating a spectrum.
Diffuse Reflectance (DRIFTS) This method is ideal for powders or rough-surfaced solids. The sample is placed in a cup, and the IR beam illuminates it. The light that scatters off the sample is collected by mirrors and sent to the detector. It is excellent for analyzing materials "as is" without grinding.
For Liquids & Solutions
Liquids are generally much simpler to analyze than solids.
Neat Liquid Films A drop of the pure (neat) liquid can be placed between two salt plates, creating a thin capillary film. This is the quickest method for analyzing pure liquids.
Solution Cells A solid or liquid sample can be dissolved in a solvent that has minimal IR absorption in the region of interest (like carbon tetrachloride or chloroform). The solution is then placed in a cell of a known path length for measurement.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single technique is perfect for every situation. Choosing the right one involves balancing convenience, sample integrity, and the quality of the resulting spectrum.
Spectrum Quality vs. Preparation Time
A well-prepared KBr pellet generally yields a high-quality, "clean" spectrum with sharp peaks and a flat baseline. However, the process is time-consuming and requires skill.
In contrast, ATR is incredibly fast and requires almost no skill, but the resulting spectra can sometimes have peak distortions or shifts compared to traditional transmission methods. A Nujol mull is also fast but introduces interfering peaks from the oil itself, which can obscure parts of the spectrum.
Destructive vs. Non-Destructive Analysis
Techniques like the KBr pellet method are destructive; the sample is ground and mixed, and cannot be recovered in its original form.
ATR and Diffuse Reflectance are largely non-destructive. The sample is simply placed in contact with the measurement surface and can be recovered unaltered, which is critical for valuable or limited materials.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Goals
For qualitative analysis (identifying a substance), ATR is often sufficient and highly convenient.
For quantitative analysis (determining the concentration of a substance), traditional transmission methods using solution cells or KBr pellets are often preferred. This is because the Beer-Lambert Law, which relates absorbance to concentration, requires a well-defined and consistent path length, which is easier to control with a cell or pellet thickness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Sample
Your analytical goal and sample type dictate the best technique.
- If your primary focus is quick and easy identification of most solids and liquids: Use Attenuated Total Reflection (ATR) for its speed and minimal sample prep.
- If your primary focus is obtaining a high-resolution, interference-free spectrum of a stable solid: Use the KBr pellet method, provided you can grind the sample.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a moisture-sensitive solid or a sample that reacts to pressure: Use the Nujol mull technique to protect the sample within the oil.
- If your primary focus is non-destructive analysis of a powder or a precious solid: Use Diffuse Reflectance or ATR to analyze the sample in its native state.
By understanding that IR "technique" is about sample handling, you can select the right tool to turn a sample into a clear and definitive answer.
Summary Table:
| Technique | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| KBr Pellet | Stable Solids | High-quality, sharp spectra | Time-consuming, destructive |
| ATR | Most Solids & Liquids | Fast, minimal prep, non-destructive | Potential peak shifts/distortions |
| Nujol Mull | Moisture-sensitive Solids | Protects sample | Oil peaks obscure parts of spectrum |
| Diffuse Reflectance | Powders/Rough Solids | Non-destructive, 'as is' analysis | - |
| Neat Liquid/Solution | Liquids & Solutions | Quick for pure liquids, good for quantitation | Requires IR-transparent solvent |
Unlock the full potential of your materials analysis with the right IR spectroscopy equipment.
Navigating the nuances of sample preparation is key to obtaining accurate, reliable results. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific analytical challenges. Whether you're working with solids, liquids, or gases, our range of IR accessories—including ATR units, pellet dies, and solution cells—ensures you have the right tools for effective sample handling.
Let us help you achieve superior spectral clarity and streamline your workflow. Our experts understand the trade-offs between speed, quality, and sample integrity. Contact our team today via our simple form to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success in chemical identification and analysis.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Infrared High Resistance Single Crystal Silicon Lens
- Lab Electrochemical Workstation Potentiostat for Laboratory Use
- Laboratory Ten-Body Horizontal Jar Mill for Lab Use
- Proton Exchange Membrane for Batteries Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- What is the speed of a sieving machine? Optimize Vibration for Maximum Efficiency and Accuracy
- What does a vibrating sieve do? Automate Particle Size Analysis for Accurate Results
- What is the operating procedure of a sieve shaker? Master Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- What are the applications of sieving machine? From Mining to Pharmaceuticals



















