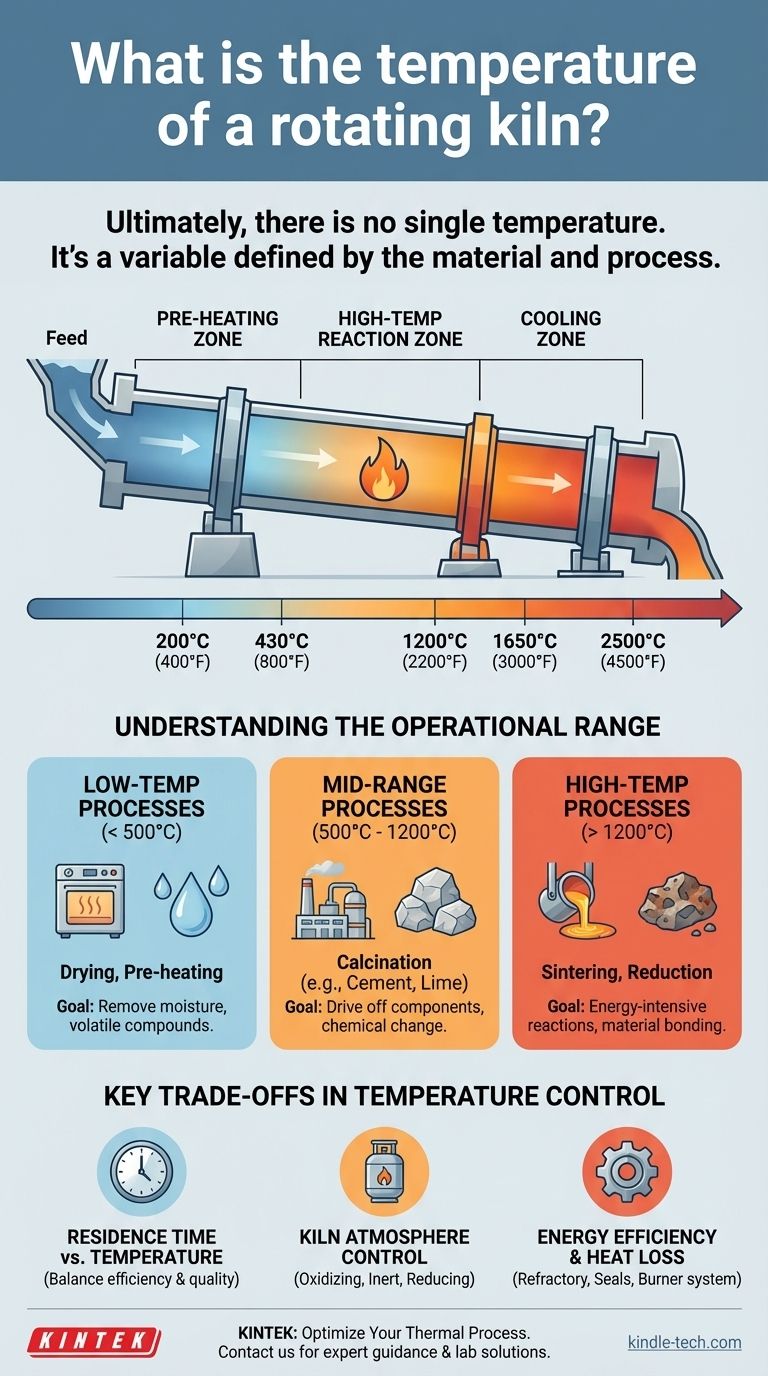
Ultimately, there is no single temperature for a rotating kiln. The required temperature is entirely dictated by the specific material being processed and the desired chemical or physical transformation. While kilns can operate across a vast range, generally from 430°C to 1650°C (800°F to 3000°F), some specialized applications can push this range from as low as 200°C to as high as 2500°C.
The temperature of a rotary kiln is not a fixed property of the equipment itself. Instead, it is a precisely controlled process variable that is set to meet the unique reaction requirements of the material being heated.

Why Temperature Is a Variable, Not a Constant
Thinking of a kiln's temperature as a single number is a common misconception. In reality, it is a dynamic profile designed to achieve a specific outcome.
The Material Defines the Process
The primary factor determining a kiln’s operating temperature is the end-product requirement. Different thermal processes demand vastly different heat levels to trigger the necessary reactions.
For example, a sintering process, which bonds particles together at high heat, may require a peak temperature of 1288°C (2350°F) or more. In contrast, simply drying a material to remove moisture might only need 200°C.
The Concept of Temperature Zones
A rotary kiln does not maintain one uniform temperature throughout its length. It is engineered with multiple temperature zones to optimize the process and improve energy efficiency.
A typical setup includes a pre-heating zone at the feed end, a central high-temperature reaction zone, and a cooling section. Each zone can be set and controlled independently to gradually bring the material up to the reaction temperature and then cool it down in a controlled manner.
Understanding the Operational Range
The wide temperature capability of rotary kilns allows them to handle an immense variety of industrial tasks. We can group these tasks into general temperature brackets.
Low-Temperature Processes (< 500°C)
This range is typically used for processes like drying, pre-heating, and low-temperature thermal desorption. The goal is to remove unbound water or volatile compounds without initiating major chemical changes in the material itself.
Mid-Range Processes (500°C - 1200°C)
This is the workhorse range for many industrial applications, most notably calcination.
Calcination involves heating a material to drive off a component, such as converting limestone (calcium carbonate) into lime (calcium oxide) by driving off carbon dioxide. This is a fundamental process in cement and lime manufacturing.
High-Temperature Processes (> 1200°C)
This range is reserved for energy-intensive reactions. Applications include the sintering of minerals, the reduction of metal ores, and the thermal treatment of specific hazardous wastes.
Reaching and maintaining these temperatures, which can exceed 1650°C, requires specialized kiln designs, advanced refractory linings, and significant energy input.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Achieving the correct temperature is a balancing act involving several critical factors. Mismanaging these can lead to an inefficient process or a poor-quality product.
Residence Time vs. Temperature
Residence time—the duration a material spends inside the kiln—is inversely related to temperature. A higher temperature may allow for a shorter residence time to achieve the same reaction, but it consumes more energy and can risk damaging the material.
Finding the optimal balance between temperature and residence time is key to process efficiency.
Kiln Atmosphere Control
The gas composition inside the kiln is as critical as the temperature. A process may require an oxidizing (oxygen-rich), inert (non-reactive), or reducing (oxygen-starved) atmosphere to proceed correctly.
This atmosphere must be maintained alongside the temperature profile, adding a layer of complexity to the kiln's operation.
Energy Efficiency and Heat Loss
A kiln is a massive thermal system, and heat loss is a primary operational cost. The quality of the refractory lining, the integrity of the air seals at the feed and discharge ends, and the efficiency of the burner system all impact the ability to maintain a target temperature without wasting fuel.
Defining the Right Temperature for Your Process
To determine the correct operating temperature, you must first define your material and your goal. The temperature is a result of that definition, not a starting point.
- If your primary focus is drying or removing moisture: You will operate at the lower end of the spectrum, typically between 200°C and 500°C.
- If your primary focus is calcination (e.g., producing cement clinker or lime): You will require a mid-range process, generally operating between 900°C and 1200°C.
- If your primary focus is sintering, induration, or high-temperature ore reduction: You must specify a high-temperature kiln capable of reaching 1200°C to over 1600°C.
Ultimately, the temperature of the kiln is a tool you must configure to serve the needs of your process.
Summary Table:
| Process Goal | Typical Temperature Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Drying / Pre-heating | < 500°C | Removing moisture, low-temperature thermal desorption |
| Calcination | 500°C - 1200°C | Cement clinker production, lime manufacturing |
| Sintering / Reduction | > 1200°C | Sintering minerals, metal ore reduction, hazardous waste treatment |
Struggling to define the right temperature profile for your thermal process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving diverse laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal rotary kiln and configure the precise temperature zones and atmosphere control required for your specific material—from drying and calcination to high-temperature sintering. Contact us today to optimize your process efficiency and product quality! Get in Touch
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals



















