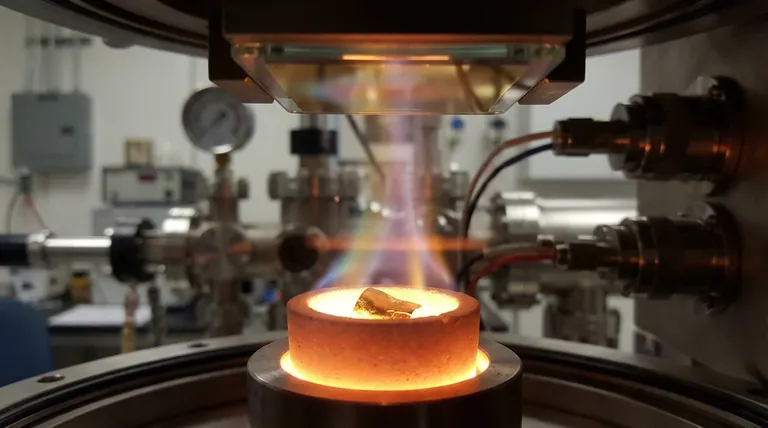
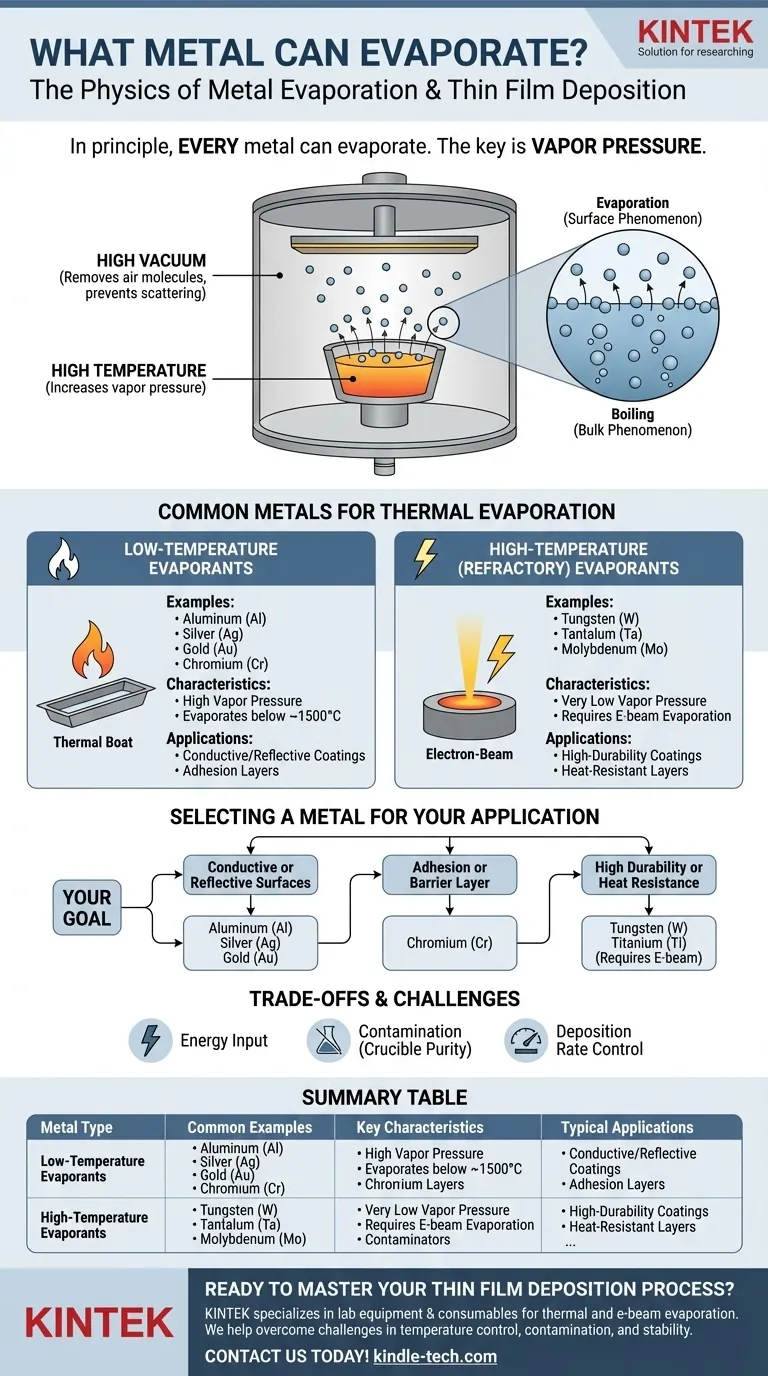
In principle, every metal can evaporate. Evaporation is a physical process that occurs when an element or compound transitions from a liquid or solid phase to a gas phase. For metals, this process is governed by temperature and pressure, with common examples in technical applications including the thermal evaporation of gold (Au), chromium (Cr), and germanium (Ge) to create thin films.
The core issue is not if a metal can evaporate, but how easily it does so. This is determined by the metal's intrinsic vapor pressure—a measure of its tendency to become a gas at a given temperature. Metals with higher vapor pressure are far easier to evaporate.

The Physics of Metal Evaporation
To understand which metals are practical for evaporation, you must first understand the principles that control the process. It is a balance between the material's properties and the environment you create.
What is Vapor Pressure?
Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in equilibrium with its solid or liquid phase. Every material has a vapor pressure, and it increases significantly with temperature.
A metal with a high vapor pressure will evaporate at a much higher rate at a given temperature than a metal with a low vapor pressure. This is the single most important property determining its suitability for evaporation.
The Role of Temperature and Vacuum
To achieve a useful evaporation rate for most metals, you need very high temperatures, often hundreds or thousands of degrees Celsius.
This process is almost always performed in a high-vacuum chamber. The vacuum removes air molecules, which would otherwise collide with the evaporating metal atoms, scattering them and preventing them from reaching their target substrate.
Evaporation vs. Boiling
Evaporation is a surface phenomenon where individual atoms gain enough energy to escape. Boiling is a bulk phenomenon where the vapor pressure equals the surrounding atmospheric pressure, forming bubbles within the material.
In vacuum deposition, the goal is to achieve a controlled rate of evaporation, not to violently boil the source material.
Common Metals Used in Thermal Evaporation
Metals are often categorized by the temperatures required to evaporate them effectively in a vacuum.
Low-Temperature Evaporants
These metals have relatively high vapor pressures, allowing them to be evaporated at manageable temperatures (typically below 1500°C). They are widely used for creating coatings.
Common examples include Aluminum (Al), Silver (Ag), Gold (Au), and Chromium (Cr). Their ease of use makes them staples in electronics and optics.
High-Temperature (Refractory) Evaporants
Refractory metals have extremely low vapor pressures and very high melting points, making them difficult to evaporate with simple thermal methods.
Metals like Tungsten (W), Tantalum (Ta), and Molybdenum (Mo) require specialized techniques, such as electron-beam evaporation, which can achieve the much higher localized temperatures needed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simply choosing a metal is not enough; you must understand the practical challenges and limitations of the evaporation process.
The Challenge of Refractory Metals
Evaporating a metal like Tungsten requires immense energy input. The equipment is more complex and expensive, as it must be able to generate and withstand extreme temperatures without contaminating the process.
Source Purity and Contamination
The material of the crucible or "boat" holding the metal can also be a source of contamination. At high temperatures, the boat material itself can evaporate or react with the molten metal, introducing impurities into your final thin film.
Deposition Rate and Control
A metal's evaporation rate can change dramatically with small fluctuations in temperature. Maintaining a stable, repeatable deposition process requires highly precise temperature control, which is easier for low-temperature materials than for refractory metals.
Selecting a Metal for Your Application
Your choice of metal should be driven entirely by the goal of the thin film you are creating.
- If your primary focus is creating conductive or reflective surfaces: Metals like Aluminum (Al), Silver (Ag), and Gold (Au) are excellent choices due to their high conductivity/reflectivity and relatively easy evaporation.
- If your primary focus is an adhesion or barrier layer: Chromium (Cr) is a standard choice as it adheres well to many substrates like glass, making it a great intermediate layer for subsequent depositions.
- If your primary focus requires high durability or heat resistance: You will need to use a refractory metal like Tungsten (W) or Titanium (Ti), but be prepared for a more complex and energy-intensive e-beam evaporation process.
Ultimately, understanding a metal's vapor pressure is the key to mastering its evaporation for any technical application.
Summary Table:
| Metal Type | Common Examples | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Temperature Evaporants | Aluminum (Al), Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), Chromium (Cr) | High vapor pressure, evaporates below ~1500°C | Conductive coatings, reflective surfaces, adhesion layers |
| High-Temperature (Refractory) Evaporants | Tungsten (W), Tantalum (Ta), Molybdenum (Mo) | Very low vapor pressure, requires e-beam evaporation | High-durability coatings, heat-resistant layers |
Ready to Master Your Thin Film Deposition Process?
Choosing the right metal and evaporation technique is critical for achieving high-quality, consistent results. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for thermal and e-beam evaporation, providing the precise tools and expert support you need.
We help our customers in R&D and manufacturing overcome challenges like temperature control, contamination, and deposition rate stability. Contact us today to discuss your specific application and let our experts guide you to the optimal solution for your laboratory's needs.
Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs



















