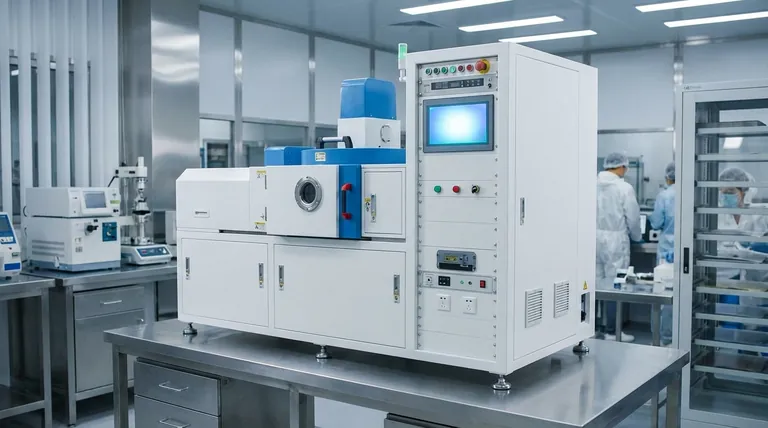
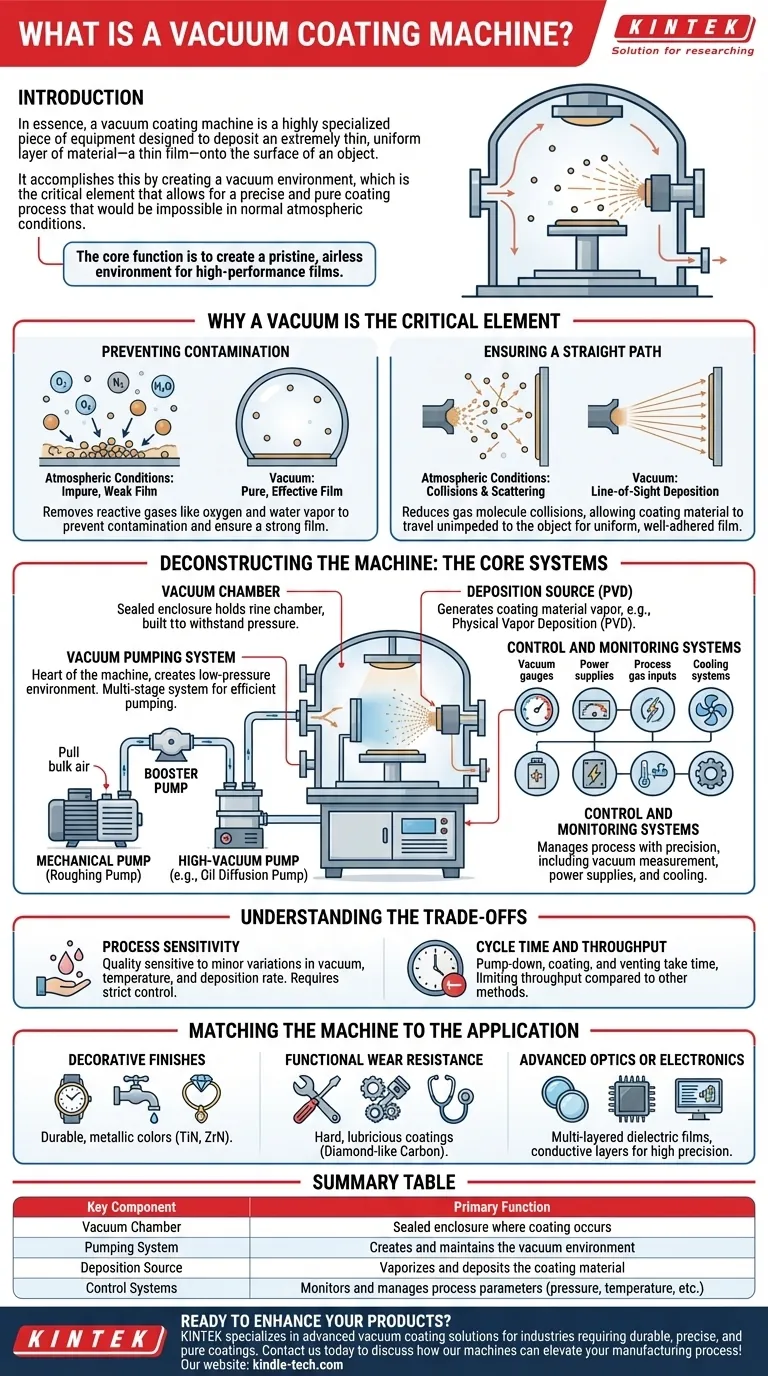
In essence, a vacuum coating machine is a highly specialized piece of equipment designed to deposit an extremely thin, uniform layer of material—a thin film—onto the surface of an object. It accomplishes this by creating a vacuum environment, which is the critical element that allows for a precise and pure coating process that would be impossible in normal atmospheric conditions.
The core function of a vacuum coating machine is not just to coat an object, but to create a pristine, airless environment where coating materials can travel unimpeded from a source to a target, resulting in high-performance films with specific functional or decorative properties.

Why a Vacuum is the Critical Element
To understand the machine, you must first understand the role of the vacuum. Removing air and other gases from the chamber is fundamental to the entire process for two primary reasons.
Preventing Contamination
The air around us is filled with particles like oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor. These particles would react with the coating material and contaminate the target surface, leading to a weak, impure, and ineffective film.
Ensuring a Straight Path
In a vacuum, there are far fewer gas molecules for the coating particles to collide with. This allows the vaporized coating material to travel in a straight line from its source to the object being coated, a principle known as "line-of-sight" deposition. This ensures a dense, uniform, and well-adhered film.
Deconstructing the Machine: The Core Systems
While designs vary, all vacuum coating machines are built around several fundamental systems working in unison. These systems manage the environment, the material, and the process itself.
The Vacuum Chamber
This is the sealed central enclosure where the coating takes place. It's built to withstand the immense pressure difference between the inside and the outside atmosphere and houses both the object to be coated and the deposition source.
The Vacuum Pumping System
This is the heart of the machine, responsible for creating the low-pressure environment. It's typically a multi-stage system, as no single pump can efficiently go from atmospheric pressure to a high vacuum.
- Mechanical Pumps: These "roughing pumps" do the initial work, removing the bulk of the air from the chamber.
- Booster & High-Vacuum Pumps: Once a certain pressure is reached, high-vacuum pumps like booster (Roots) pumps or oil diffusion pumps take over to remove the remaining molecules and achieve the required deep vacuum.
The Deposition Source
This is the system that generates the coating material vapor. The most common method mentioned is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), where a solid material is vaporized through physical means (like sputtering or evaporation) and then deposits as a thin film on the target.
Control and Monitoring Systems
A host of interconnected systems are required to manage the process with precision. This includes vacuum measurement gauges, power supplies for the deposition source, systems to input specific process gases, and cooling systems to manage the intense heat generated.
Understanding the Trade-offs
It's important to recognize that vacuum coating is a highly technical and capital-intensive process. The machinery is complex, requiring specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance.
Process Sensitivity
The quality of the final coating is extremely sensitive to process parameters. Minor variations in vacuum level, temperature, or deposition rate can significantly impact the film's properties, requiring strict process control.
Cycle Time and Throughput
Creating a high vacuum is not an instantaneous process. The time it takes to pump down the chamber, run the coating process, and vent the chamber back to atmospheric pressure (the "cycle time") can limit the overall throughput compared to other coating methods like painting or electroplating.
Matching the Machine to the Application
The specific design of a vacuum coating machine is dictated entirely by its intended purpose. Understanding your final goal is key to understanding the technology.
- If your primary focus is decorative finishes: You need a system optimized for depositing materials like titanium nitride or zirconium nitride to create durable, metallic colors on items like watches, faucets, or jewelry.
- If your primary focus is functional wear resistance: Your application demands a machine capable of applying very hard, lubricious coatings (like diamond-like carbon) to industrial tools, engine components, or medical implants.
- If your primary focus is advanced optics or electronics: You require a highly precise machine with advanced monitoring to deposit multi-layered dielectric films for anti-reflection coatings on lenses or conductive layers for semiconductors.
Ultimately, a vacuum coating machine is a sophisticated tool that enables the creation of advanced materials by manipulating matter on an atomic scale within a controlled environment.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber | Sealed enclosure where coating occurs |
| Pumping System | Creates and maintains the vacuum environment |
| Deposition Source | Vaporizes and deposits the coating material |
| Control Systems | Monitors and manages process parameters (pressure, temperature, etc.) |
Ready to enhance your products with high-performance thin films? KINTEK specializes in advanced vacuum coating solutions for industries requiring durable, precise, and pure coatings—from decorative finishes to functional wear resistance and advanced optics. Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures you get the right system for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum coating machines can elevate your manufacturing process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the disadvantage of CVD? High Heat, Hazardous Materials, and Logistical Hurdles
- What are the features and benefits of Low Pressure Chemical Vapour Deposition (LPCVD)? Expert Guide to Film Uniformity
- What are the benefits of diamond-like carbon coating? Boost Component Life with Extreme Hardness & Low Friction
- What affects deposition rate? Master the 4 Key Levers for Thin Film Growth Speed
- What are the two main types of vapor deposition systems? PVD vs. CVD Explained
- Why is physical vapor deposition conducted in a high vacuum? To Ensure Purity and Performance
- What is the full form of CVD graphene? Unlocking Scalable, High-Quality Production
- What is CVD method chemical Vapour deposition? The Process for High-Purity Thin Films



















