In metallurgy, VAR stands for Vacuum Arc Remelting, a secondary melting process used to produce exceptionally clean and high-performance metals and alloys. It is not a primary method for creating metal from ore, but rather a refining step for specialty materials that have already been melted once. The goal of VAR is to remove impurities and create a highly uniform internal structure, which is impossible to achieve with standard melting techniques.
The essential purpose of VAR is not just to remelt metal, but to perfect it. By using an electric arc under a strong vacuum, the process purifies the material and controls its solidification, yielding an alloy with superior strength, purity, and reliability for the most demanding applications.

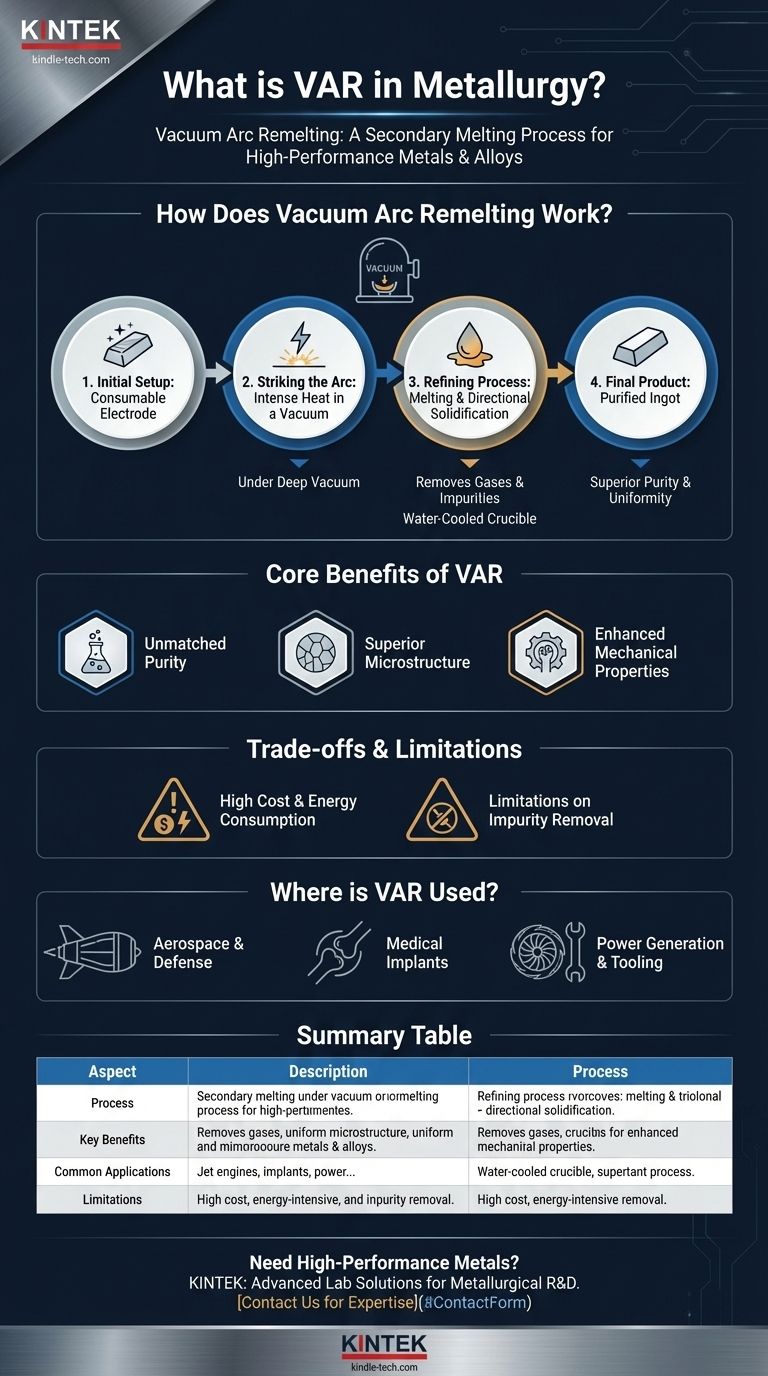
How Does Vacuum Arc Remelting Work?
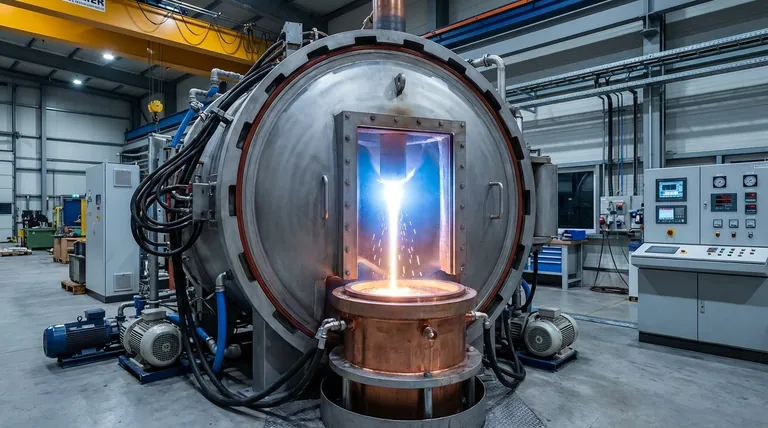
The VAR process is a highly controlled batch operation that transforms a solid metal ingot into a new, significantly improved one. It follows a precise sequence to achieve its refining effects.
The Initial Setup: The Consumable Electrode
First, an ingot of the alloy to be refined is cast using a primary method, often Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM). This initial ingot, known as a consumable electrode, is placed inside a sealed, water-cooled copper crucible.
Striking the Arc: Intense Heat in a Vacuum
The entire chamber is placed under a deep vacuum. An electric arc, similar to a bolt of lightning, is struck between the bottom of the electrode and a small amount of starter material in the crucible. This arc generates intense, localized heat, causing the tip of the electrode to melt.
The Refining Process: Melting and Solidification
As droplets of molten metal fall from the electrode into the crucible, the vacuum environment provides two key benefits. First, it pulls out dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen. Second, it causes low-boiling-point impurities to vaporize and be drawn away.
Simultaneously, the molten metal collects in the water-cooled crucible and begins to solidify directionally, from the bottom up and the outside in. This controlled cooling prevents the chemical segregation and porosity found in conventional castings.
The Final Product: A Purified Ingot
The result is a new, solidified ingot with significantly higher purity, fewer defects, and a dense, uniform grain structure. This ingot is now ready for forging or machining into a final component.
The Core Benefits of the VAR Process
Engineers specify VAR not because it is easy or cheap, but because it delivers specific, critical advantages for high-performance materials like superalloys, titanium alloys, and specialty steels.
Unmatched Purity and Cleanliness
The vacuum environment is extremely effective at removing dissolved gases and volatile metallic impurities. This process also breaks down and reduces the size and number of non-metallic inclusions (oxides, nitrides), which are common points of failure in metals.
Superior Microstructure and Homogeneity
The slow, directional solidification produces an ingot with a highly uniform chemical composition and grain structure. It eliminates the internal voids (porosity) and segregation that can weaken a conventionally cast part.
Enhanced Mechanical Properties
The combination of high purity and a homogeneous microstructure directly translates to superior mechanical performance. VAR-processed materials exhibit significantly improved fatigue life, ductility, and fracture toughness, making them more resistant to cracking and failure under stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While VAR is a powerful tool, it is not a universal solution. Its use involves significant trade-offs that limit it to specific applications.
High Cost and Energy Consumption
VAR is a secondary, energy-intensive process that adds substantial cost to the final material. The equipment is complex, and the cycle times are long, making it economically unfeasible for common metals.
Limitations on Impurity Removal
The process relies on vacuum and high temperatures to vaporize impurities. It is ineffective at removing elements that have a low vapor pressure and do not easily turn into a gas.
Comparison to Electroslag Remelting (ESR)
VAR is often compared to another refining process called Electroslag Remelting (ESR). While VAR excels at removing gases and is essential for reactive metals like titanium, ESR uses a molten slag bath to dissolve certain impurities (like sulfur) more effectively. The choice between them depends on the specific alloy and the type of impurities that need to be removed.
Where is VAR Used?
The unique benefits of VAR make it essential for industries where material failure could have catastrophic consequences.
Aerospace and Defense
This is the largest user of VAR materials. Critical rotating components in jet engines, such as turbine disks and compressor shafts, as well as landing gear and structural airframe parts, rely on the fatigue resistance of VAR alloys.
Medical Implants
The human body is an aggressive environment. VAR-processed titanium and cobalt-chrome alloys are used for joint replacements and dental implants due to their biocompatibility, strength, and excellent corrosion resistance.
Power Generation and Tooling
Components in industrial gas turbines and nuclear power plants operate under extreme stress and temperature, requiring the reliability of VAR superalloys. The process is also used for high-performance tool steels where durability is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Selecting a refining process is a critical decision driven entirely by the performance requirements of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum fatigue life and fracture toughness (e.g., a jet engine disk): VAR is often the non-negotiable standard due to its ability to create an exceptionally clean and uniform microstructure.
- If your primary focus is removing specific sulfur-based inclusions in steel: Electroslag Remelting (ESR) might be a more effective or complementary choice to achieve the desired cleanliness.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose structural components: VAR is almost certainly overkill; conventional casting and forging methods are far more cost-effective for these applications.
Ultimately, choosing VAR is a strategic decision to invest in metallurgical perfection for applications where failure is not an option.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Secondary melting under vacuum using an electric arc to refine pre-melted metals. |
| Key Benefits | Removes gases, reduces impurities, creates uniform microstructure, enhances fatigue life and toughness. |
| Common Applications | Jet engine components, medical implants, power generation turbines, and high-performance tooling. |
| Limitations | High cost, energy-intensive, not suitable for all impurities or general-purpose metals. |
Need High-Performance Metals for Demanding Applications?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for metallurgical research and development. Whether you're refining superalloys for aerospace or developing biocompatible materials for medical implants, our expertise can support your quest for superior material performance.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and help you achieve metallurgical perfection.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is var in metals? A Guide to Vacuum Arc Remelting for Superior Alloys
- What is the process of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Ultimate Purity for High-Performance Alloys
- How does vacuum arc remelting work? Achieve Ultra-Clean, High-Performance Metal Alloys
- What is the overview of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Ultra-Clean, High-Performance Alloys
- What is the benefit of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Structural Integrity



















