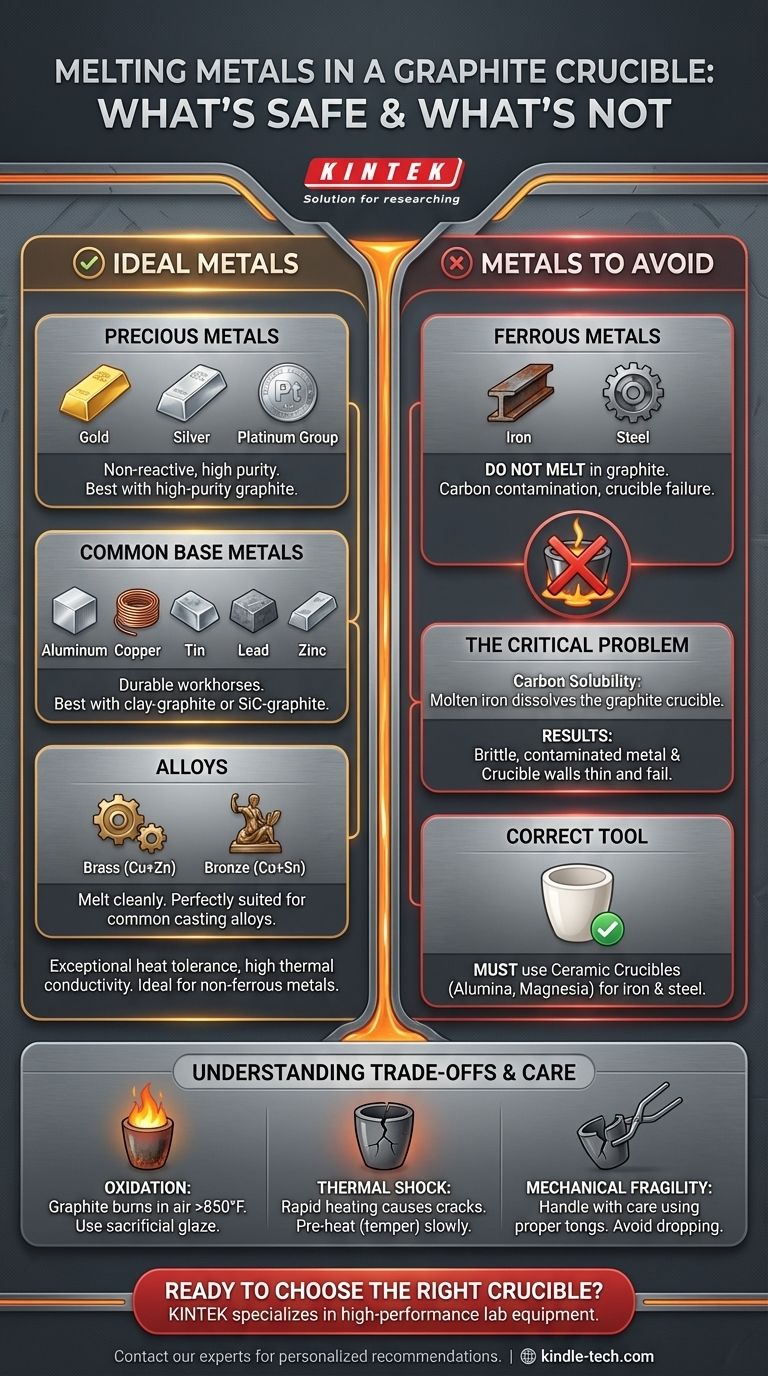
In short, graphite crucibles are the standard for melting a wide range of non-ferrous and precious metals. Their exceptional heat tolerance and thermal conductivity make them ideal for materials like gold, silver, copper, and aluminum. However, their suitability is determined by chemical compatibility, not just melting point.
The most critical factor when choosing a graphite crucible is not what you can melt, but what you cannot. While perfect for most non-ferrous metals, using a graphite crucible to melt ferrous metals like iron or steel will contaminate your metal and destroy the crucible.

The Ideal Metals for Graphite Crucibles
Graphite's high sublimation point (around 6600°F or 3650°C) means it can physically withstand the melting temperature of virtually any metal you can melt in a workshop or small foundry. The real question is chemical reaction.
Precious Metals: The Gold Standard
For precious metals like gold, silver, and the platinum group, high-purity graphite crucibles are the preferred choice. These metals are largely non-reactive with carbon, ensuring your final product remains uncontaminated. This is critical when purity is directly tied to value.
Common Base Metals: The Workhorses
Graphite is excellent for melting common base metals. Clay-graphite or silicon carbide-graphite crucibles are durable, cost-effective workhorses for these applications.
Metals that work exceptionally well include:
- Aluminum
- Copper
- Tin
- Lead
- Zinc
Alloys: A Natural Fit
Because alloys are mixtures of base metals, they are also perfectly suited for graphite crucibles. This includes common casting alloys like brass (copper and zinc) and bronze (copper and tin), which melt cleanly without issue.
The Critical Limitation: Why You Can't Melt Iron and Steel
The most common and dangerous mistake is attempting to melt ferrous metals in a graphite crucible. While the crucible can handle the heat, the result is a catastrophic failure on a chemical level.
The Problem of Carbon Solubility
Molten iron is an aggressive solvent for carbon. When you heat iron or steel in a graphite crucible, the crucible itself begins to dissolve directly into the molten metal.
The Result: Contamination and Failure
This process has two disastrous effects. First, your steel or iron becomes saturated with carbon, fundamentally changing its properties and making it brittle, more like low-quality cast iron. Second, the crucible walls thin out, weaken, and will eventually fail, potentially spilling molten metal.
The Correct Tool for Ferrous Metals
For melting iron and steel, you must use a ceramic crucible. Materials like alumina, magnesia, or zirconia are designed to withstand the high temperatures without reacting with the molten ferrous metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Even when used with the correct metals, graphite crucibles have specific characteristics and weaknesses you must manage.
Oxidation: Graphite's Primary Weakness
Graphite is carbon, and at high temperatures (above 850°F or 450°C), it will react with oxygen in the air and essentially burn away. This process of oxidation degrades the crucible over time, making it thinner and weaker. Using a sacrificial glaze of borax can help extend its life.
Thermal Shock: The Risk of Cracking
Rapidly heating a crucible, especially if it has absorbed any ambient moisture, can cause it to crack or even shatter from thermal shock. New crucibles must be slowly and carefully pre-heated (tempered) to drive out any moisture before their first use.
Mechanical Fragility
Graphite crucibles are brittle. They must be handled with care, using tongs that fit them properly. Dropping a crucible or grabbing it too aggressively, especially when hot, can easily cause it to break.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Choosing the correct crucible is fundamental to safety and success in metal casting. Your choice should be dictated entirely by the metal you intend to melt.
- If your primary focus is precious metals (gold, silver, platinum): Use a high-purity graphite crucible to ensure the highest quality and prevent contamination of your valuable metal.
- If your primary focus is base metals (aluminum, copper, brass): A durable and cost-effective clay-graphite or silicon carbide-graphite crucible is your best and most reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is iron or steel: Do not use graphite. You must use a ceramic crucible (such as alumina) to prevent carbon contamination and crucible failure.
Understanding this fundamental chemical compatibility is the first step toward safe and repeatable results in your foundry work.
Summary Table:
| ✅ Ideal Metals | ❌ Metals to Avoid |
|---|---|
| Gold, Silver, Platinum | Iron, Steel |
| Aluminum, Copper, Brass | (Any ferrous metals) |
| Tin, Lead, Zinc, Bronze |
Ready to choose the right crucible for your lab or foundry? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of graphite and ceramic crucibles designed for your specific metal melting needs. Ensure purity, safety, and efficiency in your work—contact our experts today for a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
People Also Ask
- Why use an alumina crucible in a stainless steel autoclave? Ensure Purity in Liquid Lead and LBE Exposure Experiments
- What is the best type of crucible? The Answer Depends on Your Application's Needs
- What is the efficiency of a crucible furnace? A Guide to Thermal Performance & Trade-offs
- How does an alumina crucible function during NZSP sintering? Optimize Your Solid Electrolyte Performance
- Why are high-temperature crucibles necessary for LAGP synthesis? Ensure Purity in Glass-Ceramic Electrolyte Production
- How much heat can a ceramic crucible withstand? A Guide to Material-Specific Temperature Limits
- What are the types of crucible furnace? Choose the Right Heat Source for Your Melting Needs
- What are the pros and cons of a crucible furnace? Maximize Versatility for Small-Scale Melting



















