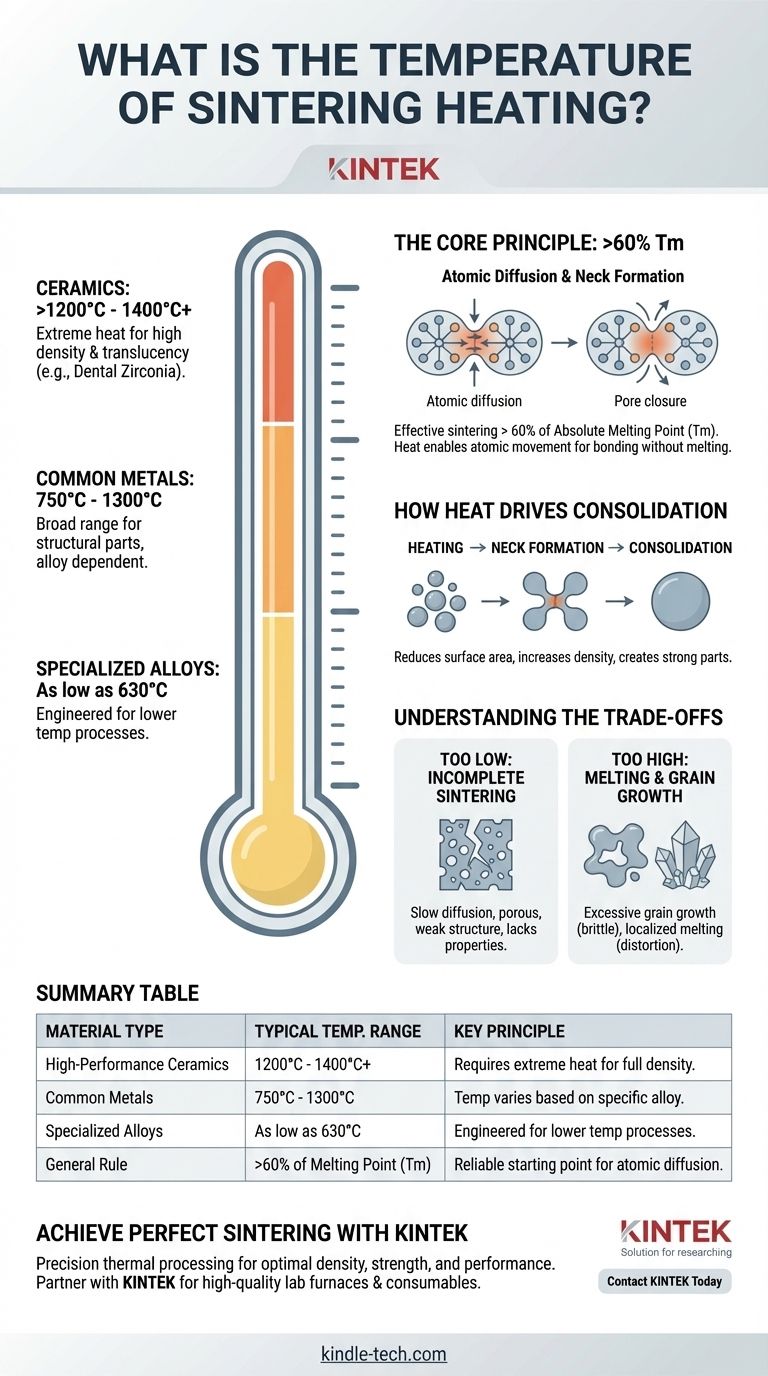
There is no single sintering temperature. Instead, the correct temperature is entirely dependent on the material being processed, with a vast operational window ranging from as low as 630°C for certain metals to over 1400°C for high-performance ceramics. The key is that this temperature must be high enough to enable atoms to move and bond the material together without actually melting it.
The most critical principle to understand is that sintering temperature is not an arbitrary number but is fundamentally tied to a material's melting point (Tm). As a rule of thumb, effective sintering occurs at a temperature greater than 60% of the material's absolute melting temperature.

The Core Principle: Temperature and Atomic Diffusion
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat and pressure without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Temperature is the primary catalyst for this transformation.
Why Temperature is Proportional to Melting Point
The goal of sintering is to give the atoms in a powder enough energy to move, or diffuse, across the boundaries of individual particles. This atomic movement is what closes the pores between particles, increases the material's density, and creates a strong, coherent part.
A material with a high melting point has very strong atomic bonds, requiring more thermal energy (a higher temperature) to get its atoms moving. Conversely, a material with a lower melting point requires less energy. The ">0.6 Tm" rule provides a reliable starting point for any material.
How Heat Drives Consolidation
As the material is heated, atoms at the contact points between powder particles begin to form "necks," which grow over time. This process reduces the surface area and minimizes the surface energy of the powder compact, pulling the particles together and shrinking the part as it becomes denser.
More Than Just a Peak Temperature
An industrial sintering process isn't about reaching a single temperature. It involves a carefully controlled thermal profile. Key control points, such as the ignition temperature and the end temperature, are monitored to ensure the process happens uniformly and completely, resulting in a high-quality finished product.
Why Sintering Temperatures Vary So Widely
The specific temperature used is a function of both the material and the desired final properties of the component.
The Decisive Role of the Material
Different materials require vastly different thermal environments.
- High-Performance Ceramics: Materials like zirconia used in dental applications require extremely high temperatures, typically between 1200°C and 1400°C, to achieve full density and translucency.
- Common Metals: The sintering of iron-based powders for structural parts generally occurs in the 750°C to 1300°C range.
- Specialized Alloys: Some metal alloys are specifically designed to sinter at lower temperatures. It is possible to achieve full density in certain materials at temperatures as low as 630°C.
The Impact on Final Properties
The exact temperature and the time spent at that temperature directly influence the final part's characteristics. A higher temperature or a longer hold time will generally lead to greater density and strength, but there is a point of diminishing returns.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the correct sintering temperature is a balancing act. Deviating from the optimal range in either direction has significant consequences.
Too Low: Incomplete Sintering
If the temperature is insufficient, atomic diffusion will be slow and incomplete. The resulting part will be porous, weak, and will lack the desired mechanical properties because the bonds between the initial powder particles never fully formed.
Too High: Risk of Melting and Grain Growth
Exceeding the optimal temperature is equally problematic. At best, it can cause excessive grain growth, where individual crystals within the material grow too large, often making the final part brittle. At worst, it can lead to localized melting, causing the part to distort, slump, or lose its intended shape entirely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The ideal sintering temperature is not a universal constant but a specific parameter tuned to your material and objective.
- If your primary focus is on ceramics (e.g., dental zirconia): Your process will require very high temperatures, typically in the 1200°C to 1400°C range, to achieve the necessary density and strength.
- If your primary focus is on common industrial metals: Plan for a broad range between 750°C and 1300°C, and consult material-specific data for the precise alloy you are using.
- If your primary focus is on understanding the principle: Always start by calculating 60-80% of the material's absolute melting temperature (Tm) to find your theoretical processing window.
Ultimately, temperature is the most powerful lever you have to control the density, strength, and final performance of a sintered component.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Typical Sintering Temperature Range | Key Principle |
|---|---|---|
| High-Performance Ceramics | 1200°C - 1400°C+ | Requires extreme heat for full density and translucency. |
| Common Metals | 750°C - 1300°C | Temperature varies based on the specific alloy. |
| Specialized Alloys | As low as 630°C | Engineered for lower temperature sintering processes. |
| General Rule | >60% of Melting Point (Tm) | A reliable starting point for any material to enable atomic diffusion. |
Achieve Perfect Sintering Results with KINTEK
Selecting the precise temperature profile is critical to achieving the desired density, strength, and performance in your sintered components. The wrong temperature can lead to weak, porous parts or catastrophic melting and distortion.
KINTEK is your partner in precision thermal processing. We specialize in supplying high-quality lab furnaces and consumables designed for the exacting demands of sintering applications, whether you are working with advanced ceramics, metal alloys, or specialized powders.
Let our experts help you optimize your process. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific material and application requirements. We'll help you select the right equipment to ensure consistent, high-quality results every time.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the physical description of a tube furnace? A Detailed Breakdown of its High-Temperature Design
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning



















