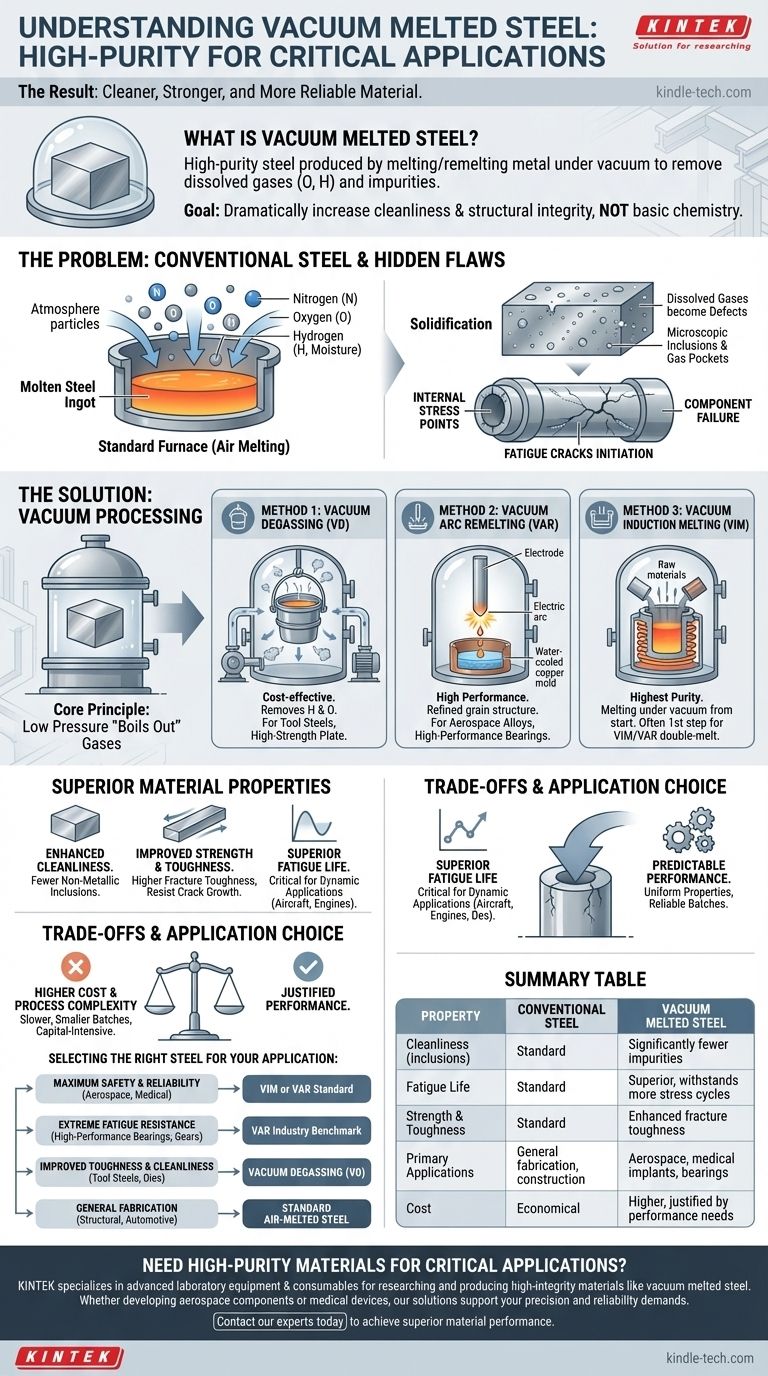
In short, vacuum melted steel is a class of high-purity steel produced by melting or remelting the metal under a vacuum. This specialized process removes dissolved gases like oxygen and hydrogen, along with other trace impurities, that are normally trapped during conventional air-melting. The result is a cleaner, stronger, and far more reliable material engineered for the most demanding applications.
The fundamental purpose of vacuum melting is not to change the steel's basic chemistry, but to dramatically increase its cleanliness and structural integrity. By eliminating the microscopic imperfections caused by trapped gases, you create a material with superior fatigue life, toughness, and consistency.

The Problem: Hidden Flaws in Conventional Steel
To understand the value of vacuum melting, you must first understand the inherent limitations of steel melted in open air.
The Role of Dissolved Gases
When steel is melted in a standard furnace, it is exposed to the atmosphere, which is primarily nitrogen and oxygen. These gases, along with hydrogen from moisture, readily dissolve into the molten metal, much like sugar dissolves in water.
From Gas to Defect
As the steel cools and solidifies, the amount of gas it can hold in solution drops dramatically. The excess gas is forced out, forming microscopic bubbles or reacting with elements like carbon and aluminum to create tiny, hard, non-metallic particles called inclusions.
The Impact of Imperfections
These inclusions and gas pockets act as internal stress points. Under load or repeated stress cycles, microscopic cracks can initiate at these points, eventually growing until the component fails. This is a primary cause of fatigue failure in mechanical parts.
How Vacuum Processing Solves the Problem
Vacuum melting techniques are secondary refining processes designed specifically to remove these harmful dissolved gases and the inclusions they form.
The Core Principle: Using Low Pressure
By placing the molten steel in a vacuum, the pressure above the metal is reduced to near zero. This creates a powerful driving force for the dissolved gases to "boil" out of the liquid, leaving behind a much purer metal.
Method 1: Vacuum Degassing (VD)
This is the most common and cost-effective method. A ladle of molten steel from a primary furnace is placed inside a vacuum chamber. The low pressure pulls out hydrogen and some oxygen, resulting in a cleaner final product for applications like tool steels or high-strength plate.
Method 2: Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR)
For higher performance, VAR is used. This process takes a solid, conventionally produced steel bar (the electrode) and uses it as one side of a high-current electric circuit inside a vacuum chamber. The arc melts the tip of the electrode, and the metal falls drop by drop into a water-cooled copper mold, solidifying as it builds up a new, highly refined ingot.
The combination of the vacuum and the controlled solidification process produces steel with exceptional cleanliness and a refined grain structure, making it a standard for aerospace alloys and high-performance bearings.
Method 3: Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM)
VIM is the highest-purity process. The raw, solid metals are loaded into a furnace that is already inside a vacuum chamber. The melting occurs entirely under vacuum, preventing any atmospheric contamination from the very beginning. This is often the first step in producing the electrodes used for the VAR process, creating a "VIM/VAR" double-melted steel of unparalleled quality.
The Result: Superior Material Properties
Removing microscopic impurities has a profound effect on the steel's bulk mechanical properties.
Enhanced Cleanliness
Vacuum melted steels have significantly fewer non-metallic inclusions. This is the primary benefit from which all others are derived.
Improved Strength and Toughness
With fewer internal weak points, the steel is better able to resist the initiation and growth of cracks. This directly translates to higher fracture toughness and impact strength.
Superior Fatigue Life
This is the most critical improvement for dynamic applications. By eliminating the stress risers where fatigue cracks begin, vacuum melted steel can withstand many more stress cycles before failure. This is why it is essential for parts like aircraft landing gear, engine crankshafts, and ball bearings.
Predictable Performance
The reduction in random impurities leads to a more homogenous and consistent material. This ensures that performance is reliable from batch to batch and that properties are uniform throughout a single component, a critical factor for safety and design optimization.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are significant, vacuum melting is not a universal solution.
The Primary Drawback: Cost
Each vacuum processing step adds significant cost and time to production. VIM/VAR steel can be many times more expensive than its conventional air-melted equivalent.
Process Complexity and Scale
Vacuum furnaces are complex, capital-intensive pieces of equipment. The processes are slower and typically produce smaller batches than primary steelmaking, limiting their use to applications where the performance benefits are non-negotiable.
When Is It Overkill?
For most applications, such as structural beams, automotive body panels, or general hardware, the inherent properties of conventional steel are more than sufficient. The added cost of vacuum melting would provide no functional benefit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right steel manufacturing process depends entirely on the demands of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum safety and reliability: For aerospace, medical implants, or power generation components where failure is catastrophic, VIM or VAR grades are the required standard.
- If your primary focus is extreme fatigue resistance: For high-performance bearings, gears, and racing engine components, VAR steel is the industry benchmark.
- If your primary focus is improved toughness and cleanliness over standard grades: For demanding tool steels, dies, and molds, Vacuum Degassing provides a significant performance boost at a moderate cost increase.
- If your primary focus is general fabrication or construction: Standard air-melted steel provides the necessary performance at the most economical price point.
Ultimately, understanding the role of vacuum melting allows you to specify a material with the precise level of integrity required for your design's success.
Summary Table:
| Property | Conventional Steel | Vacuum Melted Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Cleanliness (Inclusions) | Standard levels | Significantly fewer impurities |
| Fatigue Life | Standard | Superior, withstands more stress cycles |
| Strength & Toughness | Standard | Enhanced fracture toughness |
| Primary Applications | General fabrication, construction | Aerospace, medical implants, bearings |
| Cost | Economical | Higher, justified by performance needs |
Need high-purity materials for your critical applications? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced laboratory equipment and consumables essential for researching and producing high-integrity materials like vacuum melted steel. Whether you're developing next-generation aerospace components or medical devices, our solutions support the precision and reliability your work demands. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior material performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals



















