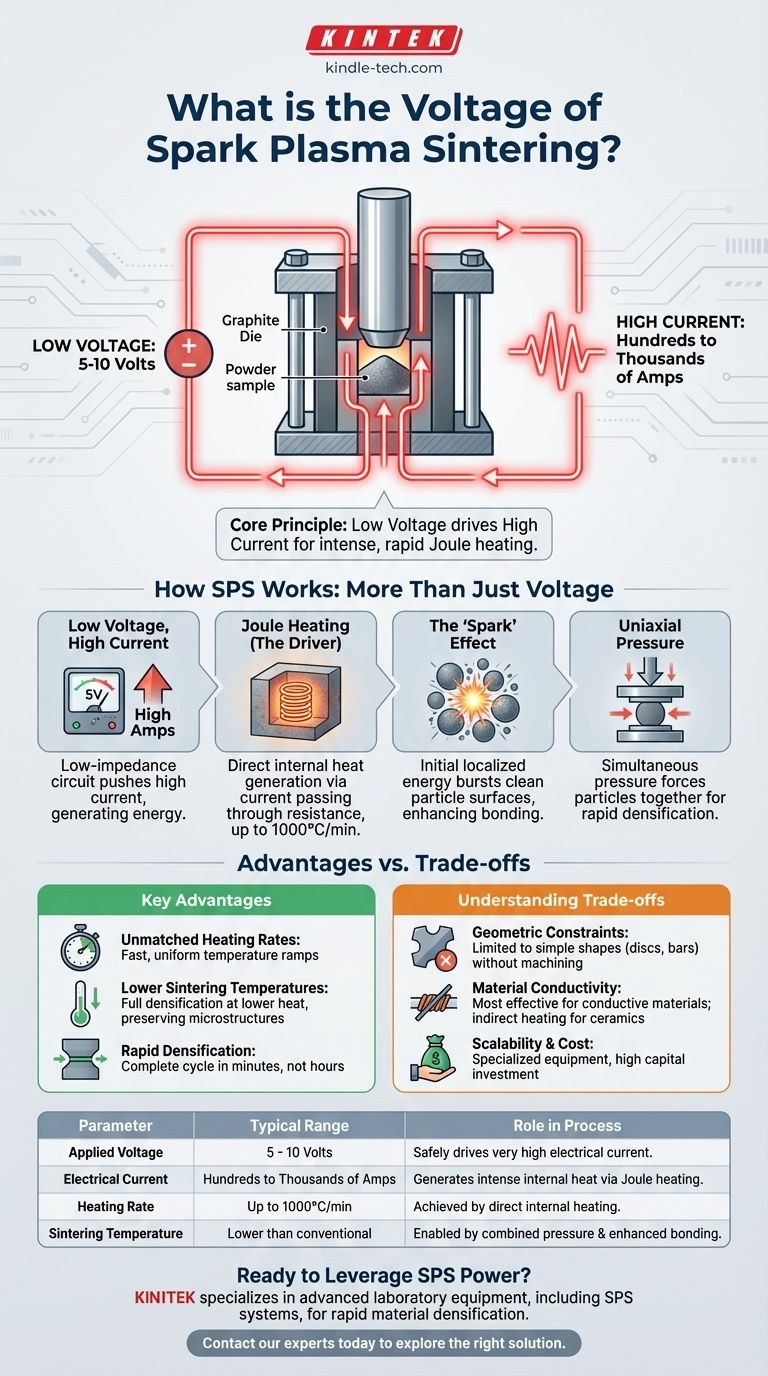
In Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), the applied voltage is typically very low, usually in the range of 5 to 10 volts. This low voltage is paired with a very high direct or pulsed electrical current, which is the true driver of the process's unique heating capabilities.
The core principle of SPS is not about high voltage, but about using low voltage to safely drive a high electrical current. This current generates rapid, intense, and localized heat through a phenomenon called Joule heating, enabling faster sintering at lower overall temperatures than conventional methods.

How SPS Works: It's More Than Just Voltage
Understanding Spark Plasma Sintering requires looking beyond the voltage and focusing on how the electrical energy is used. The process combines electrical current, pressure, and thermal fields to achieve rapid densification of powdered materials.
The Role of Low Voltage, High Current
The system is designed to be a low-impedance circuit. A low voltage (5-10 V) is sufficient to push a very high current—often hundreds or thousands of amperes—through the conductive graphite die and, in many cases, through the material being sintered. This high current is the source of the energy that heats the sample.
Joule Heating: The Primary Driver
The primary heating mechanism in SPS is Joule heating. This is the same principle that makes a toaster element glow red. As the high electrical current passes through the resistive graphite die and the powder compact, it generates intense heat directly within the tooling and sample. This allows for extremely high heating rates, sometimes up to 1000°C/min.
The "Spark" in Spark Plasma Sintering
The name refers to the belief that at the initial stage, spark discharges or plasma can form in the microscopic gaps between powder particles. This localized energy burst is thought to clean the particle surfaces by stripping away contaminants and oxides. This cleaning action enhances particle-to-particle bonding and accelerates the initial stages of sintering.
Uniaxial Pressure: The Final Piece
Simultaneously with the electrical current, a uniaxial mechanical pressure is applied via punches. This pressure forces the particles together, aiding in the collapse of pores and promoting the plastic deformation of the material once it has been heated. The combination of clean particle surfaces, rapid heating, and applied pressure results in highly dense parts in a fraction of the time.
Key Advantages of the SPS Process
The unique mechanism of SPS provides several distinct advantages over traditional furnace-based sintering techniques.
Unmatched Heating Rates
Because heat is generated directly within the die and sample, the system does not have to wait for radiative or convective heat transfer. This internal heating allows for exceptionally fast and uniform temperature ramps.
Lower Sintering Temperatures
The combination of pressure and enhanced particle bonding from the electrical field often allows for full densification at temperatures several hundred degrees lower than required by conventional sintering. This is crucial for preserving fine-grained microstructures or processing temperature-sensitive materials.
Rapid Densification
The entire SPS cycle, from heating to a short hold at temperature and cooling, can often be completed in just a few minutes. This dramatically shortens processing time compared to the many hours required for traditional methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, SPS is not a universal solution. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging its limitations.
Geometric Constraints
The use of a rigid, uniaxial die-and-punch setup generally limits the process to producing simple shapes, such as discs, cylinders, and rectangular bars. Complex, three-dimensional geometries are not feasible without extensive and costly secondary machining.
Material Conductivity Matters
SPS is most effective for electrically conductive materials where Joule heating can occur within the sample itself. While non-conductive materials like many ceramics can be sintered, they heat indirectly from the conductive graphite die, which can lead to less uniform temperature distribution.
Scalability and Cost
SPS equipment is specialized and represents a significant capital investment compared to conventional furnaces. Furthermore, scaling the process for very large components can be challenging due to the immense current and pressure requirements.
Is SPS Right for Your Application?
Choosing the correct sintering method depends entirely on your specific goals for material properties, production volume, and component geometry.
- If your primary focus is rapid material development or prototyping: SPS is an exceptional tool, as its speed allows for quick iteration and testing of new compositions and microstructures.
- If your primary focus is preserving nano-scale or fine-grained features: The low temperatures and short sintering times of SPS are ideal for preventing grain growth.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing large or complex-shaped parts: Conventional methods like press-and-sinter or metal injection molding are likely more cost-effective and geometrically flexible.
Ultimately, understanding the role of low voltage and high current in SPS empowers you to leverage its unique advantages for the right applications.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Typical Range in SPS | Role in the Process |
|---|---|---|
| Applied Voltage | 5 - 10 Volts | Safely drives a very high electrical current through the system. |
| Electrical Current | Hundreds to Thousands of Amps | Generates intense internal heat via Joule heating. |
| Heating Rate | Up to 1000°C/min | Achieved by direct internal heating, not external furnace elements. |
| Sintering Temperature | Often several hundred °C lower than conventional methods | Enabled by combined pressure and enhanced particle bonding. |
Ready to Leverage the Power of Spark Plasma Sintering?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment, including SPS systems, to help you achieve rapid material densification with fine-grained microstructures. Whether you're in materials development, prototyping, or processing temperature-sensitive compounds, our expertise can help you unlock the unique advantages of SPS for your specific application.
Let's discuss how SPS can accelerate your research and development. Contact our experts today to explore the right solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of SPS process? A Deep Dive into Rapid, Low-Temperature Sintering
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application



















