Virtually any metal can be deposited using vacuum deposition, though the specific method and ease of application vary. Common metals like aluminum, gold, silver, and copper are frequently used for their reflective or conductive properties. The technology also extends to more challenging reactive and refractory metals, including titanium, zirconium, and tantalum, which are valued for their durability and high melting points.
The essential question is not simply which metals can be deposited, but what final properties you need to achieve. Vacuum deposition is a versatile platform capable of depositing not just pure metals, but also precise alloys and engineered ceramic compounds like nitrides and oxides, created directly within the chamber.

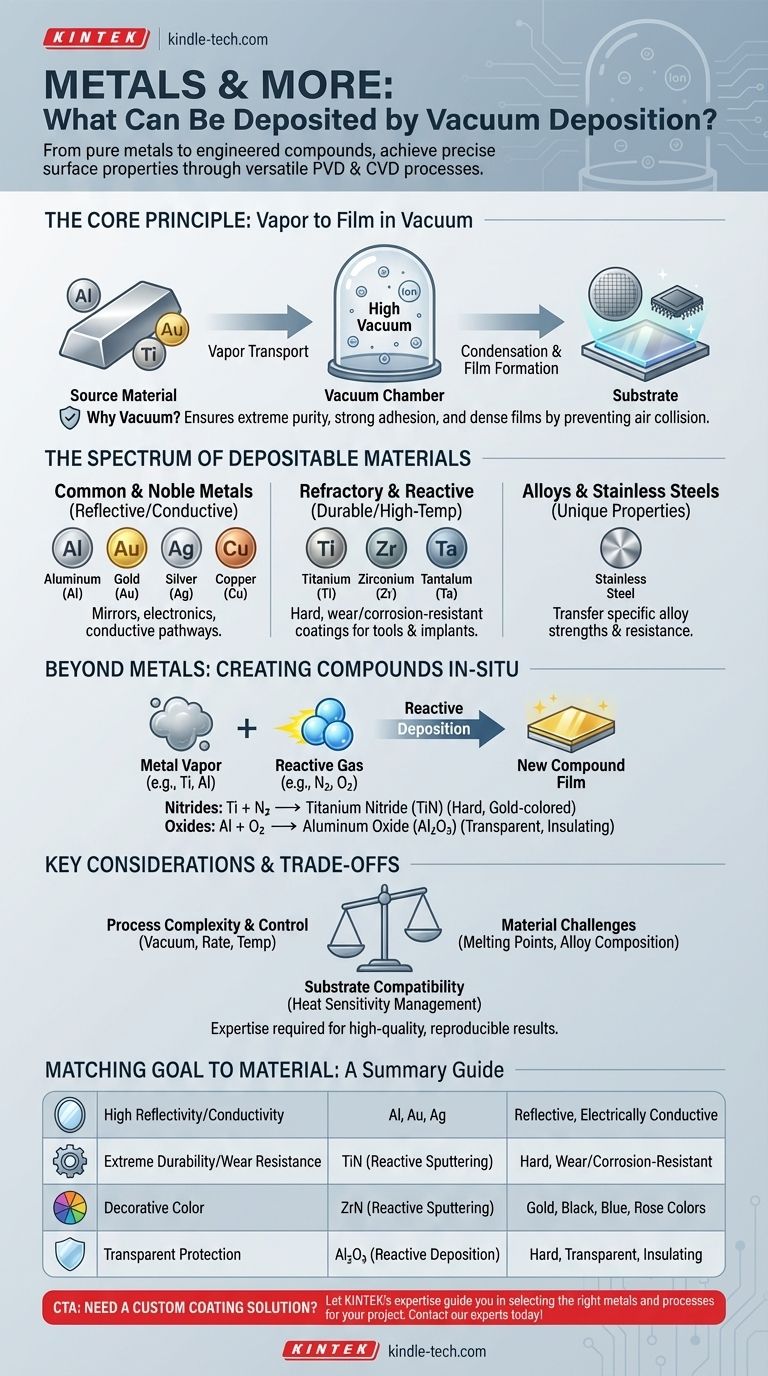
How Vacuum Deposition Enables Material Versatility
Vacuum deposition is not a single process, but a family of techniques—most commonly Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Understanding the core principle explains why it works for so many materials.
The Fundamental Principle
At its core, vacuum deposition involves turning a solid source material into a vapor, transporting it through a vacuum, and condensing it onto a target surface (the substrate) as a thin film. This is typically achieved through heating and evaporation or by bombarding the source with ions (a process called sputtering).
Why the Vacuum is Critical
The process must occur in a high vacuum to prevent the vaporized metal atoms from colliding with air particles. This ensures the coating is extremely pure and adheres strongly to the substrate, creating a dense, high-quality film.
The Spectrum of Depositable Materials
The true power of vacuum deposition lies in the breadth of materials that can be used and even created during the process.
Common and Noble Metals
For applications requiring high reflectivity or electrical conductivity, common metals are the go-to choice.
- Aluminum (Al): The most common for creating reflective surfaces, like in mirrors and food packaging.
- Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), Copper (Cu): Used in electronics for conductive pathways and contacts, as well as for decorative and corrosion-resistant coatings.
Refractory and Reactive Metals
These materials are known for their hardness and high melting points, making them ideal for protective coatings.
- Titanium (Ti), Zirconium (Zr), Tantalum (Ta): These are deposited to create hard, wear-resistant, and corrosion-resistant surfaces on tools, medical implants, and aerospace components.
Alloys and Stainless Steels
It is also possible to deposit from a source material that is already an alloy, such as stainless steel or a cemented carbide. This allows the unique properties of the alloy—like its specific strength or corrosion resistance—to be transferred as a thin film onto another material.
Beyond Pure Metals: Creating Compounds In-Situ
This is where the technology becomes truly transformative. By introducing a controlled amount of a reactive gas into the vacuum chamber during deposition, you can form new compounds on the substrate surface.
- Nitrides: Introducing nitrogen gas while sputtering titanium creates Titanium Nitride (TiN), a famously hard, gold-colored ceramic coating used on cutting tools and for decorative finishes.
- Oxides: Introducing oxygen gas can create materials like Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃), a transparent, hard, and electrically insulating layer.
- Carbides: Introducing a carbon-containing gas like acetylene can form extremely hard metal carbides.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, vacuum deposition is a complex industrial process with important considerations.
Process Complexity and Control
Achieving a high-quality, reproducible coating requires precise control over the entire system. Factors like vacuum level, deposition rate, substrate temperature, and chamber cleanliness are critical and demand significant expertise to manage.
Material-Specific Challenges
Not all metals behave the same way. Refractory metals with very high melting points are difficult to evaporate thermally and are better suited for sputtering. When depositing alloys, components can sometimes evaporate at different rates, requiring careful process tuning to ensure the final film has the correct composition.
Substrate Compatibility
The process generates heat, which can be a problem for heat-sensitive substrates like plastics or textiles. While techniques like magnetron sputtering are considered "cool" processes, managing thermal load is a key part of successful deposition on delicate materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The ideal material and process are dictated entirely by your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high reflectivity or conductivity: Use pure noble or common metals like aluminum, silver, or gold via thermal evaporation or sputtering.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and wear resistance: Choose a refractory metal like titanium and use reactive sputtering to form a hard nitride (TiN) or carbide (TiC) coating.
- If your primary focus is a specific decorative color: Explore reactive deposition with metals like titanium or zirconium, which can produce a range of colors (gold, black, blue, rose) depending on the process parameters.
- If your primary focus is a transparent protective layer: Use reactive deposition with a metal like aluminum or silicon to create a clear oxide coating.
By matching the material capabilities to your performance requirements, you can effectively use vacuum deposition to engineer surfaces with precisely tailored properties.
Summary Table:
| Application Goal | Recommended Material/Process | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| High Reflectivity/Conductivity | Aluminum, Gold, Silver (Thermal Evaporation/Sputtering) | Reflective, Electrically Conductive |
| Extreme Durability/Wear Resistance | Titanium Nitride (Reactive Sputtering) | Hard, Wear-Resistant, Corrosion-Resistant |
| Decorative Color | Zirconium Nitride (Reactive Sputtering) | Gold, Black, Blue, Rose Colors |
| Transparent Protection | Aluminum Oxide (Reactive Deposition) | Hard, Transparent, Electrically Insulating |
Need a custom coating solution? Let KINTEK's expertise guide you. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables for vacuum deposition, helping you select the right metals and processes to achieve the precise surface properties—whether for reflectivity, durability, or decoration—that your project demands. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and explore how our solutions can enhance your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















