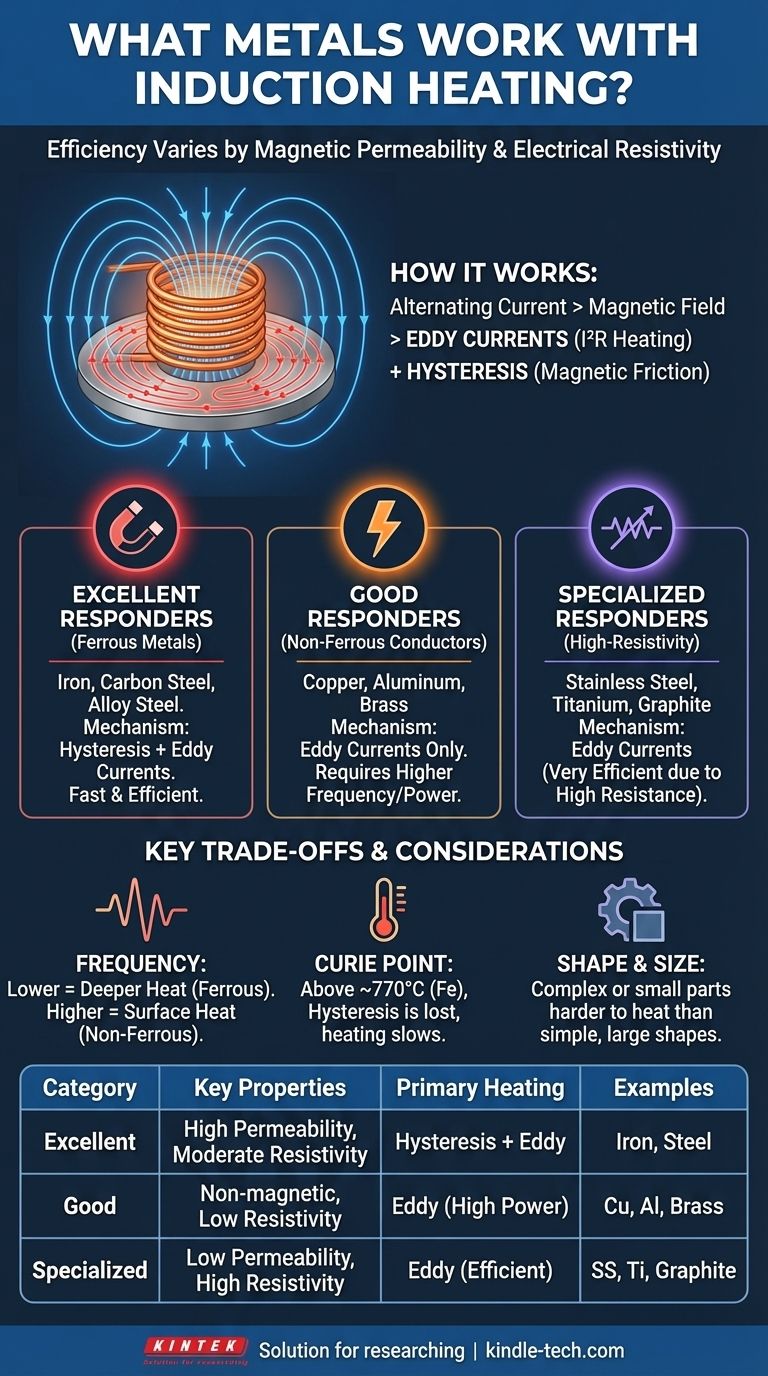
In short, most metals can be heated by induction, but their efficiency varies dramatically. The most common and effective materials are ferrous metals like iron and steel, but others like copper, aluminum, zinc, and brass also work. The key is understanding how each material responds to the process.
The effectiveness of induction heating for a specific metal is not a simple "yes" or "no" answer. It is determined by two fundamental physical properties: the metal's magnetic permeability and its electrical resistivity.

How Induction Heating Actually Works
To understand which metals work best, you first need to grasp the two phenomena that generate heat. The process starts when an alternating electrical current flows through a copper coil, creating a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field.
The Power of Eddy Currents
When a conductive material like a metal is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces circular electrical currents within the metal. These are called eddy currents.
Every metal has some level of electrical resistance. As these powerful eddy currents flow against the metal's inherent resistance, they generate immense heat. This is the same principle (I²R heating) that makes a stovetop's heating element glow red.
The Hysteresis "Bonus" for Magnetic Metals
For ferrous metals like iron and steel, a second, powerful heating effect occurs. These materials are composed of tiny magnetic regions called domains.
The rapidly alternating magnetic field forces these domains to flip back and forth millions of times per second. This rapid reversal creates enormous internal friction, which generates significant heat. This effect is known as hysteresis.
Classifying Metals for Induction Heating
Metals can be grouped into three general categories based on how they react to induction fields.
Excellent Responders: Ferrous Metals
This category includes carbon steel, alloy steel, and iron. These materials are ideal for induction heating.
They benefit from both heating mechanisms simultaneously: intense friction from hysteresis (below a certain temperature) and heat from eddy currents. This dual action makes them heat very quickly and efficiently.
Good Responders: Non-Ferrous Conductors
This group includes metals like copper, aluminum, and brass. These materials are not magnetic, so they are heated only by eddy currents.
Because they are excellent electrical conductors (low resistivity), they require a stronger magnetic field or higher frequencies to generate the same level of heat as ferrous metals. They heat well, but typically require more power.
Specialized Responders: High-Resistivity Metals
Metals such as stainless steel (depending on the grade), titanium, and graphite fall into this category.
While they may have low magnetic permeability, their very high electrical resistance makes them heat exceptionally well via eddy currents. Less current is needed to generate significant heat, making them very responsive to induction.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
The success of an induction process depends on matching the equipment's frequency and power to the material's properties.
Frequency Matters
As a general rule, lower frequencies are more effective at heating magnetic metals with greater depth. Higher frequencies are necessary to efficiently heat non-ferrous materials like copper and aluminum, as they are better at generating strong eddy currents near the surface.
The Curie Point Limitation
The powerful hysteresis effect in magnetic metals only works below a specific temperature known as the Curie point (~770°C or 1420°F for iron).
Above this temperature, the metal loses its magnetic properties. Heating continues via eddy currents alone, but the rate of heating will slow down noticeably. This is a critical consideration for applications like forging or melting steel.
Shape and Size Impact Efficiency
The geometry of the part is crucial. Induction is most efficient when the magnetic field can easily "couple" with the workpiece. Thin, small, or irregularly shaped parts can be more challenging to heat than large, solid, simple shapes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application determines which material properties are most important.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating of steel or iron for forging or hardening: You are leveraging both magnetic hysteresis and electrical resistance, making induction an ideal and highly efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum or copper: Be prepared to use higher frequencies and more power, as you are relying solely on generating powerful eddy currents to overcome their low resistance.
- If your primary focus is heating high-resistance materials like titanium or certain stainless steels: Induction is very effective due to the material's inherent resistance, which efficiently converts eddy currents into heat.
By understanding these core principles, you can select the right material and configure your induction system for maximum efficiency and control.
Summary Table:
| Metal Category | Key Properties | Primary Heating Mechanism | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Excellent Responders | High magnetic permeability, moderate resistivity | Hysteresis + Eddy Currents | Iron, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel |
| Good Responders | Non-magnetic, low electrical resistivity | Eddy Currents (requires higher frequency/power) | Copper, Aluminum, Brass |
| Specialized Responders | Low magnetic permeability, high electrical resistivity | Eddy Currents (very efficient) | Stainless Steel, Titanium, Graphite |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right metals and equipment for your induction heating application? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables for all your thermal processing needs. Whether you're working with ferrous metals, non-ferrous conductors, or specialized alloys, our team can help you configure the perfect induction heating solution for maximum efficiency and control. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between resistance brazing and induction brazing? Choose the Right Method for Your Parts
- Which material is used in an induction furnace? The Critical Refractory Lining Guide
- What is the difference between high frequency and low frequency induction heating? Master the Skin Effect for Precision Results
- What are the disadvantages of a coreless induction furnace? Key Limitations in Efficiency and Refining
- Can cast iron be remelted? Yes, and Here's How to Do It Successfully
- What role does a vacuum induction furnace play in melting 12% Chromium steel? Ensuring Purity and Alloy Integrity
- What does induction heating in induction furnace relies on? Unlock Rapid, Clean Metal Melting
- What is the temperature range for induction heating? From Ambient to 3000°C+ with Unmatched Precision



















