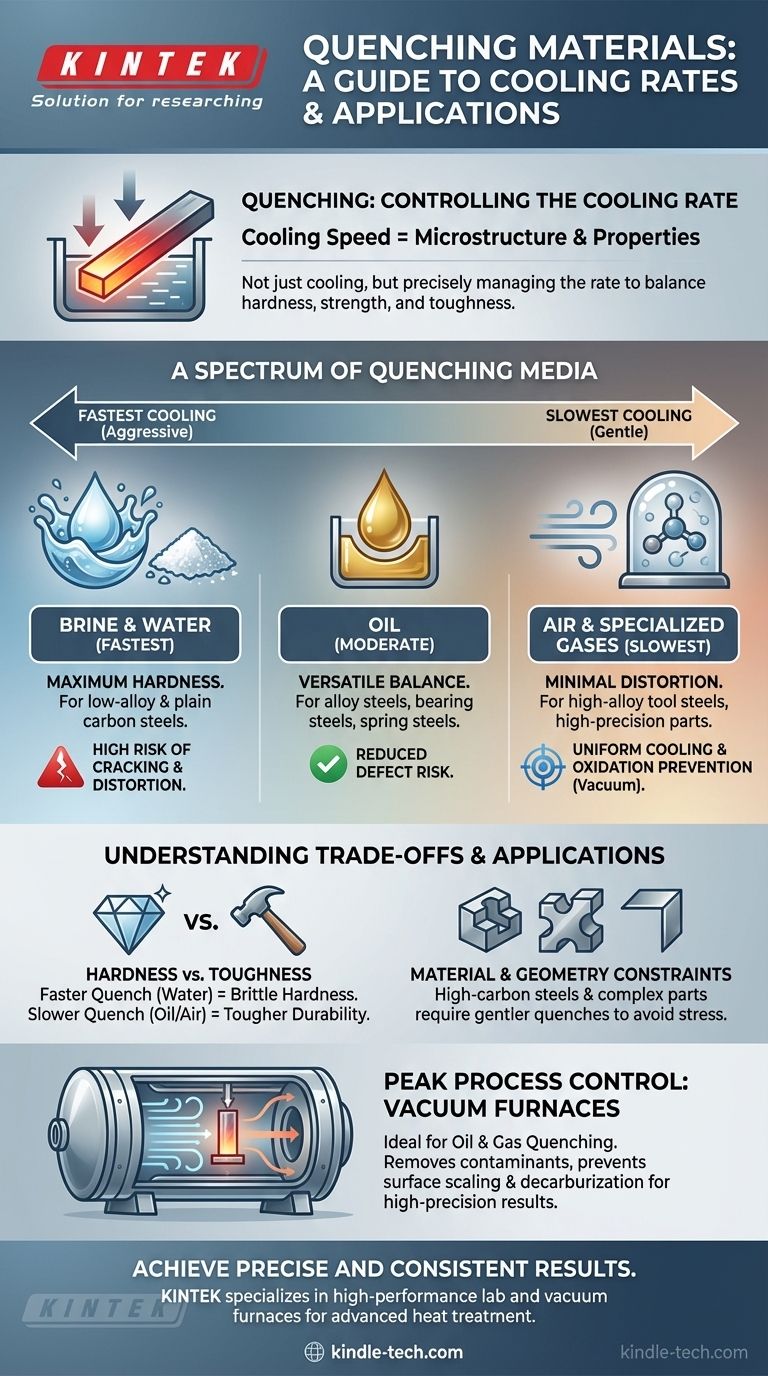
Quenching relies on a range of media, each chosen to control the cooling rate of a heated metal. The most common materials, or quenchants, are water, brine (saltwater), oil, and air. In highly controlled industrial processes, specialized gases or oils are used within a vacuum furnace to achieve very specific results.
The choice of quenching material is a critical engineering decision. It is not about simply cooling the metal, but about precisely managing the rate of cooling to achieve a target balance between hardness, strength, and toughness, while minimizing the risk of cracking or distortion.

The Role of Cooling Rate in Quenching
Why Cooling Speed Matters
Heat treatment fundamentally alters a metal's internal crystal structure, known as its microstructure. The goal of quenching is to "freeze" a desirable, high-strength structure in place by cooling the metal so rapidly that it cannot revert to its softer, more stable state.
The speed of this cooling process is the single most important variable. A faster quench generally produces a harder and more brittle material, while a slower quench results in a softer but more ductile one.
A Spectrum of Quenching Media
Each quenchant offers a different cooling rate, forming a spectrum from the most aggressive to the most gentle. The selection depends on the type of steel and the desired final properties.
Brine and Water: The Fastest Cooling
Brine and water provide the most rapid cooling possible. This aggressive quench is used to achieve maximum hardness in low-alloy and plain carbon steels that require a very fast cooling rate to harden properly.
However, this speed comes at a high risk. The extreme thermal shock can cause significant internal stress, leading to distortion or even cracking, especially in parts with complex geometries or varying thicknesses.
Oil: The Versatile Workhorse
Oil is the most common quenchant for a reason. It cools the metal significantly slower than water, providing a much less severe quench.
This moderation drastically reduces the risk of cracking and distortion. It makes oil the standard choice for many alloy steels, bearing steels, and spring steels that have higher "hardenability"—the ability to harden at slower cooling rates.
Air and Specialized Gases: The Gentlest Quench
For certain high-alloy steels, such as many tool steels and high-speed steels, even oil is too aggressive. These materials are so rich in alloying elements that they can achieve full hardness with a much slower cooling rate.
For these, air quenching (cooling in still or circulated air) is sufficient. In modern precision applications, vacuum gas quenching uses inert gases in a controlled environment to ensure uniform cooling and prevent any surface oxidation, which is critical for components like dies and high-performance tools.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a quenchant is always a balancing act. Understanding the compromises is essential for successful heat treatment.
Hardness vs. Toughness
The primary trade-off is between hardness and toughness. A very fast quench (water) maximizes hardness but creates a brittle microstructure that may need subsequent tempering to restore some toughness. A slower quench (oil or air) may not achieve maximum possible hardness but results in a tougher, more durable final part right out of the quench.
Material and Geometry Constraints
The quenchant must be compatible with the material itself. High-carbon steels are more susceptible to cracking and are rarely quenched in water. Likewise, a part with sharp corners, holes, or drastic changes in thickness is a poor candidate for an aggressive quench, as these features act as stress concentrators.
The Advantage of Vacuum Furnaces
Using a vacuum furnace for either oil or gas quenching represents the peak of process control. By removing atmospheric contaminants, it prevents surface scaling and decarburization. This ensures the component's surface properties are perfectly preserved, which is vital for bearing steels, die steels, and other high-wear applications.
Selecting the Right Quenchant for Your Goal
Your choice depends entirely on the material you are working with and the performance you require from the finished component.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness for simple carbon steels: Brine or water is the most effective choice, but you must accept the high risk of distortion and cracking.
- If your primary focus is a balance of hardness and toughness for most alloy steels: Oil is the standard and most versatile quenchant, offering good hardening with a much lower risk of defects.
- If your primary focus is precision and minimal distortion for high-alloy tool steels: Air or a controlled vacuum gas quench is necessary to safely harden the material without introducing stress.
Ultimately, selecting the right quenchant is a deliberate act of engineering that defines the final performance and reliability of the metal component.
Summary Table:
| Quenching Medium | Cooling Speed | Common Applications | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brine/Water | Fastest | Low-alloy & plain carbon steels | Maximum hardness, but high risk of cracking/distortion |
| Oil | Moderate | Alloy steels, bearing steels, spring steels | Versatile; good balance of hardness and lower defect risk |
| Air/Gas | Slowest | High-alloy steels (tool steels, high-speed steels) | Minimal distortion; ideal for complex, high-precision parts |
Achieve precise and consistent results in your heat treatment processes. The right quenching equipment is critical for controlling cooling rates and achieving the desired material properties in your components. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces, including advanced vacuum furnaces for oil and gas quenching, serving the precise needs of laboratories and material science teams.
Let our experts help you select the ideal system for your application. Contact us today via our contact form to discuss your requirements and ensure your heat treatment delivers maximum hardness, toughness, and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is sintering easier in the presence of a liquid phase? Unlock Faster, Lower-Temperature Densification
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness
- What is vacuum sintering? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Performance for Advanced Materials









