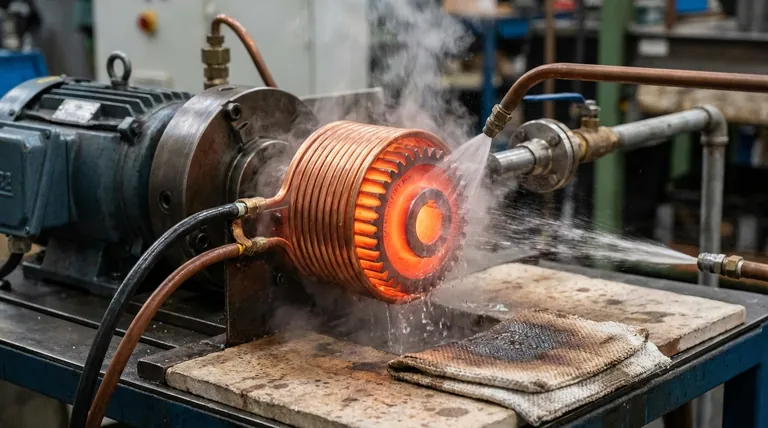
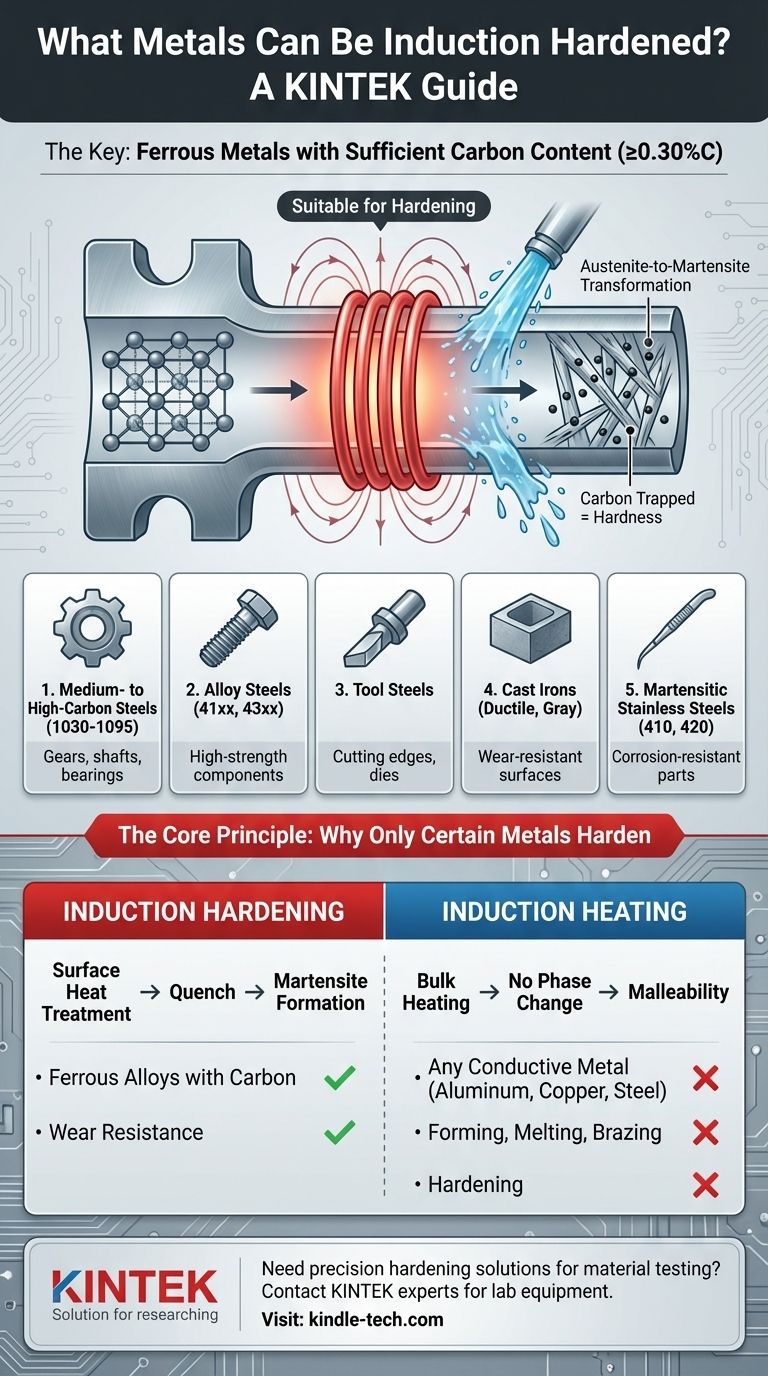
The primary candidates for induction hardening are ferrous metals with sufficient carbon content. This includes a wide range of carbon steels, alloy steels, tool steels, and certain types of cast iron. The process fundamentally relies on a specific metallurgical transformation that does not occur in non-ferrous metals like aluminum, copper, or brass, even though those metals can be heated by induction for other purposes.
Induction hardening is not determined by a metal's ability to be heated by induction, but by its internal crystal structure's ability to change when heated and rapidly cooled. This is why the process is exclusive to iron-based alloys with adequate carbon.

The Core Principle: Why Only Certain Metals Harden
Induction hardening is a two-step process: extremely fast heating followed by immediate quenching (cooling). The success of this process is entirely dependent on the metallurgy of the material being treated.
The Role of Carbon and Phase Transformation
For steels and cast irons, the heating stage does more than just make the metal hot. As the material passes a critical temperature (the austenitizing temperature, typically between 750-900°C), its crystal structure transforms into a state called austenite.
In the austenite phase, the iron lattice can dissolve a significant amount of carbon. The induction process is highly effective because it generates this heat rapidly and precisely within the material itself.
The Quench: Locking in Hardness
Immediately following the heating cycle, the material is rapidly cooled by a water, oil, or polymer-based quench. This rapid cooling does not give the carbon atoms time to move out of the iron crystal lattice as they normally would during slow cooling.
This "trapping" of carbon atoms forces the iron crystals into a new, highly strained, and very hard structure known as martensite. It is the formation of martensite that constitutes the hardening of the metal.
Why Non-Ferrous Metals Don't Work
Metals like aluminum, copper, and their alloys do not undergo this austenite-to-martensite phase transformation.
While you can easily heat them with induction, their crystal structure does not change in a way that allows for this type of hardening. Quenching them does not produce a martensitic structure, and therefore does not significantly increase their hardness.
A Practical Guide to Suitable Materials
The key requirement for any candidate material is a carbon content high enough to form a hard martensitic structure, typically 0.30% or higher.
Medium- to High-Carbon Steels
This is the most common category for induction hardening. Plain carbon steels from 1030 to 1095, as well as numerous alloy steels (like the 41xx, 43xx, and 52xxx series), are excellent candidates. These are used for gears, shafts, bearings, and tools where a hard, wear-resistant surface is needed.
Cast Irons
Certain cast irons, such as ductile iron and gray iron, can be successfully induction hardened. The process transforms the pearlitic matrix of the iron into martensite, creating a hard surface layer that dramatically improves wear resistance.
Tool Steels
Many tool steels, including hot-worked and cold-worked varieties, are designed for hardening and respond very well to the precision of induction. The process can be localized to the cutting edges or working surfaces of a tool.
Martensitic Stainless Steels
Only certain families of stainless steel can be hardened. Martensitic grades (like 410, 420, and 440) have the necessary carbon content and crystal structure to allow for hardening. In contrast, the more common austenitic (304, 316) and ferritic grades cannot be hardened by heat treatment.
Understanding the Critical Distinction: Heating vs. Hardening
A common point of confusion is the difference between induction heating and induction hardening. They use the same physical principle but have completely different goals and material requirements.
Induction Hardening: A Surface Treatment
The goal of induction hardening is to modify the metallurgical properties of a material, almost always on its surface. It creates a hard, wear-resistant "case" while leaving the inner "core" of the component tough and ductile. This is a heat treatment process.
Induction Melting or Forging: A Bulk Process
For applications like melting, brazing, or forging, induction is simply used as a clean and efficient heat source. The goal is to get the entire workpiece hot enough to become liquid or malleable.
Any electrically conductive metal—including steel, aluminum, copper, brass, gold, and silver—can be heated by induction for these purposes. The ability to be heated does not mean the ability to be hardened.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if induction hardening is the correct process, you must first consider your material and your engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is increasing wear resistance on a component: You must use a ferrous alloy with sufficient carbon, such as medium-carbon steel, an alloy steel, or a martensitic stainless steel.
- If your primary focus is simply heating a metal for forming or casting: You can use induction for a wide range of conductive metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper, but understand this is not a hardening process.
- If you are working with a low-carbon steel (e.g., 1018): Standard induction hardening will be ineffective. Consider alternative case-hardening processes like carburizing, which adds carbon to the surface before the hardening step.
Understanding the metallurgical requirements is the key to successfully applying induction technology.
Summary Table:
| Suitable Metals for Induction Hardening | Key Requirement (Carbon Content) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Medium- to High-Carbon Steels (e.g., 1030-1095) | ≥ 0.30% | Gears, shafts, bearings |
| Alloy Steels (e.g., 41xx, 43xx series) | ≥ 0.30% | High-strength components |
| Tool Steels | Varies, but designed for hardening | Cutting tools, dies |
| Cast Irons (Ductile, Gray) | Sufficient carbon in matrix | Wear-resistant surfaces |
| Martensitic Stainless Steels (e.g., 410, 420) | ≥ 0.15% | Corrosion-resistant hardened parts |
Need precision hardening for your components? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for material testing and heat treatment processes. Whether you're developing new alloys or ensuring quality control, our solutions help you achieve consistent, reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in metallurgy and materials science.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of high frequency heating? Achieve Unmatched Speed and Precision
- How many times can metal be melted down and used again? The Key to Infinite Recyclability
- How does an induction furnace work? A Guide to Efficient, Contactless Metal Melting
- Why do we use induction furnace? For Clean, Precise, and Efficient Metal Melting
- What are the disadvantages of core type induction furnace? Key Limitations in Flexibility and Refining
- What are the cons of induction heating? High Cost, Material Limits, and Operational Complexity
- What is the power factor of a core type induction furnace? Discover High Efficiency for Your Lab
- Can gold be induction heated? Yes, and it's the superior method for high-purity melting.



















