In essence, vacuum hardening is a high-purity heat treatment process. It involves heating a metal component to a specific temperature in an oxygen-free environment and then rapidly cooling it to increase its hardness and strength. By performing the heating cycle in a vacuum, the process prevents surface reactions like oxidation, resulting in a clean, bright part that often requires no further mechanical finishing.
The core advantage of vacuum hardening is its ability to strengthen a metal without compromising its surface. By eliminating oxygen, it delivers a part that is not only hardened internally but also has a superior, scale-free finish right out of the furnace.
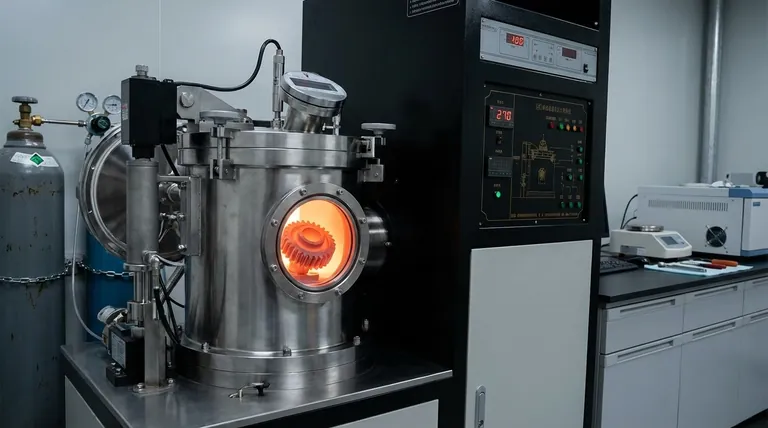

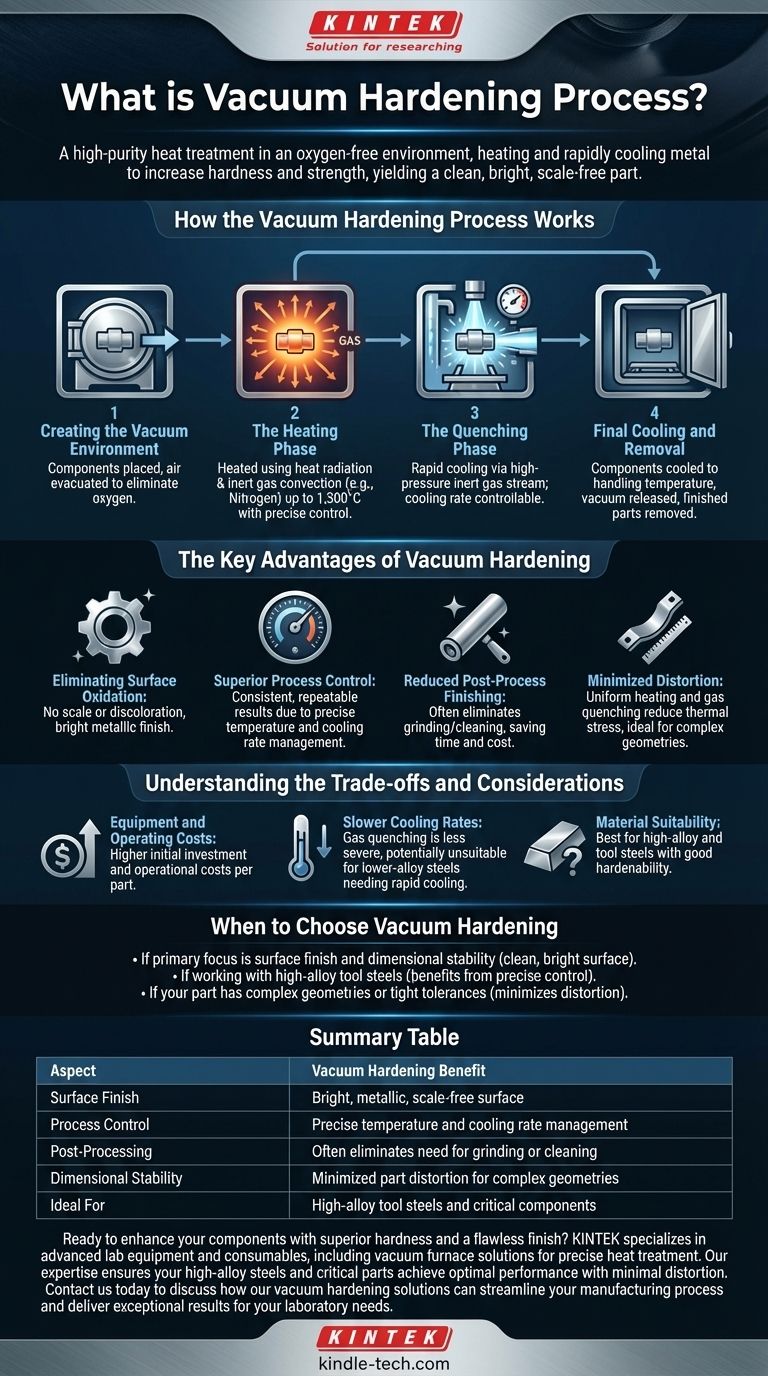
How the Vacuum Hardening Process Works
The process is a precise, multi-stage operation that takes place entirely within a sealed vacuum furnace. Each step is carefully controlled to achieve the desired material properties.
Creating the Vacuum Environment
The first step is to place the components into the furnace and remove the air. This evacuation creates a vacuum, eliminating oxygen and other atmospheric gases that could react with the metal at high temperatures.
The Heating Phase
Once the vacuum is established, the material is heated. This is done using a combination of heat radiation and convection heating with an inert gas, such as nitrogen. Temperatures can reach up to 1,300°C, and modern furnace controls allow for extremely precise and uniform temperature management.
The Quenching Phase
To achieve hardness, the heated component must be cooled rapidly in a process called quenching. In vacuum hardening, this is accomplished using a high-pressure stream of inert gas, typically nitrogen. The cooling rate can be precisely controlled by adjusting the gas pressure and flow.
Final Cooling and Removal
After the rapid quench, the components are cooled to handling temperature, the vacuum is released, and the finished parts are removed from the furnace.
The Key Advantages of Vacuum Hardening
Choosing vacuum hardening over other methods provides several distinct benefits related to quality, consistency, and final part integrity.
Eliminating Surface Oxidation
The primary benefit is the prevention of oxidation. With no oxygen present, the metal surface does not form a scale or discoloration, resulting in a bright metallic finish.
Superior Process Control
Vacuum furnaces offer exceptional control over both temperature and cooling rates. This precision ensures that hardening is consistent and repeatable across an entire batch of parts, leading to reliable and predictable results.
Reduced Post-Process Finishing
Because parts emerge from the furnace clean and bright, the need for secondary operations like grinding, sandblasting, or chemical cleaning is often completely eliminated. This saves significant time and cost in the manufacturing workflow.
Minimized Distortion
The controlled, uniform heating and gas quenching inherent to the vacuum process minimize the thermal stress placed on the component. This leads to less distortion, which is especially critical for parts with complex geometries or tight dimensional tolerances.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, vacuum hardening is a specialized process with specific considerations.
Equipment and Operating Costs
Vacuum furnaces are sophisticated and expensive pieces of equipment. This initial investment and the operational costs mean the process is typically more expensive per part than conventional atmosphere hardening.
Slower Cooling Rates
Gas quenching, while highly controllable, is generally less severe than quenching in a liquid medium like oil or water. This means it may not be suitable for some lower-alloy steels that require an extremely rapid cooling rate to achieve full hardness.
Material Suitability
The process is best suited for high-alloy and tool steels that have good "hardenability"—the ability to harden during a slower cooling process. Materials that require a very aggressive quench may not be ideal candidates for this method.
When to Choose Vacuum Hardening
Your material choice and final part requirements will determine if vacuum hardening is the right approach.
- If your primary focus is surface finish and dimensional stability: Vacuum hardening is ideal for parts where a clean, bright surface is critical, eliminating the need for post-heat-treat machining.
- If you are working with high-alloy tool steels: These materials benefit greatly from the precise temperature and cooling control of a vacuum furnace, ensuring consistent and predictable hardening results.
- If your part has complex geometries or tight tolerances: The uniform heating and controlled gas quenching minimize distortion compared to harsher liquid quenching methods.
Ultimately, vacuum hardening is the premier choice when the final integrity of a component's surface is just as important as its internal hardness.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vacuum Hardening Benefit |
|---|---|
| Surface Finish | Bright, metallic, scale-free surface |
| Process Control | Precise temperature and cooling rate management |
| Post-Processing | Often eliminates need for grinding or cleaning |
| Dimensional Stability | Minimized part distortion for complex geometries |
| Ideal For | High-alloy tool steels and critical components |
Ready to enhance your components with superior hardness and a flawless finish? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including vacuum furnace solutions for precise heat treatment. Our expertise ensures your high-alloy steels and critical parts achieve optimal performance with minimal distortion. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum hardening solutions can streamline your manufacturing process and deliver exceptional results for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Which method of heat transfer can work through vacuum? Unlock the Power of Thermal Radiation
- How thick is vacuum deposition? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings
- How does a high-temperature calcination furnace contribute to the formation of Si-RuO2 catalysts? Optimize Your Synthesis
- What are the different types of furnaces used for melting? Choose the Right Technology for Your Material
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum brazing furnace for TLP bonding? Achieve Superior Joint Integrity
- What are the factors that control the sintering process? Master Temperature, Time, Pressure & Material
- Why are high-purity argon and vacuum necessary for 14Cr ODS steel? Essential Protection for Mechanical Alloying
- What are the important safety precautions for heat treatment? Protect Your Team from Extreme Heat and Invisible Hazards



















