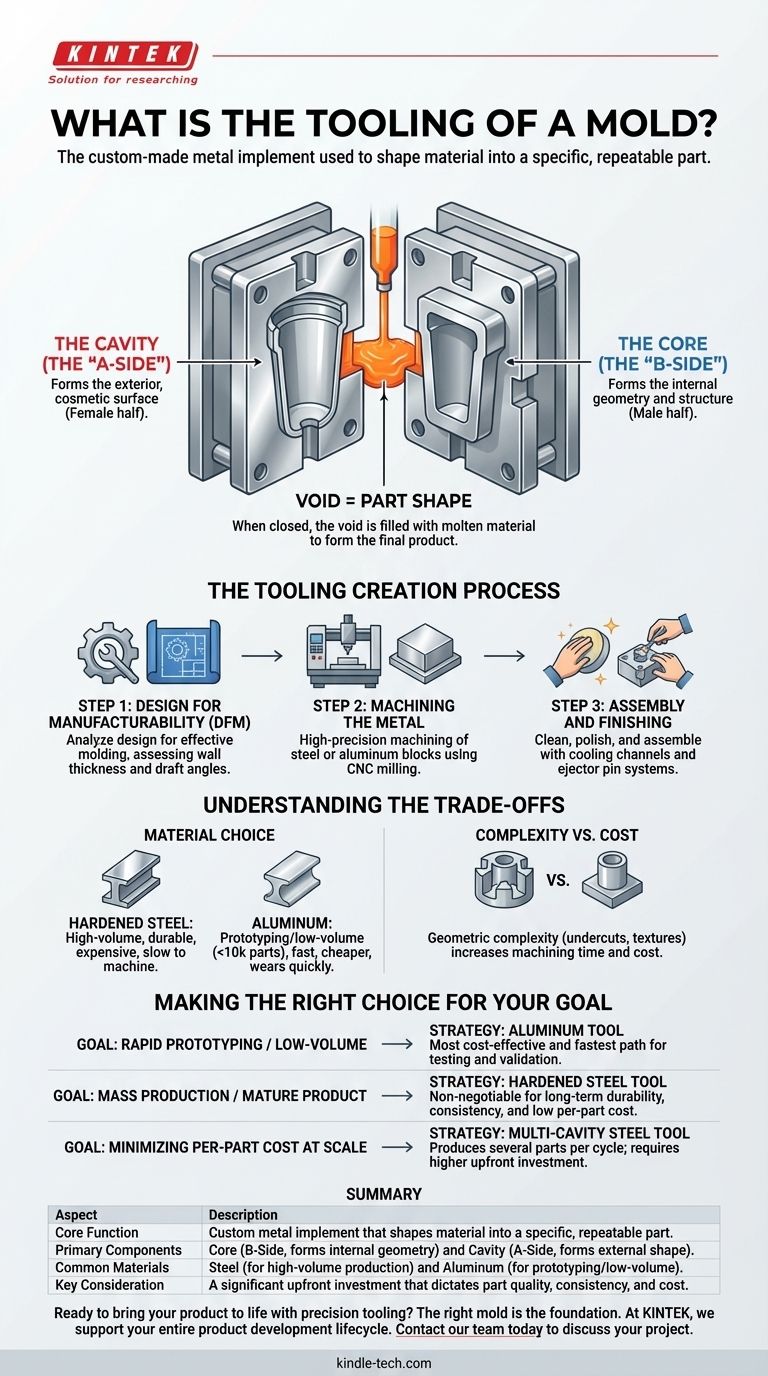
In manufacturing, mold tooling refers to the custom-made metal implement used to shape a material, like molten plastic, into a specific, repeatable part. It is the heart of processes like injection molding and consists of precisely machined components—primarily a core and cavity—that form a negative of the final product's geometry. The tooling is not just the mold itself, but the entire engineered system that enables high-volume production.
The central concept to grasp is that mold tooling is a permanent manufacturing asset, not a disposable item. The precision and quality of this tool, machined from steel or aluminum, directly dictate the quality, consistency, and cost of every single part produced from it.

Deconstructing the Mold Tool: Core Components
A mold tool, at its most basic, is a two-part system designed to fit together perfectly, creating a hollow space in the shape of the desired product.
The Cavity (The "A-Side")
The cavity is the stationary half of the mold. It typically forms the exterior, cosmetic surface of the part and is considered the "female" half of the tool.
Think of it as the outer shell of a Jell-O mold; it defines the final external shape.
The Core (The "B-Side")
The core is the moving half of the mold. It fits inside the cavity and forms the internal geometry and structure of the part. It is the "male" half of the tool.
In a part like a plastic cup, the core would be the central block of metal that creates the empty space you drink from.
How They Work Together
When an injection molding machine closes, it pushes the core and cavity together under immense pressure. The void between these two halves is the shape of the part.
Molten plastic is then injected into this void. Once it cools and solidifies, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected.
The Tooling Creation Process
"Tooling" also refers to the process of designing and manufacturing the mold itself, a critical phase in product development.
Step 1: Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Before any metal is cut, the part design is analyzed to ensure it can be molded effectively. Engineers assess factors like wall thickness, draft angles (tapers for easy ejection), and material flow.
Step 2: Machining the Metal
Based on the final design, large blocks of industrial-grade steel or aluminum are machined into the core and cavity. This is a highly precise process using techniques like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling.
Step 3: Assembly and Finishing
The machined core and cavity are cleaned, polished to the desired surface finish, and assembled into a complete mold base. This assembly also includes critical subsystems like cooling channels and an ejector pin system to push the part out.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decisions made during tooling have significant and lasting financial and operational consequences.
Material Choice: Steel vs. Aluminum
Hardened steel is the standard for high-volume production. It is extremely durable and can produce millions of parts, but it is expensive and time-consuming to machine.
Aluminum is a common choice for prototyping or low-volume production (typically under 10,000 parts). It is much faster and cheaper to machine but wears out quickly.
Complexity vs. Cost
The geometric complexity of your part is the single biggest driver of tooling cost. Features like undercuts (which require mechanical slides or lifters) and intricate textures dramatically increase machining time and tooling expense.
The Upfront Investment Reality
Mold tooling is a significant capital expense, often costing tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars. While this investment makes the per-part cost exceptionally low at scale, it represents a major initial financial hurdle that must be planned for.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right tooling strategy is about aligning your manufacturing plan with your business objectives.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or low-volume runs: An aluminum tool offers the most cost-effective and fastest path to getting physical parts for testing and market validation.
- If your primary focus is mass production for a mature product: Investing in a hardened P20 or H13 steel tool is non-negotiable for ensuring long-term durability, consistency, and a low per-part cost.
- If your primary focus is minimizing per-part cost at scale: A multi-cavity steel tool, which produces several parts per cycle, is the ideal approach, though it requires a higher upfront investment.
Ultimately, viewing your tooling as a core manufacturing asset, not just a one-time expense, is the key to successful and profitable product scaling.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Custom metal implement that shapes material into a specific, repeatable part. |
| Primary Components | Core (B-Side, forms internal geometry) and Cavity (A-Side, forms external shape). |
| Common Materials | Steel (for high-volume production) and Aluminum (for prototyping/low-volume). |
| Key Consideration | A significant upfront investment that dictates part quality, consistency, and cost. |
Ready to bring your product to life with precision tooling?
The right mold is the foundation of successful manufacturing. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the laboratory equipment and consumables that support the entire product development lifecycle, from prototyping to production.
Let our expertise help you make informed decisions about your tooling strategy. Contact our team today to discuss your project needs and discover how we can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Assemble Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- No Demolding Lab Infrared Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hydrothermal Synthesis Reactor Polytetrafluoroethylene Carbon Paper and Carbon Cloth Nano-growth
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the role of high-strength graphite molds in vacuum hot pressing Beryllium? Enhance Densification & Precision
- What role do high-strength graphite molds play during vacuum hot pressing? Enhance Precision in CuAlMn Composites
- What is the lifespan of a mold? It's Immortal Unless You Control Moisture
- How do laboratory hydraulic presses and forming molds create 3D superlattice nanocatalysts? Enhance Material Density
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity














