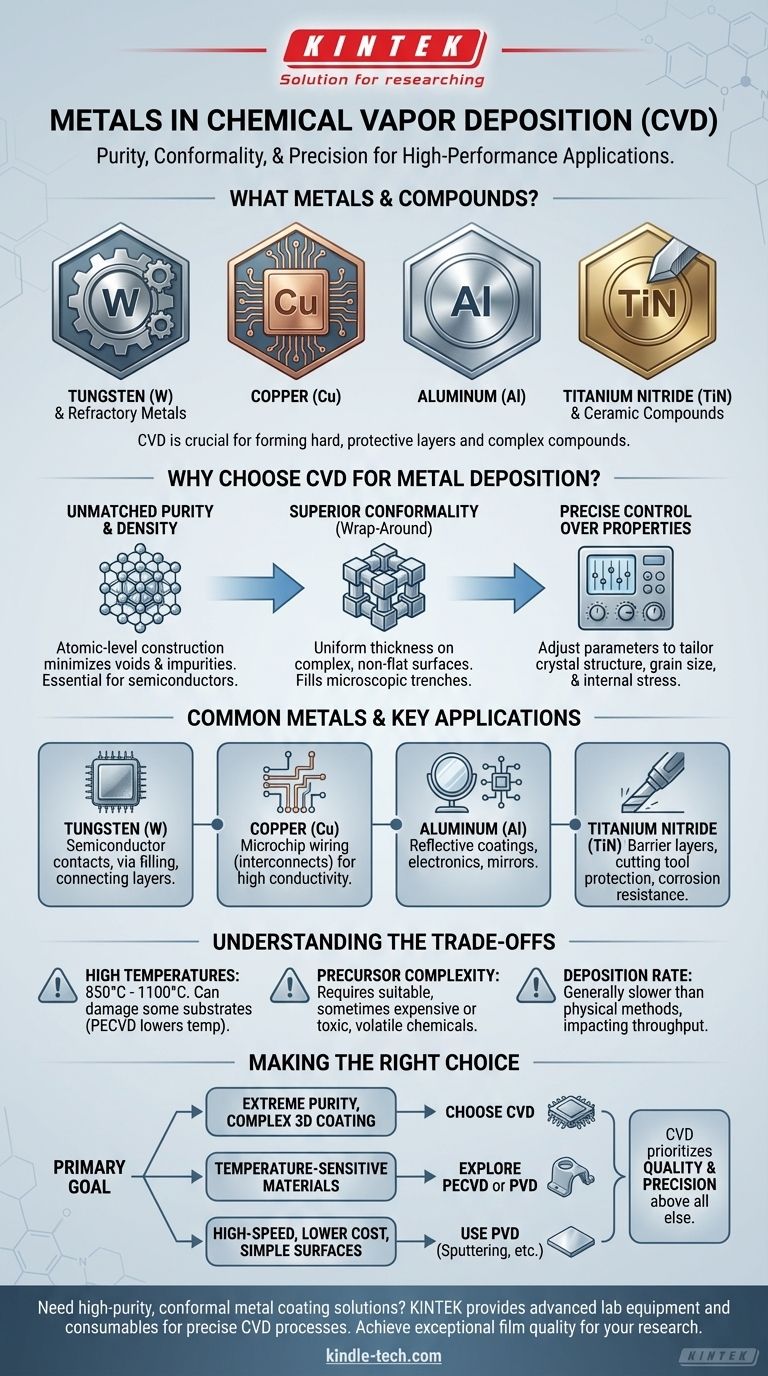
To be direct, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is capable of depositing a wide variety of metals, most notably refractory metals like Tungsten (W) and Molybdenum (Mo), as well as others such as Aluminum (Al), Copper (Cu), and Titanium (Ti). It is also extensively used to create metal-based compounds like Titanium Nitride (TiN), which form hard, protective ceramic layers.
The crucial insight is not just which metals can be deposited, but why CVD is chosen. CVD's unique strength lies in its ability to create exceptionally pure, dense, and perfectly conforming films on complex 3D surfaces, making it essential for high-performance applications where material quality is paramount.

Why Choose CVD for Metal Deposition?
While other methods exist to deposit metals, CVD is selected when the specific properties of the final film are more critical than deposition speed or cost. The process's chemical nature provides a level of control that physical methods often cannot match.
Unmatched Purity and Density
The CVD process builds a film atom by atom from chemical precursors. This results in coatings with extremely high purity and excellent denseness.
This atomic-level construction minimizes voids and impurities, which is critical for applications like semiconductor manufacturing, where such defects could cause device failure.
Superior Conformality (Wrap-Around)
CVD excels at coating complex, non-flat surfaces uniformly. Because the precursor gases can reach every part of a component, the resulting film has a consistent thickness everywhere.
This "wrap-around" capability is essential for filling microscopic trenches and holes in integrated circuits, ensuring complete and reliable electrical connections.
Precise Control Over Film Properties
By carefully adjusting deposition parameters like temperature, pressure, and gas flow rates, engineers can precisely control the final film's characteristics.
This includes its crystal structure, grain size, and even internal stress, allowing the metal layer to be tailored for specific mechanical or electrical performance requirements.
Common Metals and Compounds in CVD
The choice of metal is often dictated by the application and the availability of a suitable volatile precursor chemical—a gas that contains the metal to be deposited.
Tungsten (W)
Tungsten is a workhorse in the semiconductor industry. It is used to create robust electrical contacts and to fill tiny vertical channels (vias) that connect different layers of an integrated circuit.
Copper (Cu)
Copper is the primary material for the wiring (interconnects) on modern microchips due to its high conductivity. Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) or related techniques are often used to deposit copper at lower temperatures.
Aluminum (Al)
While largely replaced by copper in advanced microchips, aluminum is still used in other electronic applications and for creating highly reflective coatings on surfaces like mirrors.
Titanium Nitride (TiN)
Although a ceramic compound, TiN is a vital material deposited by CVD. It forms an extremely hard, corrosion-resistant, and conductive barrier layer used in both microelectronics and as a protective coating on cutting tools.
Understanding the Trade-offs
CVD is a powerful technique, but it is not the solution for every metal-coating challenge. Its limitations are important to understand.
The High-Temperature Challenge
Traditional thermal CVD processes operate at very high temperatures, often between 850°C and 1100°C.
This heat can damage or warp many substrate materials, limiting its use to components that can withstand such extreme conditions. However, techniques like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) can significantly lower this temperature.
Precursor Chemistry Complexity
The entire process depends on having a suitable precursor gas for the desired metal. For some metals, these chemicals can be expensive, highly toxic, or difficult to handle safely, adding complexity and cost to the operation.
Deposition Rate
Compared to physical methods like sputtering, CVD can be a slower process. This can impact manufacturing throughput for applications where a thick coating is needed quickly on a simple surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method depends entirely on your project's specific priorities.
- If your primary focus is extreme purity and coating complex 3D features (like in microchips): CVD is often the superior choice due to its chemical nature and unmatched conformal deposition.
- If your primary focus is depositing on temperature-sensitive materials (like plastics or certain alloys): Traditional CVD is unsuitable; you should explore low-temperature PECVD or a physical vapor deposition (PVD) method like sputtering.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, lower-cost coating on simple surfaces: Physical methods like sputtering or thermal evaporation are typically more practical and economical than CVD.
Ultimately, choosing CVD for metal deposition is a decision to prioritize the quality and precision of the final film above all other factors.
Summary Table:
| Common CVD Metals & Compounds | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Tungsten (W) | Semiconductor contacts, via filling |
| Copper (Cu) | Microchip interconnects |
| Aluminum (Al) | Reflective coatings, electronics |
| Titanium Nitride (TiN) | Protective barrier layers, cutting tools |
Need a high-purity, conformal metal coating for your lab's most demanding applications? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise Chemical Vapor Deposition processes. Our solutions help you achieve the exceptional film quality, density, and wrap-around coverage essential for semiconductor manufacturing and high-performance materials research. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is the temperature of PECVD deposition? Achieve High-Quality Films at Low Temperatures
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating



















