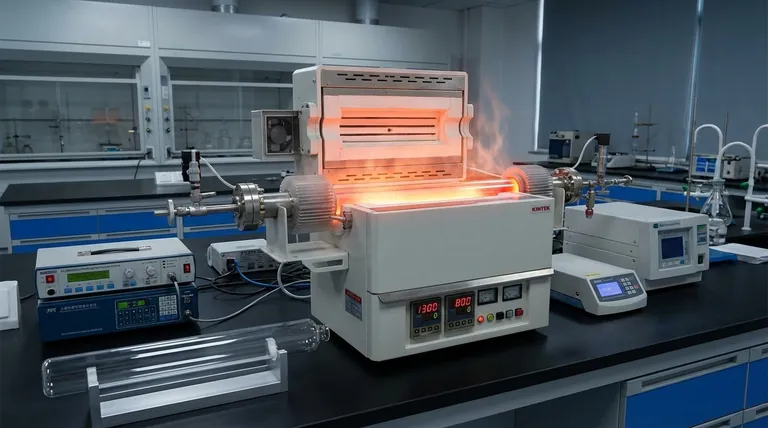
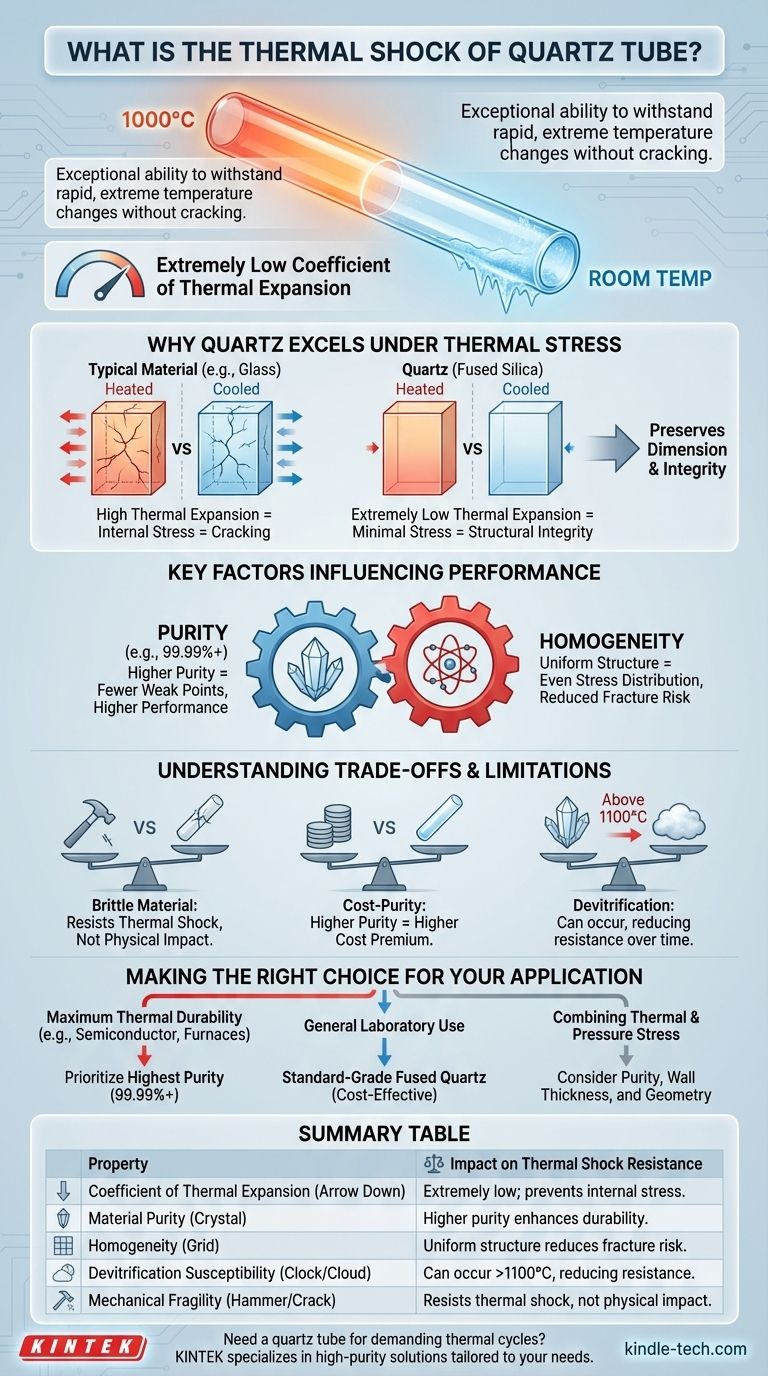
The thermal shock resistance of a quartz tube is its exceptional ability to withstand rapid and extreme changes in temperature without cracking or failing. A quartz tube can typically endure a temperature drop from 1000°C down to room temperature almost instantly. This remarkable durability is a direct result of its extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion, a core physical property of the material.
The defining characteristic of a quartz tube is not just its high-temperature tolerance, but its structural stability during rapid temperature changes. Understanding that its resistance to thermal shock is directly linked to material purity and a low expansion rate is key to leveraging it effectively in demanding applications.

Why Quartz Excels Under Thermal Stress
To understand the performance of a quartz tube, we must first understand the fundamental principle that causes other materials to fail under the same conditions.
The Principle of Thermal Expansion
Nearly all materials expand when heated and contract when cooled. When this temperature change happens rapidly, different parts of the material expand or contract at different rates. This creates immense internal stress, which is what leads to cracking and structural failure.
Quartz's Unique Stability
Quartz, specifically fused quartz, has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means that when it is heated or cooled, its physical size changes very little. This inherent stability is the primary reason for its superior thermal shock resistance.
The Impact on Structural Integrity
Because a quartz tube does not significantly expand or contract, rapid temperature changes do not generate the destructive internal stresses seen in other materials. The tube remains dimensionally stable, preserving its structural integrity even under the most demanding thermal cycles.
Key Factors Influencing Performance
While all quartz exhibits excellent thermal properties, certain factors determine the ultimate performance and reliability of a specific tube.
The Critical Role of Purity
The temperature resistance of a quartz tube is directly related to its purity. High-purity grades, often 99.99% pure fused silica, offer the highest performance ceiling. Impurities within the material can create weak points that are more susceptible to failure under thermal stress.
Material Homogeneity
Higher purity also leads to better material homogeneity. A uniform internal structure ensures that thermal stress, however minimal, is distributed evenly. This prevents the formation of localized stress concentrations that could initiate a fracture.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect for every situation. Objectively evaluating quartz requires understanding its limitations.
Mechanical Fragility
While thermally robust, quartz is a brittle material. It has excellent compressive strength but can be easily fractured by sharp physical impacts. Its resistance to thermal shock does not translate to resistance to mechanical shock.
The Purity-Cost Balance
Achieving higher levels of purity is an energy-intensive and expensive process. Consequently, the highest-purity quartz tubes come at a significant cost premium. For applications with less extreme thermal demands, a lower-grade tube may be a more practical economic choice.
Susceptibility to Devitrification
At sustained high temperatures (typically above 1100°C), fused quartz can begin to devitrify, or crystallize back into a more ordered state (cristobalite). This process can make the material opaque and, more importantly, can compromise its structural integrity and reduce its resistance to thermal shock over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct quartz tube depends entirely on the demands of your specific process.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal durability: Prioritize the highest purity (99.99%+) quartz tube available to ensure the best performance in extreme temperature cycling, such as in semiconductor processing or advanced research furnaces.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory use: A standard-grade fused quartz tube will offer excellent thermal shock resistance for most heating and cooling applications at a more accessible price point.
- If your primary focus is combining thermal and pressure stress: Pay close attention to both the material purity for thermal stability and the wall thickness and overall geometry for mechanical strength.
By understanding the relationship between purity, thermal expansion, and structural integrity, you can confidently select the right quartz tube for any demanding thermal challenge.
Summary Table:
| Property | Impact on Thermal Shock Resistance |
|---|---|
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | Extremely low; prevents internal stress during rapid temperature changes |
| Material Purity | Higher purity (e.g., 99.99%+) enhances durability and performance |
| Homogeneity | Uniform structure distributes stress evenly, reducing fracture risk |
| Devitrification Susceptibility | Can occur above 1100°C, potentially reducing resistance over time |
| Mechanical Fragility | Brittle nature means it resists thermal shock but not physical impact |
Need a quartz tube that can handle your most demanding thermal cycles? KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including quartz tubes engineered for superior thermal shock resistance. Whether you're in semiconductor processing, research, or general lab work, we provide solutions tailored to your specific temperature and purity requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our quartz tubes can enhance the reliability and performance of your laboratory processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What challenges do refractory lining materials face in hydrogen environments? Key Insights for Direct Reduction Furnaces
- What insulating materials can tolerate maximum temperature? Select the Right High-Temp Insulator for Your Application
- What are the primary reasons for selecting high-purity dense alumina as the inner tube material? Optimize Lab Safety
- What function do magnetic stirrers perform in SLM silver separation? Optimize Mass Transfer for Silver Recovery
- What role does a magnetic stirrer play in alpha-FeOOH precursor prep? Mastering Homogeneity & Particle Size
- What is the maximum pressure for a vacuum pump? Understanding Ultimate Vacuum for Your Lab Needs
- What is the tensile strength of a quartz tube? Understand its critical limits for safe application.
- Why is a benchtop magnetic stirrer used in electrocoagulation? Enhance Wastewater Treatment Efficiency



















