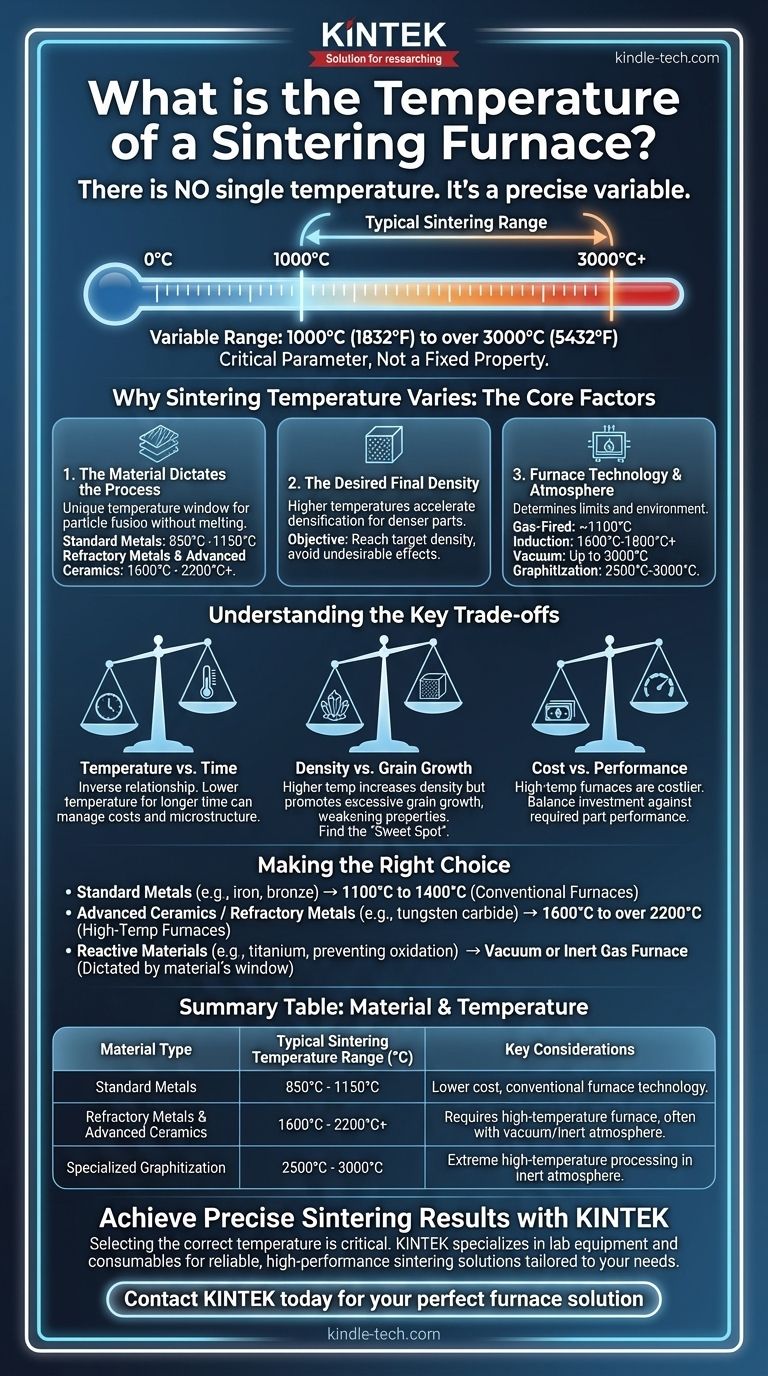
There is no single temperature for a sintering furnace. The required temperature is a precise process variable that depends entirely on the material being processed and the desired outcome, with a typical range spanning from 1000°C (1832°F) for some metals to over 3000°C (5432°F) for specialized ceramics and graphitization. The type of furnace technology used also dictates the achievable temperature ceiling.
The temperature of a sintering furnace is not a fixed property of the equipment itself, but rather a critical parameter tailored to the specific material's properties and the target density of the final component. Thinking of it as a variable to be controlled, not a static number, is key to understanding the process.

Why Sintering Temperature Varies: The Core Factors
The correct temperature is a function of a delicate balance between material science, process engineering, and the desired final properties. Several factors must be considered to determine the ideal heat profile.
The Material Dictates the Process
The primary factor is the composition of the powder being sintered. Each material has a unique temperature window where its particles will fuse without melting.
Materials like bronze or iron powders can be sintered at relatively lower temperatures, often in the range of 850°C to 1150°C.
In contrast, refractory metals like tungsten or advanced ceramics like silicon carbide require much higher temperatures, often exceeding 1600°C and sometimes reaching well over 2000°C to achieve proper densification.
The Desired Final Density
Sintering is the process of reducing the porosity of a powder compact. Higher temperatures generally accelerate this process, leading to a denser final part.
However, simply maximizing the temperature is not always the goal. The objective is to reach the target density without causing other undesirable effects.
The Furnace Technology and Atmosphere
The type of furnace determines the practical temperature limits and the environment in which sintering occurs.
- Gas-Fired Furnaces: Often used for lower-temperature applications, reaching up to approximately 1100°C (2000°F).
- Induction Furnaces: Can achieve much higher temperatures, commonly reaching 1600°C to 1800°C (2900°F to 3272°F) or more, by using electromagnetic induction to heat the material directly.
- Vacuum Furnaces: These systems are critical for processing reactive materials that would otherwise oxidize. They offer a wide operating range, with some specialized units capable of reaching nearly 3000°C (5400°F).
- Graphitization Furnaces: While a specialized process, these operate at the extreme high end, between 2500°C and 3000°C, to convert carbon materials into graphite in an inert atmosphere.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Selecting a sintering temperature is not just about hitting a number; it involves balancing competing factors to optimize the final product's quality and cost.
Temperature vs. Time
There is often an inverse relationship between sintering temperature and time. A similar level of densification can sometimes be achieved by holding a part at a lower temperature for a longer duration.
This trade-off can be used to manage energy costs, reduce thermal stress on components, and control the microstructure of the material.
Density vs. Grain Growth
While higher temperatures increase density, they can also promote grain growth. When the individual crystals within the material grow too large, it can negatively impact mechanical properties like strength, hardness, and fracture toughness.
The ideal process finds the "sweet spot" that maximizes density while minimizing excessive grain growth.
Cost vs. Performance
High-temperature furnaces (especially vacuum and controlled atmosphere systems) are more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain. The selection of a furnace and its operating temperature is a critical economic decision balanced against the performance requirements of the final part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate temperature range, you must first define your material and performance objectives.
- If your primary focus is standard powder metallurgy parts (e.g., iron, steel, bronze): You will likely operate in the 1100°C to 1400°C range, where conventional furnaces are effective.
- If your primary focus is advanced ceramics or refractory metals (e.g., alumina, tungsten carbide): You require a high-temperature furnace capable of operating from 1600°C to over 2200°C.
- If your primary focus is preventing any oxidation of reactive materials (e.g., titanium): Your choice must be a vacuum or inert gas furnace, with the specific temperature dictated by the material's sintering window.
Ultimately, the sintering temperature is a powerful tool that you must precisely control to engineer the desired material properties.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Typical Sintering Temperature Range (°C) | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Metals (e.g., Bronze, Iron) | 850°C - 1150°C | Lower cost, conventional furnace technology. |
| Refractory Metals & Advanced Ceramics | 1600°C - 2200°C+ | Requires high-temperature furnace, often with vacuum/inert atmosphere. |
| Specialized Graphitization | 2500°C - 3000°C | Extreme high-temperature processing in inert atmosphere. |
Achieve Precise Sintering Results with KINTEK
Selecting and controlling the correct sintering temperature is critical to achieving the desired density, strength, and microstructure in your components. The wrong temperature can lead to weak parts, excessive grain growth, or failed production runs.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories and R&D facilities. We understand that your success depends on reliable, high-performance sintering solutions tailored to your specific materials—from standard metals to advanced ceramics.
Let our experts help you optimize your process. We provide the equipment and support you need to precisely control this critical variable and ensure consistent, high-quality results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sintering requirements and find the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What is the role of a quartz tube in the preparation of Mo2Ga2C powder precursors? Essential Synthesis Benefits



















