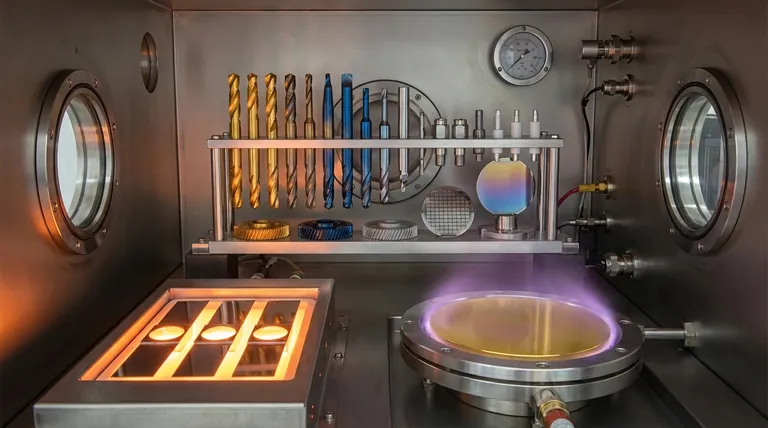
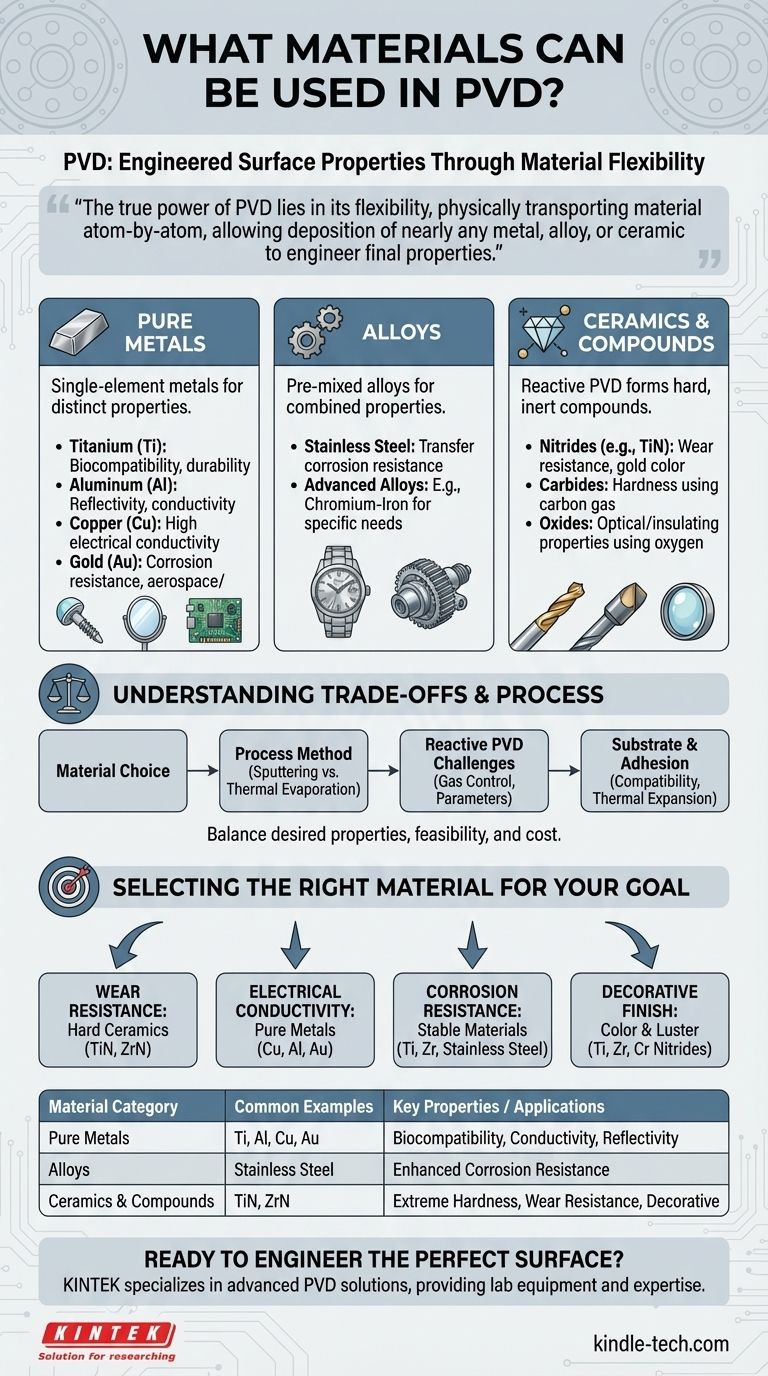
In short, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) can deposit a vast range of inorganic materials, including pure metals, complex alloys, and hard ceramics. The most common materials are metals like titanium, aluminum, and copper, as well as ceramic compounds like titanium nitride used for wear-resistant coatings.
The true power of PVD lies not in a fixed menu of materials, but in its flexibility. It is a process that physically transports material atom-by-atom, allowing you to deposit nearly any metal, alloy, or ceramic compound onto a surface to engineer its final properties.

The Fundamental Material Categories in PVD
PVD processes work by creating a vapor from a solid source material inside a vacuum, which then condenses onto a substrate to form a thin film. This fundamental mechanism allows for an exceptionally wide array of source materials.
Pure Metals
This is the most straightforward category for PVD. Single-element metals are widely used for their distinct properties.
Common examples include titanium (Ti) for its biocompatibility and durability, aluminum (Al) for its reflectivity and conductivity, and copper (Cu) for its high electrical conductivity. Precious metals like gold (Au) are also used, particularly in aerospace and electronics for corrosion resistance and conductivity.
Alloys
PVD is not limited to pure elements; it can also deposit pre-mixed alloys to achieve specific combined properties.
The source material can be an alloy like stainless steel, which is deposited to transfer its corrosion resistance to another material's surface. Advanced experimental alloys, such as those containing chromium and iron, can also be developed and applied using PVD techniques.
Ceramics and Compound Materials
This is where the versatility of PVD truly shines. Extremely hard and inert ceramic compounds can be deposited, though the source material is often a pure metal.
These compounds are typically formed through a process called reactive PVD. In this method, a reactive gas like nitrogen, oxygen, or methane is introduced into the vacuum chamber along with the vaporized metal.
- Nitrides: Introducing nitrogen gas allows for the creation of hard ceramics like Titanium Nitride (TiN), known for its gold color and exceptional wear resistance on cutting tools.
- Carbides: Using a carbon-containing gas can form hard carbides.
- Oxides: Using oxygen creates metal oxides, which are often used for their optical or insulating properties.
Semiconductors and Insulators
While less common than metals and ceramics, PVD can also be used to deposit certain semiconductor and insulating materials. This capability extends the use of PVD into highly specialized microelectronic and optical applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the range of potential PVD materials is vast, practical limitations and process considerations always apply. Choosing a material is a balance of desired properties, process feasibility, and cost.
Material Properties vs. Process Method
The two primary PVD methods, sputtering and thermal evaporation, have different strengths. Materials with extremely high melting points can be difficult or impossible to deposit via thermal evaporation but are well-suited for sputtering. Sputtering is also superior for maintaining the precise composition of an alloy during deposition.
The Challenge of Reactive PVD
Forming compounds like nitrides and oxides requires precise control over gas pressure and process parameters. Poor control can lead to inconsistent film properties or contamination, making it a more complex and demanding process than depositing a pure metal.
Substrate and Adhesion
The choice of coating material is not made in isolation. It must be compatible with the substrate material it is being applied to. Factors like thermal expansion and chemical bonding are critical for ensuring the coating adheres properly and does not fail under stress.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Goal
Your application's primary goal should dictate your material choice. PVD allows you to select a material based on the specific surface property you need to create.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance: Your best choice will be a hard ceramic compound like Titanium Nitride (TiN), Zirconium Nitride (ZrN), or other metal carbides and nitrides.
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity: You should use pure metals known for their high conductivity, such as copper, aluminum, or gold.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance: Target stable, non-reactive materials like titanium, zirconium, stainless steel, or gold.
- If your primary focus is a decorative finish: Materials are chosen for their color and luster, such as titanium, zirconium, and chromium, often deposited as nitrides to produce a range of brilliant colors.
Ultimately, PVD empowers you to treat a material's surface not as a fixed property, but as an engineered feature designed for a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Key Properties / Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Pure Metals | Titanium (Ti), Aluminum (Al), Copper (Cu), Gold (Au) | Biocompatibility, conductivity, reflectivity, corrosion resistance |
| Alloys | Stainless Steel, Chromium-Iron alloys | Combined properties like enhanced corrosion resistance |
| Ceramics & Compounds | Titanium Nitride (TiN), Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) | Extreme hardness, wear resistance, decorative colors |
Ready to engineer the perfect surface properties for your components?
KINTEK specializes in advanced PVD solutions, providing the lab equipment and expertise to deposit the ideal coating—whether you need superior wear resistance, enhanced conductivity, or reliable corrosion protection.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover how our PVD technologies can bring your material designs to life.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Tungsten Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- What are the uses of evaporation in industry? From Food Concentration to High-Tech Thin Films
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- How is deposition time calculated? Mastering the Clock for Strategic Legal Advantage
- How do you calculate coating coverage? A Practical Guide to Accurate Material Estimation



















