In essence, an electric muffle furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven designed to heat materials in an environment completely isolated from the heating elements. Its primary uses fall into two main categories: transforming the physical or chemical properties of a material through processes like heat treatment and sintering, and preparing or analyzing samples for quality control and research through processes like ashing.
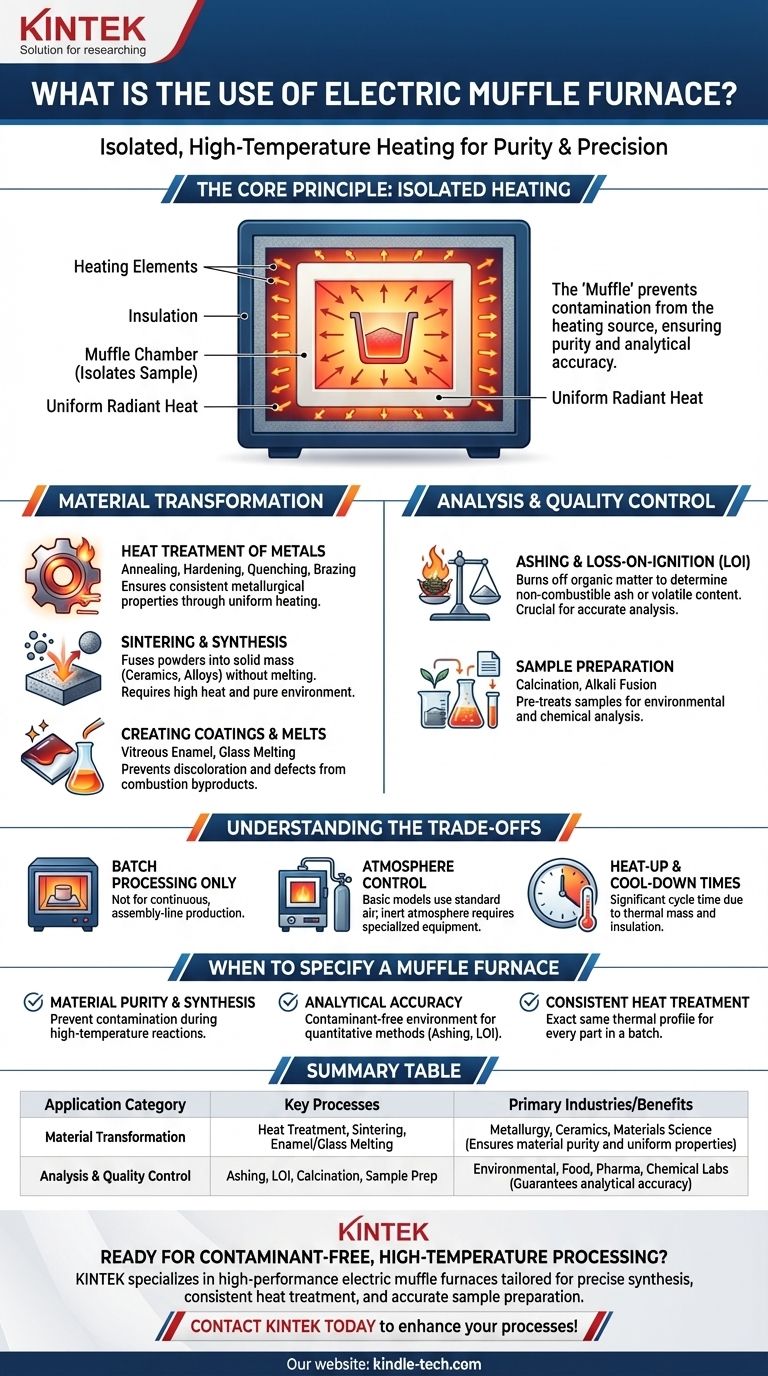
The core value of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to reach extreme temperatures, but its capacity to do so within a controlled, isolated chamber. This "muffle" prevents contamination from the heating source, ensuring the purity of the process and the accuracy of analytical results.

The Core Principle: Isolated, High-Temperature Heating
A standard oven heats materials directly. A muffle furnace introduces a critical separating layer—the muffle—which is a high-temperature chamber that houses the sample.
Why Isolation Matters
The muffle acts as a barrier, shielding the material inside from direct contact with the electric heating elements and any impurities they might release at high temperatures.
This is non-negotiable for processes where even trace amounts of contamination from the heating source could alter the chemical composition or properties of the final product or analytical result.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
By heating the exterior of the muffle chamber, the furnace creates a highly uniform radiant heat environment inside. This eliminates hot spots and ensures the entire sample experiences the same temperature, which is critical for consistent and repeatable outcomes.
Key Applications in Material Transformation
Many industries rely on muffle furnaces to create or refine materials that require precise thermal processing.
Heat Treatment of Metals
Processes like annealing (softening), hardening, quenching, and brazing all depend on subjecting metals to specific temperature cycles. The uniform, controlled heat of a muffle furnace ensures these treatments produce the desired metallurgical properties consistently.
Sintering and Synthesis
Sintering is the process of fusing powders into a solid mass using heat without melting them. This is fundamental to creating technical ceramics, special metal alloys, and other advanced materials. The furnace provides the high heat and pure environment needed for particles to bond effectively.
Creating Coatings and Melts
The furnace is used to create vitreous enamel coatings on metal and for melting glass. The isolated chamber prevents discoloration and defects caused by combustion byproducts that would be present in a fuel-fired furnace.
Critical Roles in Analysis and Quality Control
The furnace is a workhorse in analytical laboratories for preparing samples and determining material composition.
Ashing and Loss-on-Ignition
Ashing is a primary use case. The furnace is used to burn off all organic and combustible material in a sample at a high temperature, leaving only the non-combustible ash behind.
This allows researchers and QC technicians to accurately determine the ash content, volatile content, or non-combustible percentage of materials like coal, food products, plastics, and medical samples.
Sample Preparation
In environmental and chemical analysis, samples often need to be pre-treated to be analyzed by other instruments. A muffle furnace can be used for processes like calcination (decomposing a substance by heating) or alkali fusion to prepare samples for further testing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specific tool with inherent limitations.
Batch Processing Only
Standard muffle furnaces are designed for batch processing. You place a sample (or batch of samples) inside, run the heating cycle, and remove it. They are not suited for continuous, assembly-line-style production.
Atmosphere Control
A basic muffle furnace operates with a standard air atmosphere. If a process requires an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) or a reactive one, a more specialized and expensive furnace with gas-purging capabilities is necessary.
Heat-Up and Cool-Down Times
Due to their robust insulation and thermal mass, muffle furnaces can take a significant amount of time to reach their target temperature and, more importantly, to cool down. This cycle time must be factored into any workflow.
When to Specify a Muffle Furnace
Your choice depends entirely on the requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is material purity or synthesis: A muffle furnace is essential to prevent contamination from the heating elements during high-temperature reactions.
- If your primary focus is analytical accuracy: The repeatable and contaminant-free environment is critical for quantitative methods like ashing or loss-on-ignition.
- If your primary focus is consistent metal heat treatment: The furnace's excellent temperature uniformity ensures that every part in a batch receives the exact same thermal profile.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the definitive tool for any process demanding pure, uniform, and precise high-temperature heating.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Primary Industries/Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Material Transformation | Heat Treatment (Annealing, Hardening), Sintering, Enamel/Glass Melting | Metallurgy, Ceramics, Materials Science (Ensures material purity and uniform properties) |
| Analysis & Quality Control | Ashing, Loss-on-Ignition, Calcination, Sample Prep | Environmental, Food, Pharmaceutical, Chemical Labs (Guarantees analytical accuracy) |
Ready to achieve contaminant-free, high-temperature processing in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance electric muffle furnaces tailored to your specific needs, whether for precise material synthesis, consistent heat treatment, or accurate analytical sample preparation. Our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for pure, uniform heating that guarantees reliable results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our lab equipment can enhance your processes and boost your efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What heat can a muffle furnace produce? Achieve Precise High Temperatures Up to 1800°C
- What is the working temperature of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise Heat Control for Your Lab
- What is the difference between a retort and a muffle furnace? Uncover the Truth About Indirect Heating
- Why the melting temperature of ceramic is higher than for most metals? Unpacking Atomic Bond Strength
- What is a muffle furnace for laboratory use? A Guide to Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing



















