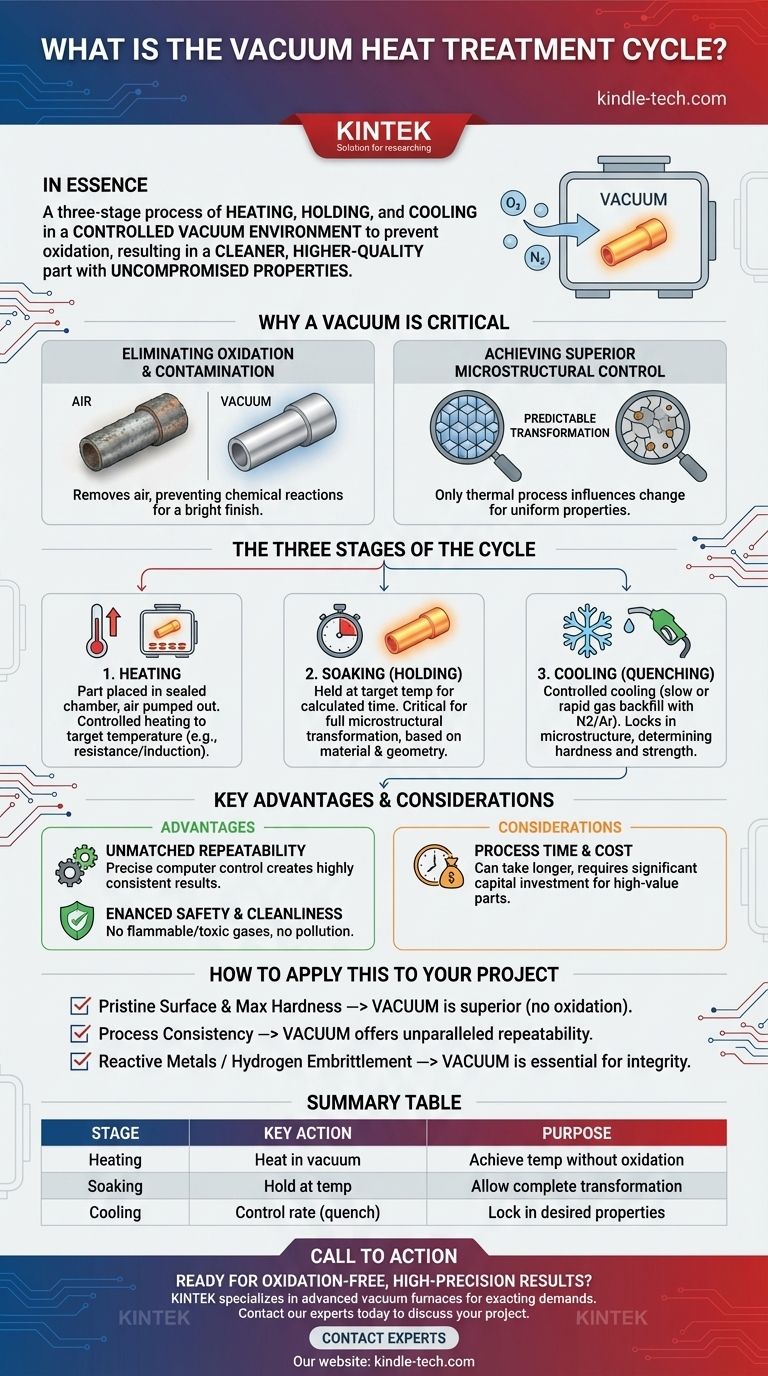
In essence, the vacuum heat treatment cycle is a three-stage process of heating, holding, and cooling a material inside a vacuum chamber. This controlled environment is the key, as it prevents the material's surface from reacting with air, which eliminates oxidation and other contaminants, resulting in a cleaner, higher-quality finished part.
The core principle is not simply heating the material, but fundamentally changing its internal structure with extreme precision. By removing the atmosphere, you gain meticulous control over the entire process, ensuring the final product has superior, repeatable, and uncompromised physical properties.

Why a Vacuum is the Critical Element
Traditional heat treatment occurs in the open air or in furnaces with specific gas atmospheres. A vacuum environment provides a fundamentally different and more controlled setting for changing a material's properties.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
When metal is heated in the presence of oxygen, its surface oxidizes, creating a layer of scale that must be cleaned off later.
By removing the air with a vacuum pumping system, you create a low-pressure environment. This prevents these undesirable chemical reactions, resulting in a bright, clean surface finish straight out of the furnace.
Achieving Superior Microstructural Control
The purpose of heat treatment is to alter a material's internal crystalline structure, or microstructure, to achieve desired characteristics like hardness or strength.
The pristine vacuum environment ensures that the thermal process is the only thing influencing this change. There are no unwanted variables from reactive gases, leading to a more predictable and uniform transformation throughout the material.
The Three Stages of the Cycle
Every vacuum heat treatment process follows a meticulously controlled sequence. The specific temperatures, times, and cooling rates are tailored to the material and the desired outcome.
Stage 1: Heating
The cycle begins by placing the workpiece in a sealed chamber and pumping out the air to create the desired level of vacuum.
Once the low-pressure environment is stable, the material is heated to a specific temperature using methods like electrical resistance or induction. This heating is done at a controlled rate to ensure the part heats uniformly.
Stage 2: Soaking (Holding)
After reaching the target temperature, the material is "soaked" or held at that temperature for a calculated period.
This holding time is critical for the internal microstructure to fully transform. It is determined by factors like the material type, the workpiece's effective thickness, and its overall geometry.
Stage 3: Cooling (Quenching)
The final stage is controlled cooling, often called quenching. The rate of cooling locks in the new microstructure and is arguably the most critical step in determining the final properties.
Cooling can be achieved by turning off the heat and letting the furnace cool slowly or by rapidly backfilling the chamber with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon to cool the part quickly. The chosen method directly influences the final hardness and strength.
Key Advantages and Considerations
While powerful, vacuum heat treatment is a specific tool for specific jobs. Understanding its benefits and context is key to using it effectively.
Benefit: Unmatched Repeatability
Because the process parameters—vacuum level, temperature ramps, and cooling rates—are so precisely controlled by computers, the results are highly consistent. This makes vacuum treatment ideal for applications where every part must meet identical specifications.
Benefit: Enhanced Safety and Cleanliness
The process is inherently safer than many atmosphere-based treatments because it avoids the use of flammable or toxic gases. It produces no pollution or hazardous byproducts, ensuring a safer work environment and easier regulatory compliance.
Consideration: Process Time and Cost
Achieving a deep vacuum and executing precise heating and cooling profiles can take longer than conventional methods. The specialized equipment also represents a significant capital investment, making the process more suitable for high-value components where quality is paramount.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing the right heat treatment method depends entirely on your material and final goal.
- If your primary focus is a pristine surface finish and maximum hardness: Vacuum treatment is the superior choice, as it completely prevents the surface degradation caused by oxidation.
- If your primary focus is process consistency for critical components: The meticulous digital control of a vacuum cycle provides unparalleled repeatability from one batch to the next.
- If you are treating reactive metals or need to prevent hydrogen embrittlement: The clean, inert environment of a vacuum is not just beneficial; it is essential for material integrity.
Ultimately, vacuum heat treatment is the definitive solution when precision, purity, and repeatability are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Heating | Heat material in a vacuum chamber | Achieve target temperature without surface oxidation |
| Soaking | Hold at target temperature | Allow complete microstructural transformation |
| Cooling | Control cooling rate (quenching) | Lock in desired material properties like hardness |
Ready to achieve oxidation-free, high-precision results for your critical components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced laboratory equipment, including vacuum furnaces designed for the exacting demands of heat treatment. Our solutions ensure the superior material purity, repeatability, and microstructural control detailed in this article.
Whether you are working with reactive metals or require unmatched process consistency, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our vacuum heat treatment solutions can bring unparalleled quality and reliability to your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can stainless steel be brazed? Yes, with the right techniques to overcome chromium oxide
- How is a vacuum oven used in the preparation of gel polymer electrolyte (GPE) membranes? Master Your Battery Research
- What are the different design schemes and common mediums used for gas cooling in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- Can aluminum and steel be brazed together? Master the Complex Joining Process
- What is the function of a laboratory oven in silver-graphene medical textiles? Optimizing Surface Modification
- What is catalytic vs thermal pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Process for Your Biomass
- What is the purpose of a vacuum system? Achieve Unmatched Process Control and Purity
- How does an industrial high-temperature electric heating furnace operate to simulate engine conditions for valve steel?



















