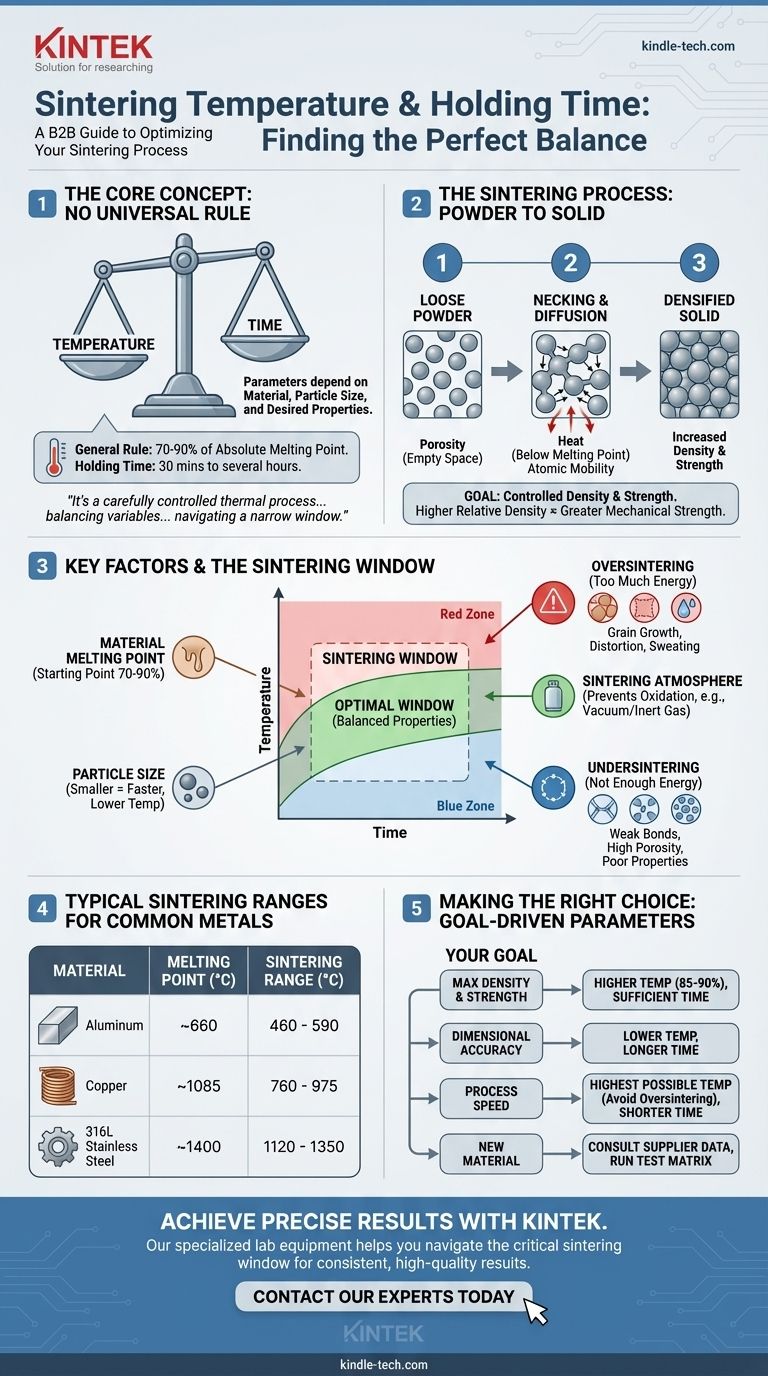
There is no single universal temperature and holding time for sintering. These parameters are critically dependent on the specific material being processed, the size of the powder particles, and the desired final properties of the component, such as its density and strength. As a general rule, the sintering temperature for a metal is typically between 70% and 90% of its absolute melting point, while the holding time can range from 30 minutes to several hours.
Sintering is not about hitting a single magic number for temperature and time. It is a carefully controlled thermal process where you are balancing these two variables against your specific material to achieve a target density and strength, navigating a narrow window between an incomplete bond and a distorted part.

The Goal of Sintering: Creating a Solid from Powder
Sintering is a micro-manufacturing process that transforms a collection of loose powder particles into a solid, coherent mass. This is achieved using heat below the material's melting point.
The Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion and "Necking"
At high temperatures, atoms in the powder particles become highly mobile. They migrate across the surfaces of adjacent particles, creating small physical bridges or "necks" at the points of contact.
As the process continues, these necks grow wider. The particles pull closer together, reducing the empty space (porosity) between them and increasing the overall density and strength of the component.
The Desired Outcome: Controlled Density and Strength
The primary goal of sintering is to achieve a specific relative density—the part's final density compared to the solid, non-porous material. A higher relative density almost always correlates with greater mechanical strength.
A finished part will still have some microscopic porosity, but its dimensions will be highly precise and predictable if the process is controlled correctly.
Key Factors That Determine Sintering Parameters
The "correct" temperature and time are a result of balancing several interacting factors. Understanding these variables is key to achieving a successful outcome.
The Material's Melting Point
This is the single most important factor. The 70-90% rule of thumb is the starting point for any sintering process development.
- For Aluminum (Melting Point ~660°C): Sintering typically occurs between 460°C and 590°C.
- For Copper (Melting Point ~1085°C): Sintering typically occurs between 760°C and 975°C.
- For 316L Stainless Steel (Melting Point ~1400°C): Sintering typically occurs between 1120°C and 1350°C.
Particle Size and Shape
Smaller particles have a much higher surface-area-to-volume ratio. This provides more energy to drive the diffusion process, allowing sintering to occur faster and at a lower temperature compared to larger particles.
Holding Time (Dwell Time)
Holding time is the duration the part is kept at the peak sintering temperature. Temperature and time have an inverse relationship.
A lower temperature can often achieve the same density as a higher temperature if the holding time is significantly increased. This trade-off is often used to prevent distortion in sensitive parts.
Sintering Atmosphere
Most metals will rapidly oxidize at high temperatures. Sintering is therefore performed in a controlled atmosphere, typically a vacuum or a flow of inert gas (like argon or nitrogen), to prevent this oxidation and ensure clean bonding between particles.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Sintering Window
Success in sintering lies in operating within an optimal processing window. Deviating from this window results in predictable failures.
Undersintering: Not Enough Energy
If the temperature is too low or the time is too short, atomic diffusion will be incomplete. The necks between particles will be weak and underdeveloped.
This results in a fragile, highly porous part with poor mechanical properties. The component will fail to meet its required strength specifications.
Oversintering: Too Much Energy
If the temperature is too high or the time is too long, negative effects begin to dominate. The material's grains can grow excessively large, which paradoxically reduces its strength and toughness.
In extreme cases, you may see distortion, blistering, or even partial melting, a defect known as sweating. This ruins the dimensional accuracy and integrity of the part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal parameters are defined by your final objective. Use your goal to guide your decision-making process when developing a sintering cycle.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength: You will operate at the higher end of the material's sintering temperature range (e.g., 85-90% of melting point) with sufficient time to minimize porosity.
- If your primary focus is preserving fine features and dimensional accuracy: You should use a lower temperature for a longer period to reduce the risk of grain growth, slumping, or distortion.
- If your primary focus is process speed and throughput: You should operate at the highest possible temperature that avoids oversintering defects to minimize the required holding time.
- If you are starting with a new material: Always begin by consulting the powder supplier's data sheet, then run a small test matrix to benchmark how the material behaves in your specific furnace.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is about methodically tuning temperature and time to achieve the precise material properties your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Material | Melting Point (°C) | Typical Sintering Range (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | ~660 | 460 - 590 |
| Copper | ~1085 | 760 - 975 |
| 316L Stainless Steel | ~1400 | 1120 - 1350 |
Achieve precise density and strength in your sintered components with KINTEK's expertise.
Our specialized lab equipment and consumables are designed to help you navigate the critical sintering window—balancing temperature and time to avoid undersintering or oversintering. Whether you're working with metals like aluminum, copper, or stainless steel, KINTEK provides the reliable solutions and support you need for consistent, high-quality results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your sintering requirements and discover how we can optimize your process for maximum efficiency and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a muffle furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the safety of a muffle furnace? Ensuring Secure Operation with Modern Design and Protocols
- What is the temperature setting of a muffle furnace? Select the Right Model for Your Process
- What are the advantages of a muffle furnace? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Precision in Your Lab
- What is the heating range of a muffle furnace? From 800°C to 1800°C for Your Lab Needs



















