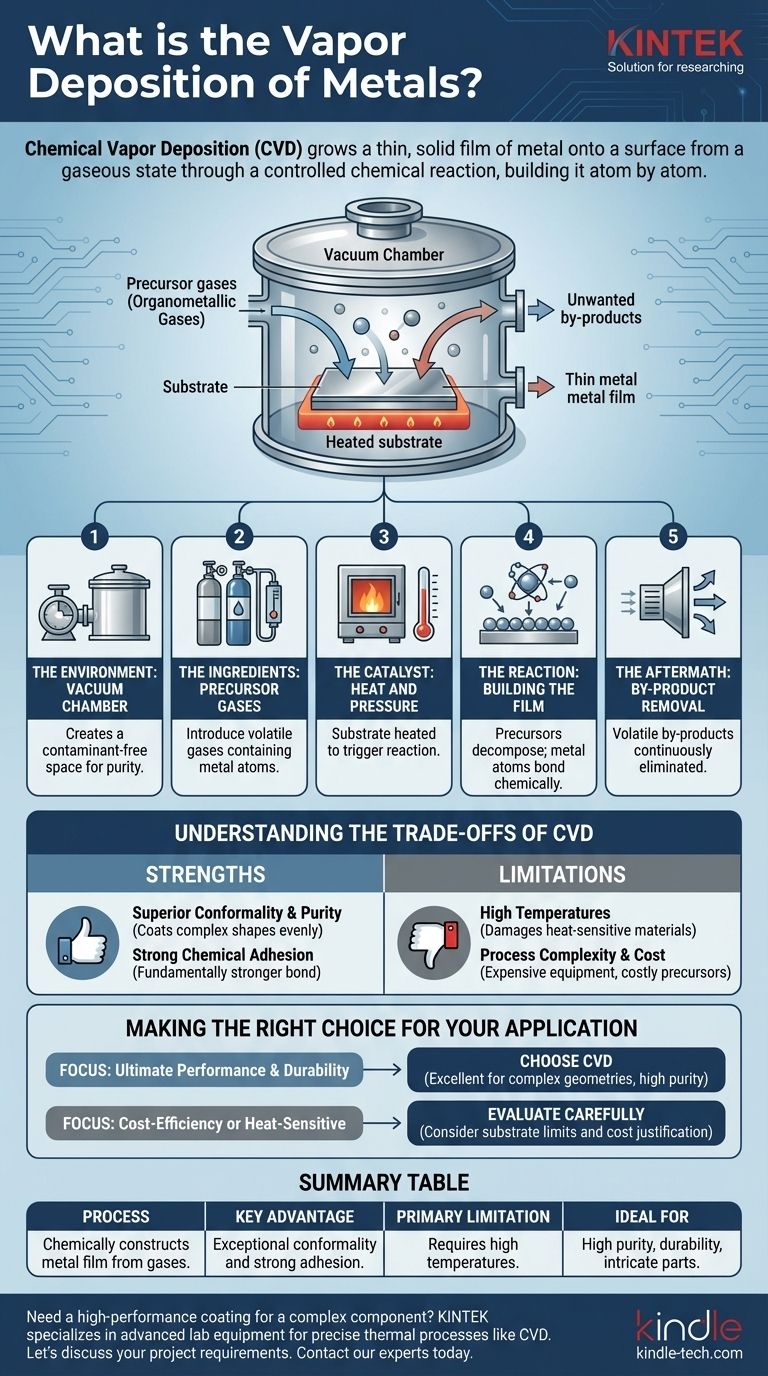
At its core, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of metals is a sophisticated process used to grow a thin, solid film of metal onto a surface from a gaseous state. Inside a vacuum chamber, chemical gases containing the desired metal are introduced, which then undergo a controlled chemical reaction directly on the target object's surface. This reaction deposits a highly pure, dense, and strongly bonded metallic coating.
The critical distinction of CVD is that you are not simply applying a pre-made coating. Instead, you are using precursor gases and energy to chemically construct the metallic film, atom by atom, directly onto the part’s surface, resulting in a fundamentally new, integrated layer.

How Chemical Vapor Deposition Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To truly grasp CVD, you must understand it as a sequence of controlled physical and chemical events. Each step is critical to achieving the final high-performance coating.
The Environment: The Vacuum Chamber
The entire process occurs within a sealed vacuum chamber. Creating a vacuum is the first step, as it removes air and other contaminants that could interfere with the chemical reaction. This ensures the final coating is exceptionally pure.
The Ingredients: Precursor Gases
Next, one or more volatile chemical gases, known as precursors, are introduced into the chamber. These gases are specifically chosen because they contain the atoms of the metal you wish to deposit (e.g., organometallic gas). The flow rate of these gases is precisely controlled.
The Catalyst: Heat and Pressure
The part to be coated, called the substrate, is heated to a specific, high temperature inside the chamber. This energy is not for melting anything; it serves as the catalyst that enables the chemical reaction to occur on the substrate's surface.
The Reaction: Building the Film
When the hot substrate interacts with the precursor gases, a chemical reaction is triggered. The precursors decompose, and the desired metal atoms bond directly to the surface of the substrate. This process builds up layer by layer, forming a dense and solid film.
The Aftermath: By-product Removal
The chemical reaction almost always creates unwanted gaseous by-products. These are volatile and are continuously removed from the chamber by the vacuum system's gas flow, leaving only the pure, solid coating behind.
Understanding the Trade-offs of CVD
Like any advanced manufacturing process, CVD has distinct advantages and limitations that make it suitable for some applications but not others.
Strength: Superior Conformality and Purity
Because the coating is built from a gas, it can penetrate and uniformly coat extremely complex shapes, sharp corners, and internal cavities. This ability to create an even layer everywhere is known as high conformality, a key advantage over line-of-sight processes.
Strength: Strong Adhesion
The CVD process forms a true chemical bond between the coating and the substrate material. This is fundamentally stronger and more durable than a purely physical bond, where a material is simply sprayed on.
Limitation: High Temperatures
The requirement for high reaction temperatures can be a major constraint. Substrates that cannot withstand this heat (like many plastics or certain metal alloys) will be damaged or warped by the process.
Limitation: Process Complexity and Cost
CVD requires expensive equipment, including vacuum chambers, high-temperature furnaces, and precise gas handling systems. The precursor gases themselves can also be costly, making it a less economical choice for low-value components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing whether to use CVD depends entirely on the technical requirements and constraints of your project.
- If your primary focus is ultimate performance and durability: CVD is often the superior choice due to its exceptional adhesion, purity, and ability to coat complex geometries.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency or your part is heat-sensitive: You must carefully evaluate if the substrate can handle the high temperatures and if the performance benefits justify the higher cost of CVD.
Ultimately, understanding CVD is understanding how to engineer superior material properties from the ground up, creating a component that is more than the sum of its parts.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | Chemically constructs a metal film from precursor gases onto a substrate surface. |
| Key Advantage | Exceptional conformality (coats complex shapes evenly) and strong chemical bond adhesion. |
| Primary Limitation | Requires high temperatures, which can damage heat-sensitive materials. |
| Ideal For | Applications demanding high purity, durability, and uniform coating on intricate parts. |
Need a high-performance coating for a complex component?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition. Whether you are developing new materials or optimizing a coating application, our expertise and solutions can help you achieve superior results with high purity and strong adhesion.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our experts today to find the right CVD solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained



















