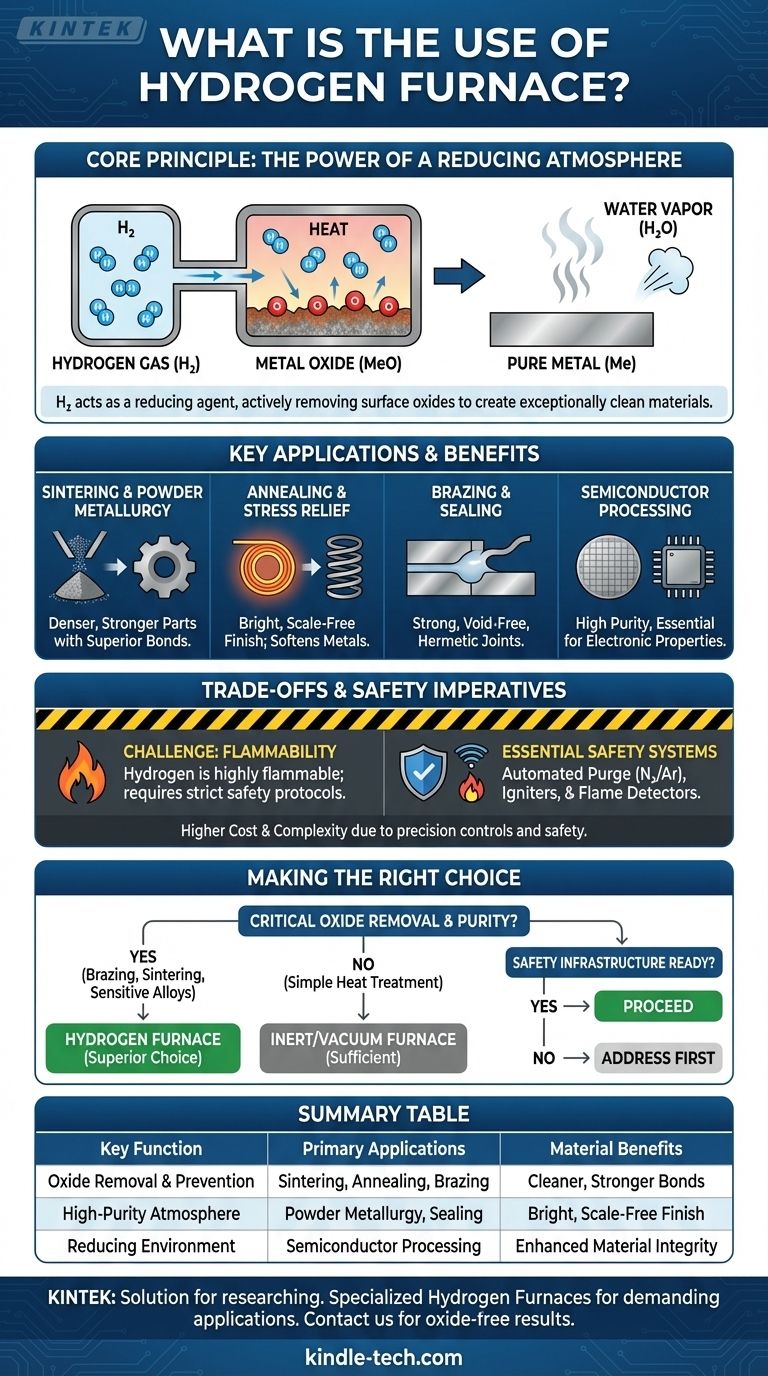
In essence, a hydrogen furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven used to process materials in a controlled, hydrogen-rich atmosphere. Its primary function is to prevent oxidation and actively remove surface oxides from materials during critical processes like sintering, annealing, and brazing. This capability creates exceptionally clean, strong, and reliable components that are often unachievable with other furnace types.
The true value of a hydrogen furnace isn't just heating materials; it's the use of hydrogen as a powerful reducing agent. This atmosphere actively purifies material surfaces by removing oxides, which is a capability that standard vacuum or inert gas furnaces cannot offer.
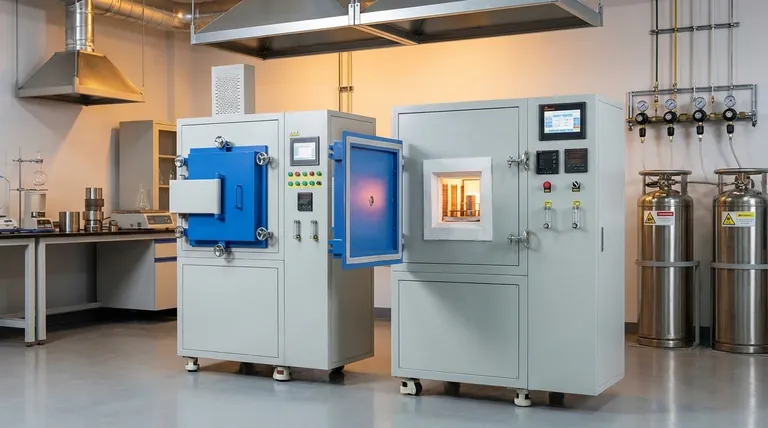

The Core Principle: Why Use a Hydrogen Atmosphere?
To understand the use of a hydrogen furnace, you must first understand the unique role of the hydrogen gas itself. Unlike inert gases like argon or nitrogen, hydrogen is chemically reactive in a highly beneficial way.
Eliminating Oxygen and Preventing Oxidation
Any high-temperature process performed in the open air will cause materials, especially metals, to oxidize. Hydrogen furnaces prevent this by completely displacing the oxygen within the heating chamber, creating a high-purity environment.
The Power of a Reducing Environment
This is the key advantage. At high temperatures, hydrogen gas (H₂) acts as a powerful reducing agent. It actively seeks out and reacts with metal oxides (MeO) on the surface of the components.
This chemical reaction strips the oxygen from the oxide, leaving behind a pure, clean metal surface (Me) and water vapor (H₂O), which is then safely vented from the furnace.
Enhancing Material Properties
By creating perfectly clean, oxide-free surfaces, a hydrogen atmosphere directly improves the final product. This leads to stronger metallurgical bonds in brazing, higher density in sintered parts, and a bright, scale-free finish in annealed components.
Key Applications and Processes
The reducing properties of hydrogen make these furnaces indispensable for a range of demanding applications where surface integrity is critical.
Sintering and Powder Metallurgy
In powder metallurgy, a hydrogen atmosphere removes the thin oxide layers on individual metal powder granules. This allows the particles to form superior metallic bonds during heating, resulting in a final sintered part that is denser, stronger, and has better mechanical properties.
Annealing and Stress Relief
Hydrogen annealing is used to soften metals and relieve internal stresses without causing surface discoloration or scale. The process yields a "bright annealed" finish, which is highly desirable for stainless steels and other specialty alloys.
Brazing and Sealing
Hydrogen brazing is the gold standard for creating strong, hermetic (airtight) seals. By ensuring both the base materials and the brazing filler alloy are completely free of oxides, the molten filler can flow perfectly into the joint, creating a void-free bond. This is also critical for metallization and sealing glass-to-metal or ceramic-to-metal components.
Semiconductor and Electronics Processing
The manufacturing of high-purity semiconductor materials and electronic components often relies on a hydrogen atmosphere. It ensures no unwanted oxides are introduced that could alter the material's electrical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Imperatives
While powerful, hydrogen furnaces introduce unique challenges that must be managed. Their use is a deliberate engineering choice based on balancing benefits against risks and complexity.
The Challenge: Hydrogen's Flammability
The primary trade-off is safety. Hydrogen gas is highly flammable and can be explosive when mixed with air in certain concentrations. Operating a hydrogen furnace requires strict, non-negotiable safety protocols.
Essential Safety Systems
Modern hydrogen furnaces are equipped with robust, automated safety systems. These include a nitrogen or argon purge cycle to remove all oxygen before hydrogen is introduced, as well as a post-process purge to remove all hydrogen before the door is opened.
They also feature safety igniters to burn off excess hydrogen at the exhaust port and flame detectors that will automatically shut off the hydrogen supply and flood the furnace with inert gas if the flame is ever extinguished.
Cost and Operational Complexity
Due to these necessary safety systems and the precision controls required, hydrogen furnaces are more complex and carry a higher capital cost than standard air or inert atmosphere furnaces. They also demand more rigorous operator training and facility safety infrastructure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice depends entirely on whether the active removal of surface oxides is critical to your material's final properties and performance.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest purity bonds in brazing or sintering: A hydrogen furnace is often the superior choice, as it actively cleans the component surfaces.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment where minor surface oxidation is acceptable: A less complex and less expensive inert gas or vacuum furnace may be sufficient.
- If you are working with materials highly sensitive to oxidation, such as stainless steels or specialty alloys: The reducing atmosphere of a hydrogen furnace is essential for maintaining material integrity and achieving a bright finish.
- If your process safety infrastructure is not equipped to handle flammable gases: You must first address these facility and training requirements before considering a hydrogen furnace.
Ultimately, a hydrogen furnace is a powerful tool for applications where material purity and surface integrity are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Primary Applications | Material Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Oxide Removal & Prevention | Sintering, Annealing, Brazing | Cleaner, Stronger Bonds |
| High-Purity Atmosphere | Powder Metallurgy, Sealing | Bright, Scale-Free Finish |
| Reducing Environment | Semiconductor Processing | Enhanced Material Integrity |
Ready to enhance your material processing with superior purity and performance? KINTEK specializes in hydrogen furnaces and lab equipment designed for demanding applications like sintering, brazing, and annealing. Our solutions ensure oxide-free results and reliable operation for laboratories and industrial users. Contact us today to discuss how a hydrogen furnace can meet your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum or atmosphere furnace required for SiBCN pyrolysis? Mastering Precision for Superior Ceramics
- What is nitriding in heat treatment? Enhance Durability with Precision Surface Hardening
- What is atmosphere controlled furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Enable Advanced Material Processing
- What role does a high-temperature annealing furnace play in regulating the properties of Cerium Oxide nanoparticles?
- What gases are used in brazing? A Guide to Choosing the Right Atmosphere for Strong Joints
- What are the atmospheres for the heat treating furnaces? A Guide to Precise Surface Control
- What is a reducing type of atmosphere? Control Oxidation & Achieve Specific Chemical Reactions
- What is the atmosphere of the annealing furnace? A Guide to Protective Gas Selection



















