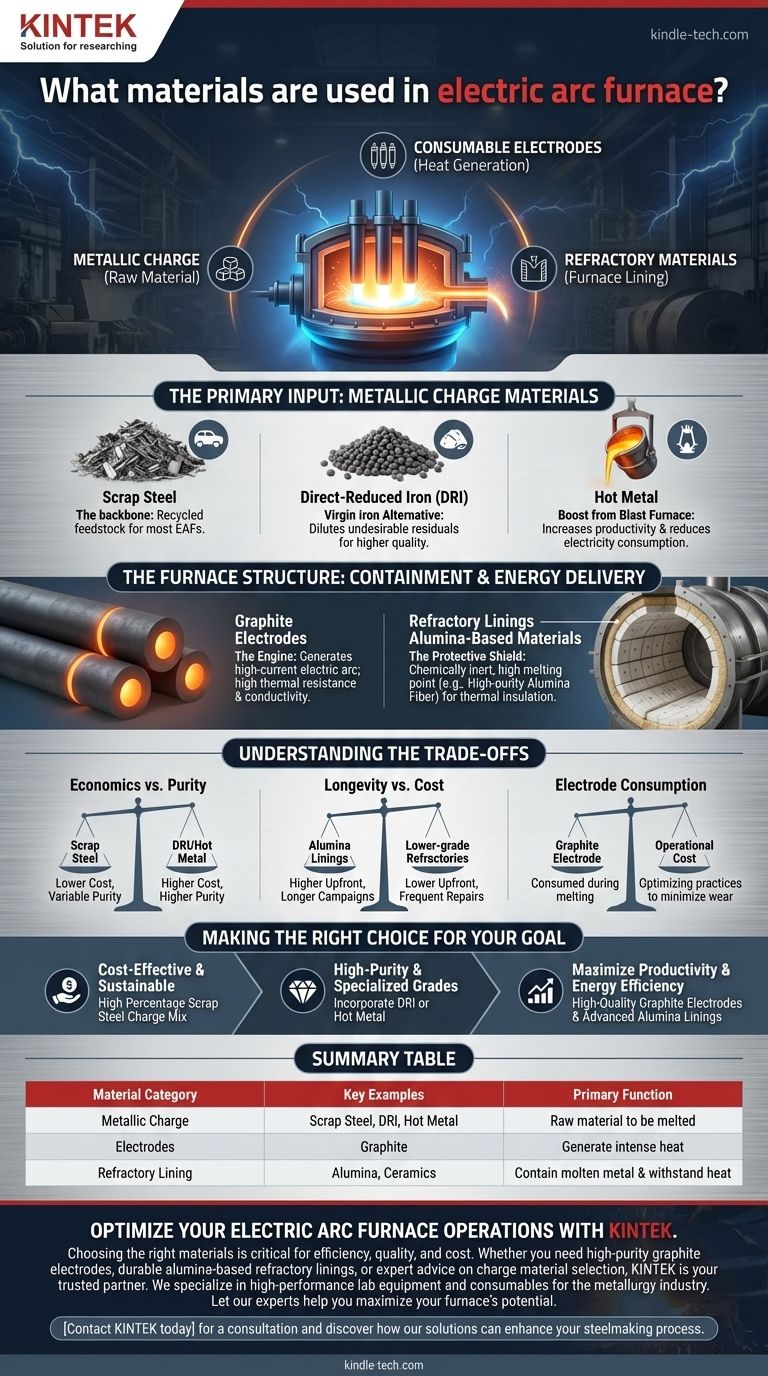
At its core, an electric arc furnace (EAF) operates using three distinct categories of materials: the metallic charge it is designed to melt, the consumable electrodes that generate the intense heat, and the refractory materials that form the furnace lining and contain the process. While scrap steel is the most common metallic charge, the furnace itself relies on graphite electrodes to create the arc and advanced ceramics like alumina to withstand the extreme temperatures.
An electric arc furnace is a system defined by a crucial interplay of materials. Understanding the function of each—from the metallic feedstock being melted to the graphite electrodes and refractory linings containing the energy—is fundamental to grasping the furnace's operational efficiency, output quality, and economic viability.

The Primary Input: Metallic Charge Materials
The charge is the raw metallic input that the furnace melts down to produce liquid steel. The choice of charge material is the single biggest factor influencing the cost, quality, and environmental footprint of the final product.
Scrap Steel: The Backbone of EAF Production
Scrap steel is the primary feedstock for the vast majority of electric arc furnaces. This includes everything from shredded automobiles and old appliances to industrial offcuts from manufacturing processes. Its use is central to the EAF's role in the recycling ecosystem.
Direct-Reduced Iron (DRI): A Virgin Iron Alternative
DRI is a form of virgin iron produced by treating iron ore with reducing gases. It is often used as a supplement to scrap steel to dilute the concentration of undesirable residual elements (like copper or tin) that can be present in scrap, allowing for the production of higher-quality steel grades.
Hot Metal: A Boost from the Blast Furnace
In some integrated steel mills, liquid iron (hot metal) produced in a traditional blast furnace can be charged into the EAF. Using hot metal can significantly increase productivity and reduce electricity consumption, as the iron is already in a molten, high-energy state. The decision to use it is almost always based on economic availability.
The Furnace Structure: Containment and Energy Delivery
Beyond what is melted, the materials used to construct and operate the furnace are critical for performance and safety. These components must endure some of the most extreme industrial conditions.
Graphite Electrodes: The Engine of the Furnace
The heat required for melting is generated by a high-current electric arc. This arc is struck between massive graphite electrodes and the metallic charge. Graphite is used for its unique ability to withstand extreme temperatures while maintaining excellent electrical conductivity, effectively acting as the furnace's heating element.
Refractory Linings: The Protective Shield
The furnace shell is protected from the molten metal and intense heat by a lining of refractory materials. These materials are designed to be chemically inert and have an extremely high melting point, providing thermal insulation and preventing the steel shell from melting.
Alumina-Based Materials: The High-Performance Insulator
Modern furnace linings and insulation often rely on high-purity alumina fiber and aluminum oxide plates. These advanced materials are chosen for their superior performance, including a very high service temperature, excellent thermal shock resistance, and low heat storage, which improves the furnace's energy efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The selection of materials for an EAF is not static; it involves a continuous assessment of competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is key to efficient plant management.
Charge Material Economics vs. Purity
The choice between scrap, DRI, and hot metal is a constant balance. Scrap is often the most cost-effective and sustainable option, but its variable quality can introduce impurities. DRI and hot metal ensure higher purity but typically come at a higher cost and with a different environmental impact.
Refractory Longevity vs. Cost
High-performance alumina linings offer excellent durability and thermal efficiency, leading to longer campaigns and less downtime. However, they come at a higher upfront cost than lower-grade refractories. A plant must balance the investment in premium linings against the operational cost of more frequent repairs and relining procedures.
Electrode Consumption
Graphite electrodes are not permanent; they are consumed during the melting process through sublimation and breakage. This consumption represents a significant operational cost. Optimizing furnace practices to minimize electrode wear is a critical aspect of running a profitable EAF.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational priorities will dictate the ideal material mix for your furnace.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, sustainable steelmaking: You will rely on a charge mix with the highest possible percentage of locally sourced scrap steel.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity or specialized steel grades: You must incorporate a calculated amount of virgin iron, either as DRI or hot metal, to dilute impurities from the scrap.
- If your primary focus is maximizing furnace productivity and energy efficiency: You will invest in high-quality graphite electrodes and advanced alumina-based refractory linings to ensure maximum uptime and minimal heat loss.
Ultimately, mastering the materials science of an EAF is the key to unlocking its full operational and economic potential.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Key Examples | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Metallic Charge | Scrap Steel, DRI, Hot Metal | Raw material to be melted into liquid steel |
| Electrodes | Graphite | Generate intense heat via electric arc |
| Refractory Lining | Alumina, Ceramics | Contain molten metal and withstand extreme heat |
Optimize Your Electric Arc Furnace Operations with KINTEK
Choosing the right materials is critical for the efficiency, output quality, and cost-effectiveness of your EAF. Whether you need to source high-purity graphite electrodes, durable alumina-based refractory linings, or expert advice on charge material selection, KINTEK is your trusted partner.
We specialize in supplying high-performance lab equipment and consumables for the metallurgy industry, helping you achieve superior results. Let our experts help you maximize your furnace's potential.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and discover how our solutions can enhance your steelmaking process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing



















