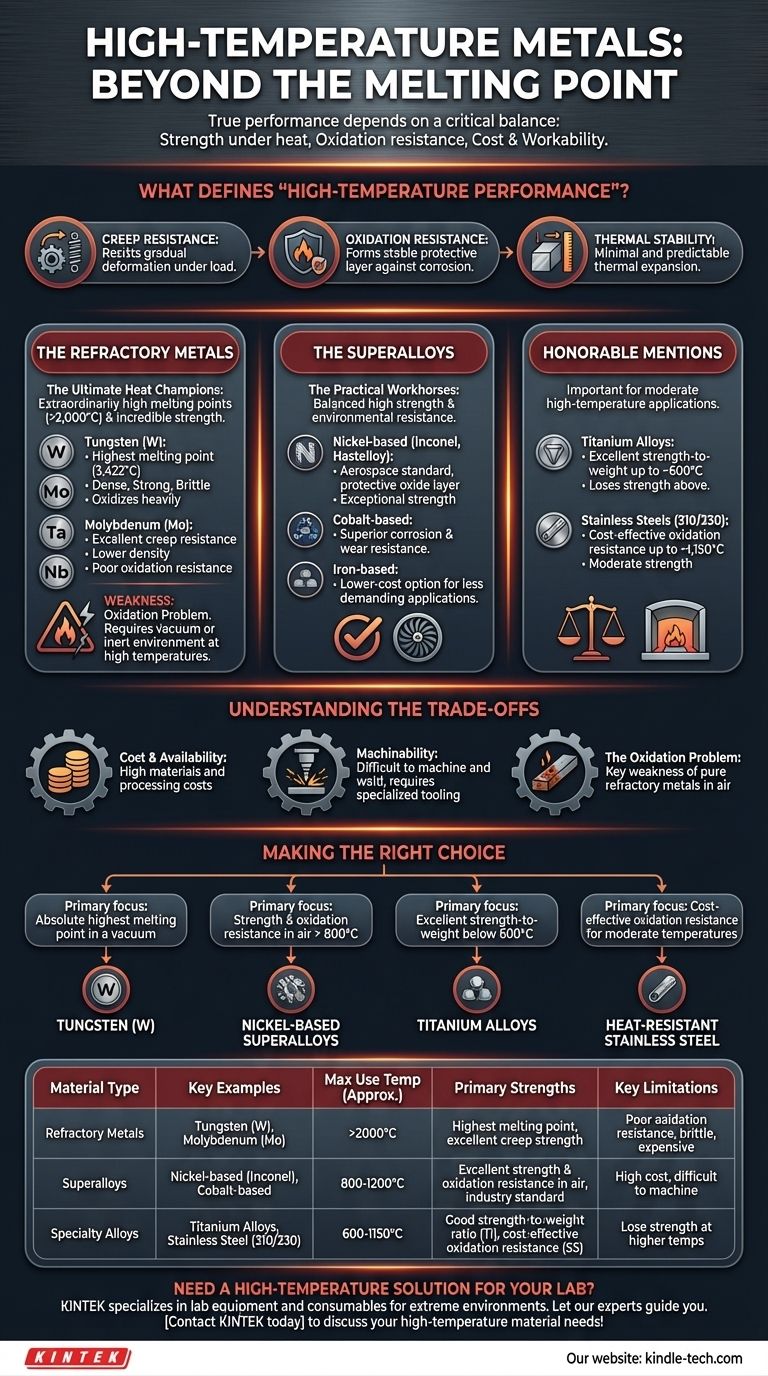
For withstanding high temperatures, the primary candidates are a group known as refractory metals and specialized superalloys. Metals like Tungsten (W) have the highest melting point of all metals at 3,422°C (6,192°F), making it a champion of pure heat resistance. However, for practical applications in oxidizing environments like a jet engine, nickel-based superalloys such as Inconel are often superior due to their combined strength and corrosion resistance at extreme temperatures.
The best "high-temperature" metal is rarely the one with the highest melting point. True performance depends on a critical balance between a material's strength under heat (creep resistance), its ability to resist oxidation, and its overall cost and workability for the specific application.

What Defines "High-Temperature Performance"?
Simply looking at a melting point chart is misleading. A metal's utility at high temperatures is a multi-faceted engineering problem. Two materials with similar melting points can have drastically different performance in a real-world environment.
Beyond Melting Point: Strength Under Heat
A metal begins to lose its structural integrity and stiffness long before it melts. This gradual deformation under a constant load at elevated temperatures is known as creep.
Excellent high-temperature materials must resist creep to maintain their shape and strength when hot. This is a critical factor in applications like turbine blades or furnace components.
The Critical Role of Oxidation Resistance
Most practical high-temperature environments involve oxygen. At high heat, many metals will rapidly corrode or oxidize, effectively burning away and losing mass.
The best materials, like superalloys, form a stable, passive oxide layer on their surface. This layer acts as a barrier, protecting the underlying metal from further attack and degradation.
Thermal Expansion and Stability
All materials expand when heated. A material with a high coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) will change size dramatically, which can cause stress and failure in assembled parts.
Predictable and minimal thermal expansion is a desirable property for components that must maintain tight tolerances across a wide temperature range.
A Closer Look at High-Temperature Metals
Engineers classify high-temperature metals into several key groups, each with a distinct profile of strengths and weaknesses.
The Refractory Metals: The Ultimate Heat Champions
Refractory metals are defined by their extraordinarily high melting points (above 2,000°C or 3,632°F) and incredible strength at temperature.
- Tungsten (W): Has the highest melting point of any metal. It is extremely dense and strong but is brittle at room temperature and oxidizes heavily in air at high temperatures.
- Molybdenum (Mo): Easier to work with and less dense than tungsten, it still offers superb creep resistance. Like tungsten, it has very poor oxidation resistance.
- Tantalum (Ta): Very ductile and corrosion-resistant (at lower temperatures), but still requires protection from oxidation at the highest temperatures.
- Niobium (Nb): The least dense of the refractory metals, making it useful in aerospace. It is often alloyed to create superalloys.
The Superalloys: The Practical Workhorses
Superalloys are the go-to choice for demanding applications that require both high strength and environmental resistance. Their performance comes from complex alloying and a specialized crystalline structure.
- Nickel-based Superalloys (e.g., Inconel, Hastelloy): The most common type. They are the backbone of the aerospace industry, used for turbine blades and exhaust systems due to their exceptional ability to form a protective oxide layer while retaining strength.
- Cobalt-based Superalloys: Offer superior corrosion and wear resistance at temperature compared to some nickel alloys, but are generally more expensive.
- Iron-based Superalloys: Essentially an evolution of stainless steel, they provide a lower-cost superalloy option for less demanding applications where the performance of nickel or cobalt alloys is not required.
Honorable Mentions: Titanium and Stainless Steel
While not in the same class as refractory metals or superalloys, these common materials have important high-temperature applications.
- Titanium Alloys: Are exceptionally strong for their weight up to about 600°C (1,100°F). Above this temperature, they begin to lose strength and suffer from oxidation.
- Stainless Steels: Certain grades, like 310 or 330, are designed for moderate high-temperature service (up to ~1,150°C or 2,100°F) where high strength is not the primary concern. They are a cost-effective choice for furnace liners, heat exchangers, and exhaust components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a high-temperature metal is always an exercise in managing compromises. The ideal material rarely exists.
Cost and Availability
Refractory metals and superalloys are orders of magnitude more expensive than conventional metals like steel or aluminum. The raw materials are rare, and the processes to refine and alloy them are complex and energy-intensive.
Machinability and Fabrication
These materials are notoriously difficult to machine and weld. They are tough, work-harden quickly, and require specialized tools, coolants, and slower processing speeds, which significantly increases manufacturing costs.
The Oxidation Problem
This is the key weakness of pure refractory metals. Despite their incredible melting points, metals like tungsten and molybdenum will be destroyed by oxidation in open air at high temperatures. They are therefore limited to applications in a vacuum or an inert (non-reactive) gas environment unless they have a protective coating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection must be guided by your primary goal and operating environment.
- If your primary focus is the absolute highest melting point in a vacuum: Tungsten is the undisputed choice, but you must design around its brittleness and extreme density.
- If your primary focus is strength and oxidation resistance in air above 800°C (1,500°F): Nickel-based superalloys like the Inconel family are the proven industry standard.
- If your primary focus is excellent strength-to-weight ratio below 600°C (1,100°F): Titanium alloys provide performance that lighter metals cannot match.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective oxidation resistance for moderate temperatures: Heat-resistant grades of stainless steel are your most practical starting point.
Ultimately, selecting the right material is a process of matching the unique properties of the metal to the specific demands of your environment and budget.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Examples | Max Use Temp (Approx.) | Primary Strengths | Key Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refractory Metals | Tungsten (W), Molybdenum (Mo) | >2000°C | Highest melting point, excellent creep strength | Poor oxidation resistance, brittle, expensive |
| Superalloys | Nickel-based (Inconel), Cobalt-based | 800-1200°C | Excellent strength & oxidation resistance in air, industry standard | High cost, difficult to machine |
| Specialty Alloys | Titanium Alloys, Stainless Steel (310/330) | 600-1150°C | Good strength-to-weight ratio (Ti), cost-effective oxidation resistance (SS) | Lose strength at higher temps |
Need a High-Temperature Solution for Your Lab?
Selecting the right metal is critical for the performance and safety of your high-temperature processes, whether for furnace components, reactors, or specialized tooling.
KINTEK specializes in providing lab equipment and consumables designed for extreme environments. We can help you source or design with the optimal high-temperature materials for your specific application, balancing performance, durability, and budget.
Let our experts guide you to the right solution. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your high-temperature material needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Quality Alumina Ceramic Screw for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics with High Temperature Resistance and Insulation
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to use high-temperature and corrosion-resistant ceramics for H2SO4 decomposers in the IS process?
- Why is an alumina insulation disk required in a CCPD reactor? Enhance Coating Quality with Floating Potential
- What is the maximum operating temperature of alumina? The Critical Role of Purity and Form
- What are the functional advantages of using high-purity alumina crucibles? Achieve Precise Oxidation Data
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process



















