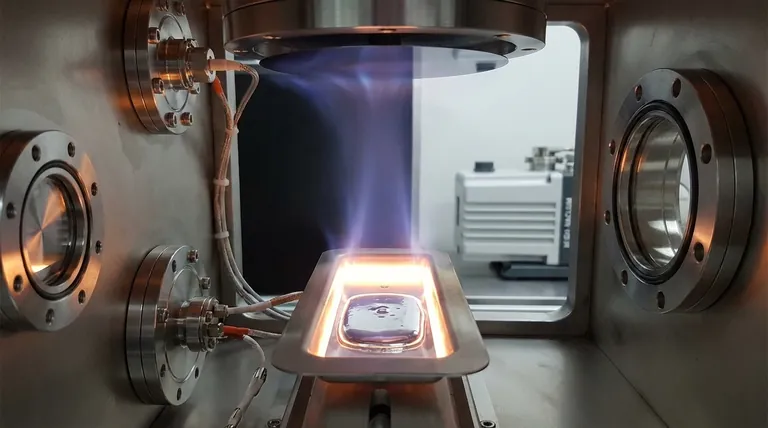
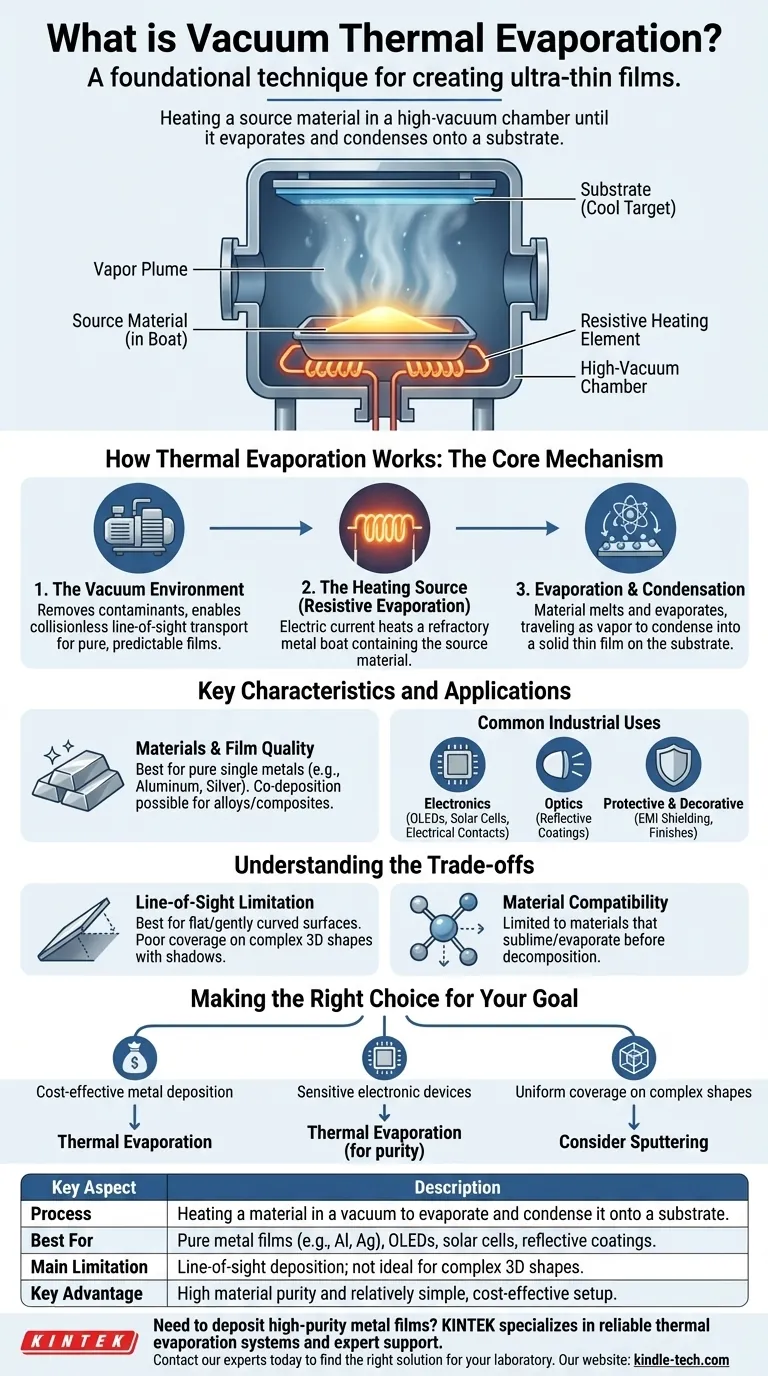
Vacuum thermal evaporation is a foundational technique used to create ultra-thin films of a material onto a surface. In this process, a source material is heated inside a high-vacuum chamber until it evaporates, turning into a vapor. This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto a cooler target object, known as a substrate, forming a precise and uniform coating.
At its core, thermal evaporation is like boiling a metal or other material in a near-perfect vacuum. The vacuum ensures the resulting vapor is pure and can travel in a straight line to coat a target surface, enabling the production of high-performance electronic and optical components.

How Thermal Evaporation Works: The Core Mechanism
The process, while conceptually simple, relies on a carefully controlled environment to achieve a high-quality film. Each step is critical to the final outcome.
The Vacuum Environment
The entire process occurs in a high-vacuum chamber. This is crucial for two reasons.
First, it removes gaseous contaminants like oxygen and water vapor that would otherwise react with the evaporated material and compromise the purity of the film.
Second, the low pressure allows evaporated atoms to travel from the source to the substrate with few or no collisions with air molecules. This is called collisionless, line-of-sight transport, ensuring the film is deposited predictably.
The Heating Source (Resistive Evaporation)
The most common method for heating is called resistive evaporation. The source material, often in the form of pellets or powder, is placed in a small container called a "boat" or "basket."
This boat is typically made of a refractory metal with high electrical resistance. A strong electric current is passed through the boat, causing it to heat up rapidly due to Joule heating.
Evaporation and Condensation
As the boat heats up, the source material melts and its temperature rises to the point of evaporation.
The resulting atoms or molecules travel through the vacuum and strike the cooler substrate, which is strategically placed above the source. Upon contact, the atoms condense back into a solid state, gradually building up a thin film on the substrate's surface.
Key Characteristics and Applications
Thermal evaporation is valued for its relative simplicity and versatility, making it a cornerstone of thin-film deposition for numerous industries.
Materials and Film Quality
This method is exceptionally well-suited for depositing thin films of single metals, such as aluminum or silver, producing layers with good purity and adhesion.
It can also be adapted for more complex applications. By using multiple crucibles with independent temperature controls, it's possible to co-deposit several materials simultaneously to create alloys or composite films.
Common Industrial Uses
The precision and purity of thermally evaporated films are essential for high-technology manufacturing.
- Electronics: It is widely used for creating electrical contacts, layers in OLED displays, solar cells, and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS).
- Optics: The process creates highly reflective coatings for light reflectors used in automotive headlamps, medical lighting, and aerospace components.
- Protective & Decorative Coatings: It is used for EMI/RFI shielding on electronic housings and for applying decorative metallic finishes to items like cosmetic packaging and sporting goods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, thermal evaporation is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Line-of-Sight Limitation
Because the vapor travels in straight lines, thermal evaporation is a line-of-sight deposition process. This means it works best for coating flat or gently curved surfaces.
It is not ideal for uniformly coating complex, three-dimensional objects with hidden surfaces or sharp angles, as those areas will be in a "shadow" and receive little or no coating.
Material Compatibility
The process is limited to materials that can be evaporated or sublimated at temperatures that are practically achievable in a vacuum system.
Some compounds may decompose or break apart when heated before they have a chance to evaporate, making them unsuitable for this method. For these materials, or for films requiring higher density, alternative methods like electron-beam evaporation or sputtering may be required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method depends entirely on the material you are using and the intended properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective metal deposition: Thermal evaporation is an excellent choice for creating pure metal films, such as aluminum for reflectors or silver for electrical contacts.
- If your primary focus is building sensitive electronic devices: This is a key process for fabricating specific layers in OLEDs and solar cells where material purity is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is achieving uniform coverage on complex shapes: You should consider alternative PVD methods like sputtering, which is less dependent on line-of-sight and can provide better coverage on intricate geometries.
Ultimately, thermal evaporation remains a vital and highly effective tool for fabricating the high-purity thin films that drive modern technology.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Heating a material in a vacuum to evaporate and condense it onto a substrate. |
| Best For | Pure metal films (e.g., Al, Ag), OLEDs, solar cells, reflective coatings. |
| Main Limitation | Line-of-sight deposition; not ideal for complex 3D shapes. |
| Key Advantage | High material purity and relatively simple, cost-effective setup. |
Need to deposit high-purity metal films for your research or production?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable thermal evaporation systems and expert support to help you achieve precise, uniform coatings for your electronics, optics, or protective coating applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific thin-film deposition needs and find the right solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- What is the evaporation process in semiconductors? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What is thermal evaporation used to deposit? A Guide to Metals, Compounds, and Key Applications
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab


















