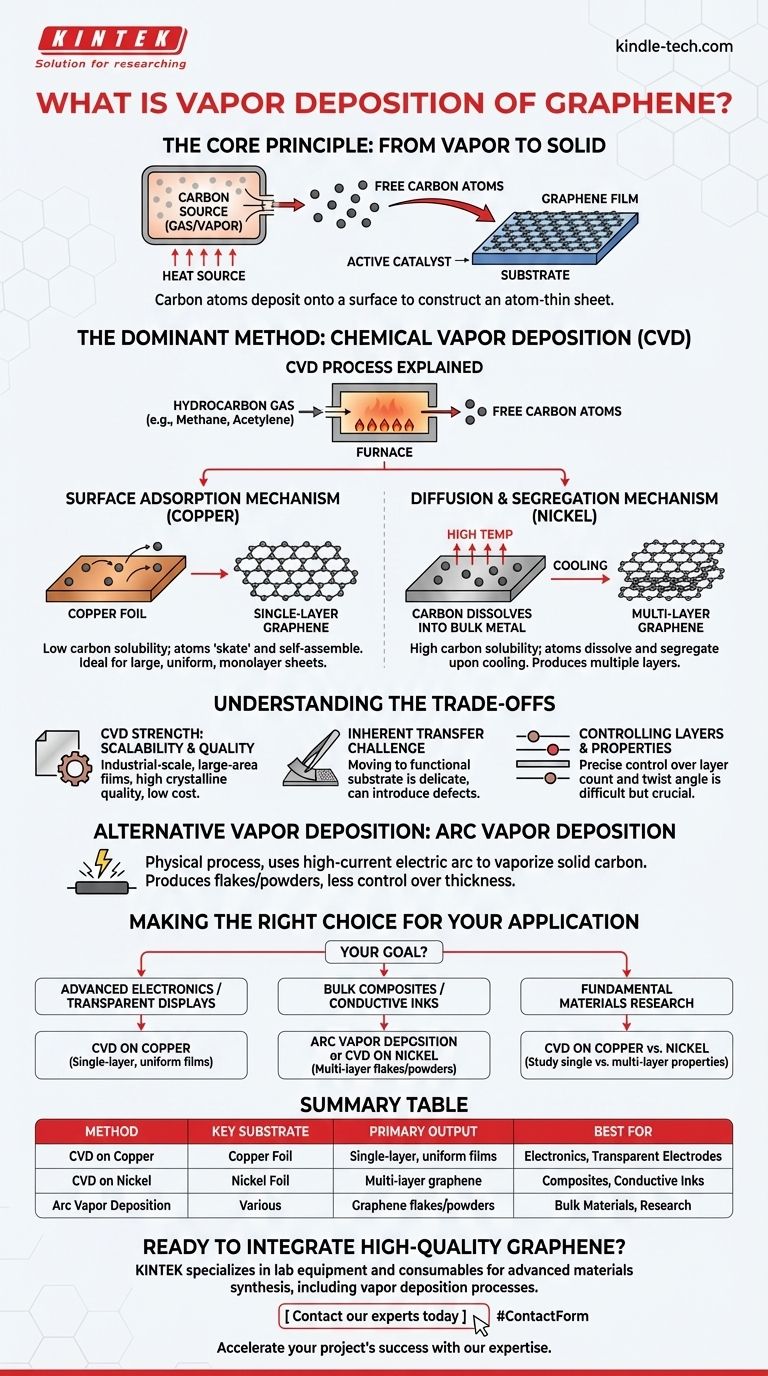
Vapor deposition of graphene is a process where carbon atoms, in a gaseous form, are deposited onto a surface to construct an atom-thin sheet of graphene. This technique transforms a carbon-rich gas or vapor into a solid, highly-ordered film on a target material, known as a substrate. The most widespread and commercially viable of these methods is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
While several "vapor deposition" methods exist, the key insight is that the choice of process and substrate material fundamentally dictates the quality and scale of the graphene produced. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) on a metal substrate has become the standard for creating the large, high-quality, single-layer sheets required for advanced electronics.

The Core Principle: From Vapor to Solid
How Vapor Deposition Works
At its heart, any vapor deposition system involves a controlled environment, typically a vacuum chamber, containing a carbon source and a substrate. A heat source vaporizes the carbon material or breaks down a carbon-containing gas. These free carbon atoms then travel and settle onto the substrate, forming a thin film.
The Critical Role of the Substrate
The substrate is not merely a passive surface; it is an active catalyst in the process. The choice of substrate material, most commonly a metal foil, determines how the graphene layer will form. Metals like copper and nickel are widely used because their atomic structure provides a template for graphene's hexagonal lattice.
The Dominant Method: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
The CVD Process Explained
In a typical CVD process, a hydrocarbon gas like methane or acetylene is introduced into a high-temperature furnace containing the substrate. The intense heat breaks the chemical bonds in the gas, releasing individual carbon atoms that are then free to deposit onto the metal surface.
The Surface Adsorption Mechanism (Copper)
Metals like copper have low carbon solubility. This means carbon atoms do not dissolve into the metal. Instead, they "skate" across the hot surface and self-assemble directly into a hexagonal lattice.
Because the process is self-limiting, it almost exclusively produces a single, continuous layer of graphene. This makes it the preferred method for applications requiring large, uniform, monolayer sheets, such as transparent electrodes and sensors.
The Diffusion & Segregation Mechanism (Nickel)
In contrast, metals like nickel have high carbon solubility. At high temperatures, carbon atoms dissolve into the bulk of the metal, like sugar dissolving in hot water.
As the nickel foil cools, its ability to hold carbon decreases, and the dissolved carbon atoms precipitate or "segregate" back to the surface, where they form graphene. This method can easily produce multiple layers of graphene, which can be an advantage or disadvantage depending on the application.
Understanding the Trade-offs
CVD's Strength: Scalability and Quality
Compared to other methods, CVD is the most promising for industrial-scale production. It is capable of producing large-area graphene films (measured in square meters) with high crystalline quality and relatively low cost.
The Inherent Transfer Challenge
A significant practical hurdle is that graphene grown on a metal substrate must be moved to a functional substrate (like silicon, glass, or plastic) to be useful. This transfer process is delicate, can introduce defects and impurities, and remains a major challenge for mass production.
Controlling Layers and Properties
Achieving perfect control over the number of graphene layers and their rotational alignment (the "twist angle") is difficult. These structural details have a profound impact on the material's final electrical and optical properties, making precise control a key area of ongoing research.
Alternative Vapor Deposition Methods
Arc Vapor Deposition
This is a physical, not chemical, process. It uses a high-current electric arc to vaporize a solid carbon source, such as a graphite rod. The resulting carbon vapor then condenses on a nearby substrate.
While effective for producing graphene flakes or powders, this method offers less control over layer thickness and film uniformity compared to CVD.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding the nuances of each deposition technique is crucial for selecting the right type of graphene for a specific goal.
- If your primary focus is advanced electronics or transparent displays: CVD on copper is the industry standard for producing the necessary large-area, single-layer graphene films.
- If your primary focus is creating bulk composites or conductive inks: Arc vapor deposition or CVD on nickel can be more efficient for producing larger quantities of multi-layer graphene flakes and powders.
- If your primary focus is fundamental materials research: The choice between copper and nickel substrates provides a direct way to study the differing properties of single-layer versus multi-layer graphene.
Mastering the synthesis of graphene through vapor deposition is the foundational step toward unlocking its revolutionary potential across science and technology.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Substrate | Primary Output | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVD on Copper | Copper Foil | Single-layer, uniform films | Electronics, Transparent Electrodes |
| CVD on Nickel | Nickel Foil | Multi-layer graphene | Composites, Conductive Inks |
| Arc Vapor Deposition | Various | Graphene flakes/powders | Bulk Materials, Research |
Ready to integrate high-quality graphene into your research or product development?
KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables essential for advanced materials synthesis, including vapor deposition processes. Our expertise can help you select the right tools to achieve precise control over your graphene's properties, whether you are scaling up for production or pushing the boundaries of fundamental research.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and accelerate your project's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















