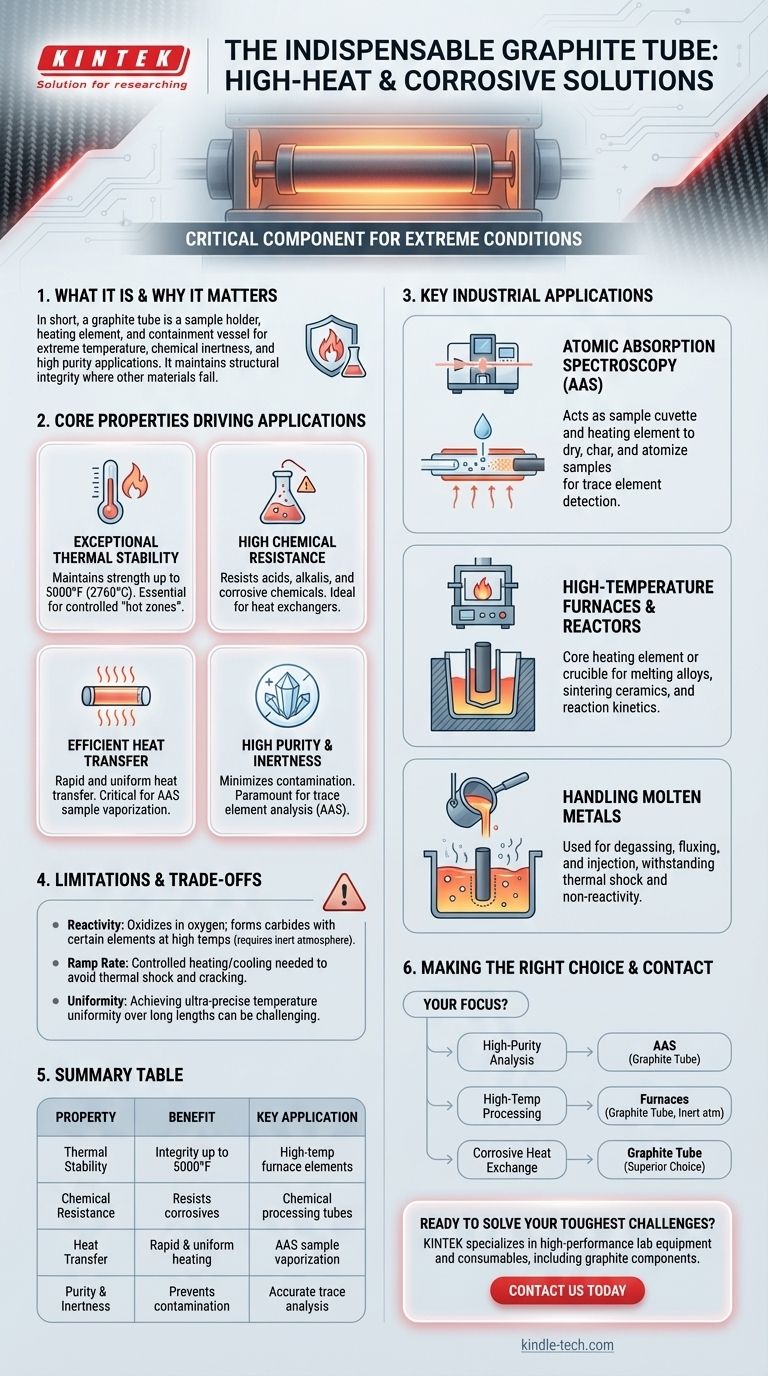
In short, a graphite tube is used as a critical component in applications requiring extreme temperature resistance, chemical inertness, and high purity. Its primary functions are to serve as a sample holder and heating element in analytical instruments, a containment vessel in high-temperature furnaces, and a conduit for heat transfer in highly corrosive chemical environments.
The true value of a graphite tube is not just its list of uses, but its unique ability to maintain structural integrity and chemical stability in extreme conditions where most other materials would fail. It is a specialized problem-solver for the most demanding high-heat and corrosive engineering challenges.

Core Properties Driving Graphite Tube Applications
To understand why graphite tubes are so widely used, we must first examine their fundamental material properties. These attributes make graphite the optimal choice for specific, challenging scenarios.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
A graphite tube maintains its structural strength and dimensional integrity at incredibly high temperatures, with some grades stable up to 5000°F (2760°C). This far exceeds the melting point of most metals.
This property makes it essential for creating controlled, high-temperature environments, often referred to as "hot zones" in furnaces and reactors.
High Chemical Resistance
Graphite is highly resistant to acids, alkalis, and other corrosive chemicals that would quickly degrade metals and alloys.
This makes it the material of choice for handling aggressive substances in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and electroplating industries, particularly for heat exchangers and injection tubes.
Efficient Heat Transfer
Graphite possesses excellent thermal conductivity, allowing for the rapid and uniform transfer of heat.
This efficiency is critical in furnace applications for consistent heating and in atomic spectroscopy for the instantaneous vaporization of a sample.
High Purity and Inertness
Graphite can be produced to exceptionally high purity levels. It does not readily react with or leach contaminants into the materials it contains.
This is paramount in applications like atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS), where even trace amounts of impurities would ruin the accuracy of an analysis.
Key Industrial Applications in Practice
These properties translate directly into specific, high-value industrial uses where performance and reliability are non-negotiable.
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS)
In a graphite furnace for AAS, the graphite tube acts as both the sample cuvette and the heating element. It is resistively heated in stages to dry, char, and finally atomize a sample for analysis.
This process is used to detect trace elements in environmental samples like seawater, clinical samples like blood, and industrial waste.
High-Temperature Furnaces and Reactors
Graphite tubes form the core heating element or crucible in various furnaces used for melting alloys, pressure sintering of ceramics, and investigating reaction kinetics at extreme temperatures.
They provide a stable, controlled environment that is free from the metallic contamination a traditional furnace might introduce.
Handling Molten Metals
In metallurgy, graphite tubes are used for degassing, fluxing, and injection. A tube can be submerged into molten metal to bubble inert gas through the melt, removing dissolved impurities like hydrogen.
Its ability to withstand the thermal shock and non-reactivity with the molten metal is critical for this process.
Understanding the Limitations and Trade-offs
While powerful, graphite is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Reactivity with Oxygen and Certain Elements
At high temperatures, graphite will oxidize (burn) in the presence of oxygen. Therefore, graphite furnaces must be operated in a vacuum or under an inert gas atmosphere (like argon).
Furthermore, it can react with certain elements at high temperatures to form carbides, making it unsuitable for processing specific materials that are sensitive to carbon.
Temperature Ramp Rate Constraints
Graphite hot zones have thermal mass and must be heated and cooled at controlled rates to avoid thermal shock, which can cause cracking.
A maximum ramp rate, for example, might be 45°F (25°C) per minute, depending on the grade and geometry of the graphite.
Inherent Temperature Uniformity
While heat transfer is efficient, achieving perfect temperature uniformity across the entire length of a long graphite tube can be challenging.
Processes requiring ultra-precise uniformity (better than +/- 10°F or 6°C) may require specialized furnace designs or alternative heating methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use this guide to determine if a graphite tube is the correct component for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is high-purity chemical analysis: A graphite tube is the industry standard for AAS, offering the necessary inertness and rapid heating for sample atomization.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature material processing: Graphite is an excellent choice for furnaces operating above the limits of metal alloys, provided your process is run in an inert atmosphere and the material does not react with carbon.
- If your primary focus is heat exchange with corrosive fluids: The combination of chemical resistance and good thermal conductivity makes a graphite tube a superior choice over many expensive metal alloys.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently leverage graphite as a powerful tool for your most demanding engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Exceptional Thermal Stability | Maintains integrity up to 5000°F (2760°C) | High-temperature furnace heating elements |
| High Chemical Resistance | Resists acids, alkalis, and corrosive substances | Heat exchangers and injection tubes in chemical processing |
| Efficient Heat Transfer | Rapid and uniform heating | Instantaneous sample vaporization in Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) |
| High Purity & Inertness | Prevents sample contamination | Critical for accurate trace element analysis in AAS |
Ready to solve your most demanding high-heat and corrosive challenges?
Graphite tubes are specialized components where performance and reliability are non-negotiable. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including graphite components designed for extreme conditions. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution for applications like Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS), high-temperature furnaces, and handling corrosive chemicals.
Contact us today to discuss how our graphite tubes can enhance your laboratory's capabilities, improve analysis accuracy, and withstand your toughest engineering challenges.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Carbon Graphite Boat -Laboratory Tube Furnace with Cover
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What function does a graphite rod serve when using induction heating to test SiC cladding? | KINTEK Thermal Solutions
- Why are graphite crucibles selected as melting vessels for AlMgZn cross-over alloys? Essential Benefits & Purity Tips
- What is the technical value of using graphite crucibles with graphite paper liners? Optimize Zr3(Al1-xSi)C2 Synthesis
- What are the advantages of high-purity graphite sample holders? Ensure Precision in C-C Composite Brazing
- What are the properties of the graphite? Unlock High-Temperature Strength & Conductivity



















