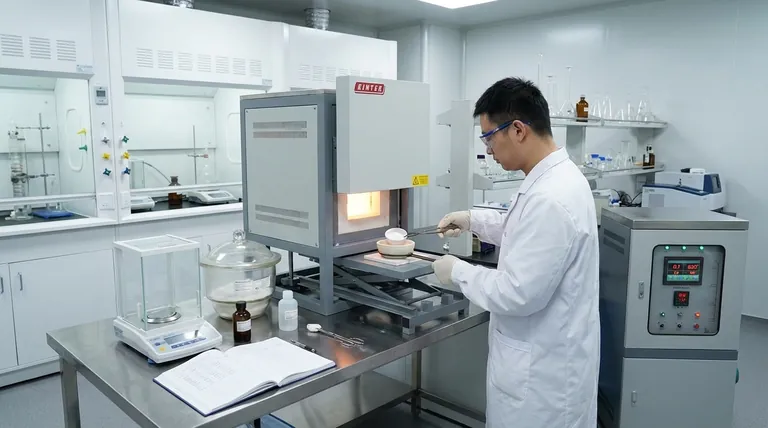
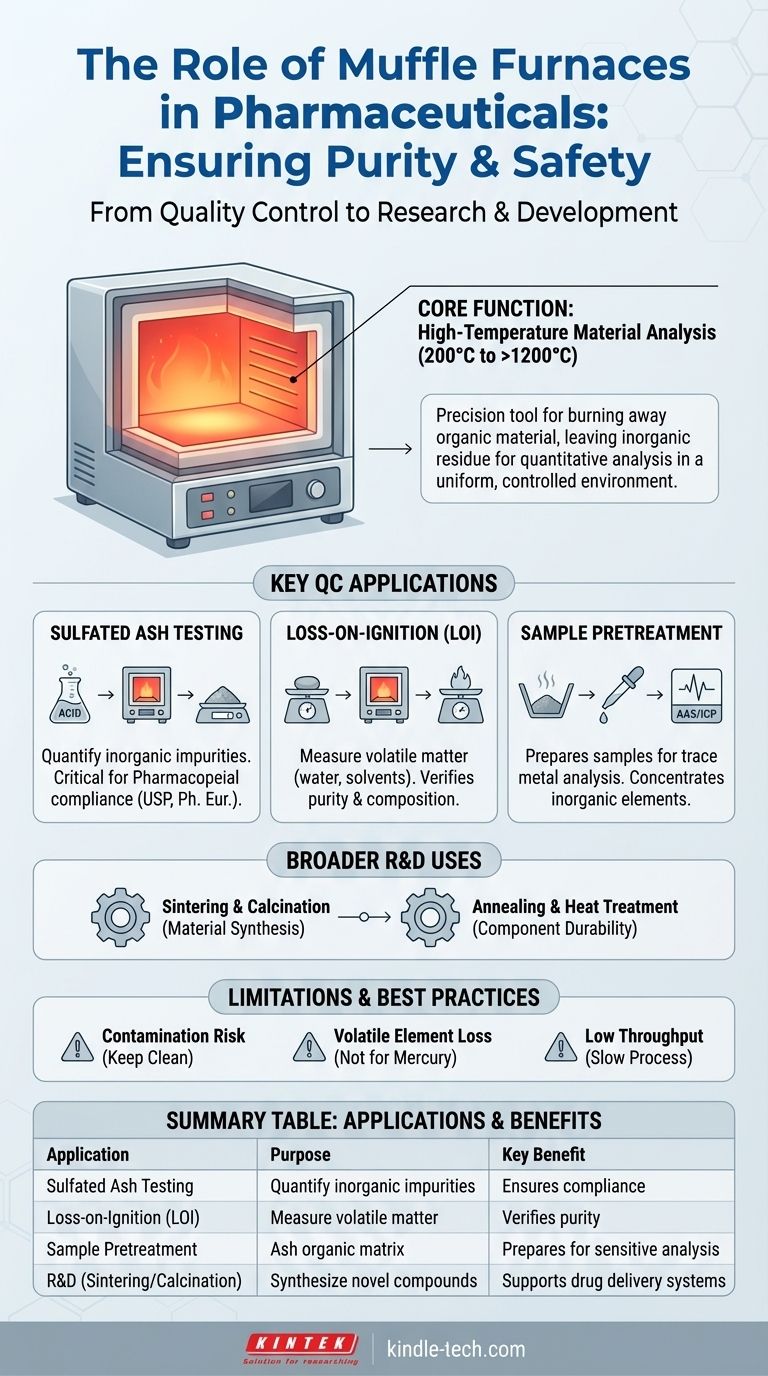
In pharmaceuticals, a muffle furnace is a critical analytical instrument used primarily for high-temperature testing that ensures the purity, safety, and quality of drug substances. Its main functions are for "drug inspection" and "sample pretreatment," which involve using extreme heat to determine the amount of non-combustible or volatile materials present in a sample.
A muffle furnace is not just a high-temperature oven; it is a precision tool for quantitative analysis. Its primary role in pharmaceuticals is to burn away all organic material, leaving behind only the inorganic residue, which allows for the precise measurement of impurities as mandated by regulatory standards.

The Core Function: High-Temperature Material Analysis
A muffle furnace is fundamentally an insulated chamber that heats its contents to a very high, specific, and uniform temperature, often ranging from 200°C to over 1200°C.
What is a Muffle Furnace?
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is the "muffle" itself—a high-temperature ceramic chamber that protects the sample from direct contact with the heating elements. This ensures that the material is heated by uniform radiation, preventing contamination and providing a highly controlled environment for analysis.
Why Precise Temperature is Critical
Pharmaceutical testing relies on precise, repeatable conditions. The furnace's ability to hold a specific temperature is essential for procedures like ashing, where complete combustion of the organic matrix is required without causing the inorganic components to decompose or vaporize.
Key Applications in Pharmaceutical Quality Control (QC)
In a regulated QC lab, muffle furnaces are used for specific pharmacopeial tests that quantify impurities and verify the composition of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients.
Determining Sulfated Ash Content
The most common use is for sulfated ash testing. In this procedure, a sample is first charred with sulfuric acid and then ignited in the furnace until all organic matter is burned away. The weight of the remaining residue (the ash) represents the total amount of inorganic impurities, a critical quality attribute that must fall within strict limits defined by pharmacopeias.
Loss-on-Ignition (LOI) Testing
Loss-on-ignition is another quantitative technique. A sample is weighed, heated to a very high temperature in the furnace for a set time, cooled, and weighed again. The weight loss represents the amount of volatile matter—such as water or residual solvents—that was driven off, providing another measure of purity and composition.
Sample Pretreatment for Elemental Analysis
A muffle furnace is often the first step in preparing a sample for trace metal analysis. By ashing the sample, the entire organic matrix is removed, concentrating the inorganic elements. This ash can then be dissolved and analyzed by more sensitive instruments (like Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy) to detect and quantify specific heavy metal contaminants like lead, cadmium, or mercury.
Broader Uses in Pharmaceutical R&D
Beyond routine quality control, muffle furnaces serve important roles in the research and development of new drugs and materials.
Sintering and Calcination
Researchers use furnaces for sintering (fusing powders together with heat) and calcination (heating solids to high temperatures to cause thermal decomposition or phase transition). These processes are used to create specialized ceramics, catalysts, or advanced excipients for novel drug delivery systems.
Material Synthesis and Heat Treatment
The controlled, high-temperature environment is ideal for synthesizing new inorganic compounds or for annealing and heat-treating metal components used in manufacturing equipment or medical devices to improve their strength and durability.
Understanding the Limitations
While essential, the muffle furnace is a tool with specific constraints that every analyst must understand to ensure accurate results.
Potential for Contamination
The muffle chamber must be kept impeccably clean. Any residue from previous tests can cross-contaminate a sample, leading to inaccurately high ash content results and failed batches.
Loss of Volatile Elements
Standard ashing procedures are not suitable for quantifying highly volatile metallic elements like mercury. The extreme heat will cause them to vaporize and be lost, requiring specialized closed-vessel digestion methods instead.
Time and Throughput
Ashing procedures are inherently slow, often requiring several hours of heating, cooling in a desiccator, and weighing. This makes it a low-throughput technique that is typically reserved for final product verification rather than in-process checks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of a muffle furnace depends entirely on your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is quality control and compliance: Use the furnace for sulfated ash and loss-on-ignition tests to verify drug purity against official pharmacopeial standards.
- If your primary focus is detecting heavy metals: Employ the furnace as a sample preparation tool to digest the organic matrix before using more advanced instrumental analysis.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Leverage the furnace's capabilities for high-temperature materials science, including sintering, calcination, and synthesizing novel compounds.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace provides an irreplaceable function in pharmaceuticals by answering a fundamental question: what remains when everything combustible is gone?
Summary Table:
| Application | Purpose in Pharma | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Sulfated Ash Testing | Quantify inorganic impurities in APIs and excipients | Ensures compliance with pharmacopeial standards (e.g., USP, Ph. Eur.) |
| Loss-on-Ignition (LOI) | Measure volatile matter (water, solvents) | Verifies purity and composition of drug substances |
| Sample Pretreatment | Ash organic matrix for trace metal analysis (e.g., heavy metals) | Prepares samples for sensitive instruments like AAS/ICP |
| R&D (Sintering/Calcination) | Synthesize novel excipients or catalysts | Supports development of advanced drug delivery systems |
Ensure your pharmaceutical quality control meets the highest standards with reliable equipment from KINTEK.
Our muffle furnaces are designed for precision, uniformity, and compliance, providing the accurate high-temperature analysis your lab needs for critical tasks like sulfated ash testing and heavy metal sample preparation.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK's lab equipment and consumables can enhance your pharmaceutical testing workflows.
Get in touch via our Contact Form for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of a furnace? From 1100°C to Over 2000°C Explained
- What is the structure of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components and Design
- What is the burnout cycle on a furnace? Stop This Destructive Overheating Pattern Now
- What is the temperature limit on a muffle furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Model
- What is the temperature for a furnace? It Depends on Your Material and Process Goal



















