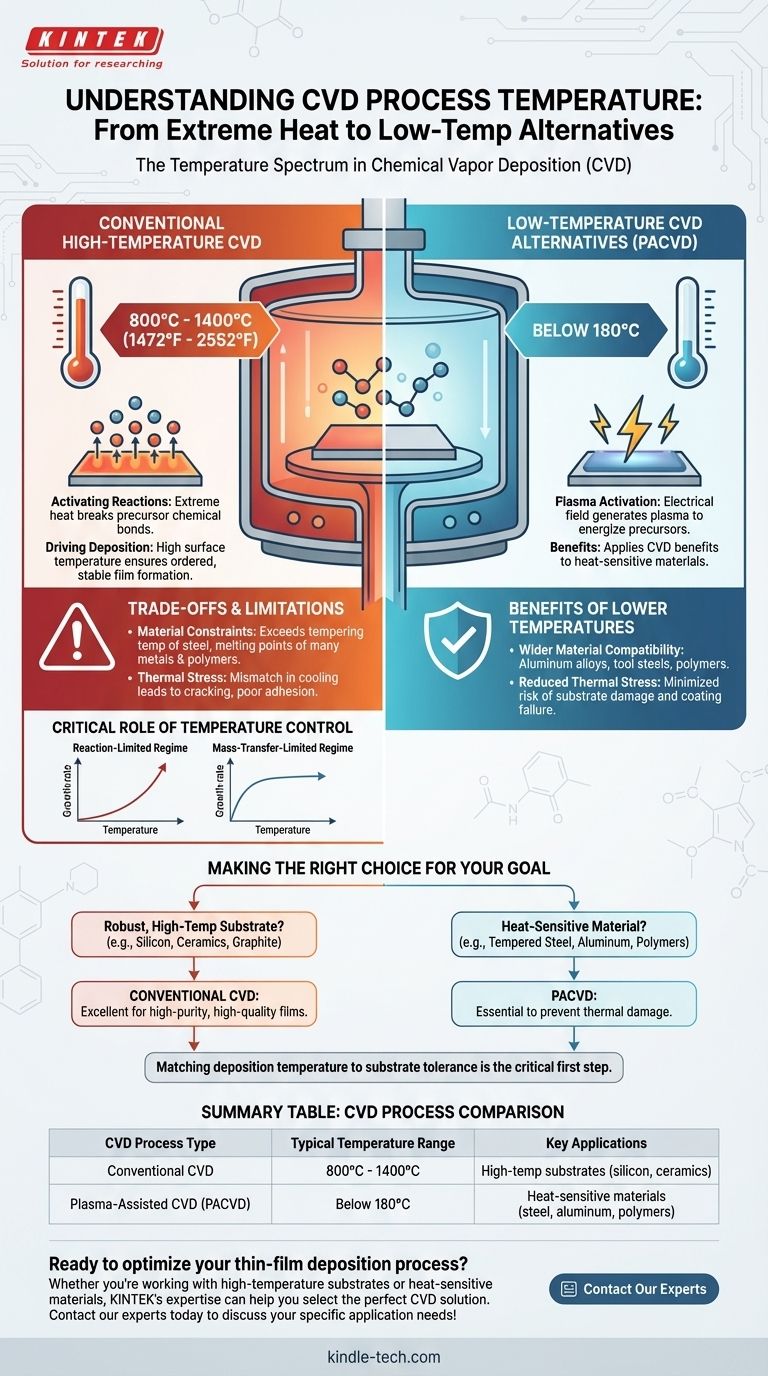
For a standard Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process, the substrate temperature is extremely high, typically falling within a range of 800°C to 1400°C (1472°F to 2552°F). This intense heat is not an incidental byproduct; it is the fundamental energy source required to initiate the chemical reactions that form the desired thin film on a material's surface.
The core principle to understand is that temperature is the primary control lever in CVD. While traditional methods require extreme heat, the specific temperature chosen dictates everything from the coating's growth rate to its final quality, and lower-temperature alternatives exist for heat-sensitive materials.

Why High Temperature is Central to CVD
The high temperatures in a CVD reactor are essential for two primary reasons: activating the precursor gases and ensuring a high-quality film forms on the substrate.
Activating Chemical Reactions
CVD works by introducing reactive gases, known as precursors, into a chamber. The high temperature provides the necessary activation energy to break the chemical bonds within these gases.
This decomposition allows the desired atoms to be released and become available for deposition.
Driving Surface Deposition
Once freed, the atoms need to settle onto the substrate in an ordered, stable structure. The high surface temperature ensures the atoms have enough energy to move around and find the ideal locations to form a dense, uniform, and often crystalline film.
The Critical Role of Temperature Control
Simply being "hot" is not enough. The exact temperature inside the reactor is a precisely controlled variable that determines the deposition mechanics and the resulting film's properties.
The Reaction-Limited Regime
At the lower end of the viable temperature range, the growth rate of the film is limited by the speed of the chemical reactions on the substrate's surface. In this state, even a small change in temperature can significantly increase or decrease the deposition rate.
The Mass-Transfer-Limited Regime
If the substrate temperature is very high, the chemical reactions occur almost instantly. The growth rate is no longer limited by the reaction speed but by how quickly fresh precursor gases can be physically transported to the substrate's surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
The reliance on extreme heat is the most significant limitation of conventional CVD, creating clear trade-offs that must be considered.
Substrate Material Constraints
The process temperature of over 800°C is higher than the tempering temperature of steel and exceeds the melting point of many other metals and polymers. This severely restricts the types of materials that can be coated without being damaged or fundamentally altered.
Thermal Stress and Defects
When a coating is deposited at such a high temperature, the substrate and the new film cool down at different rates. This mismatch in thermal expansion can introduce stress, leading to cracking, poor adhesion, or a complete failure of the coating.
Exploring Low-Temperature CVD Alternatives
To overcome the heat limitations of traditional CVD, several alternative methods have been developed. These processes use other forms of energy to activate the precursor gases.
Plasma-Assisted CVD (PACVD)
The most common alternative is Plasma-Assisted CVD (PACVD), sometimes called Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD). This process uses an electrical field to generate a plasma, which energizes the precursor gases.
Because the plasma provides the activation energy instead of heat, PACVD can be conducted at significantly lower temperatures, often below 180°C.
The Benefit of Lower Temperatures
The development of PACVD makes it possible to apply the benefits of CVD coatings—such as hardness and chemical resistance—to a much wider range of heat-sensitive materials, including aluminum alloys, tools steels, and even some plastics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The temperature is not just a setting; it defines which CVD process is viable for your application.
- If your primary focus is coating a robust, high-temperature substrate (like silicon, ceramics, or graphite): Conventional high-temperature CVD is an excellent choice for producing extremely high-purity and high-quality films.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive material (like tempered steel, aluminum, or polymers): You must use a low-temperature alternative like PACVD to prevent thermal damage to the substrate.
Ultimately, matching the deposition temperature to your substrate's tolerance is the first critical step toward a successful coating application.
Summary Table:
| CVD Process Type | Typical Temperature Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional CVD | 800°C - 1400°C | High-temp substrates (silicon, ceramics) |
| Plasma-Assisted CVD (PACVD) | Below 180°C | Heat-sensitive materials (steel, aluminum, polymers) |
Ready to optimize your thin-film deposition process? Whether you're working with high-temperature substrates or heat-sensitive materials, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables can help you select the perfect CVD solution. Our specialized knowledge ensures you achieve superior coating quality and process efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















